Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Communication Services Call Automation provides developers the ability to build server-based, intelligent call workflows, and call recording for voice and Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) channels. The SDKs, available in C#, Java, JavaScript, and Python, use an action-event model to help you build personalized customer interactions. Your communication applications can listen to real-time call events and perform control plane actions (such as answer, transfer, play audio, start recording, and so on) to steer and control calls based on your business logic.
Common use cases
Some of the common use cases that you can build using Call Automation:
- Program VoIP or PSTN calls for transactional workflows such as click-to-call and appointment reminders to improve customer service.
- Build interactive interaction workflows to self-serve customers for use cases like order bookings and updates, using Play (Audio URL, Text-to-Speech, and SSML) and Recognize (DTMF and Voice) actions.
- Integrate your communication applications with Contact Centers and your private telephony networks using Direct Routing.
- Protect your customer's identity by building number masking services to connect buyers to sellers or users to partner vendors on your platform.
- Increase engagement by building automated customer outreach programs for marketing and customer service.
- Analyze in a post-call process your unmixed audio recordings for quality assurance purposes.
Use Azure Communication Services Call Automation to build calling workflows for customer service scenarios, as depicted in the high-level architecture. You can answer inbound calls or make outbound calls. Execute actions like play a welcome message or connect the customer to a live agent on an Azure Communication Services Calling SDK client app to answer the incoming call request. With support for Azure Communication Services PSTN or Direct Routing, you can then connect this workflow back to your contact center.
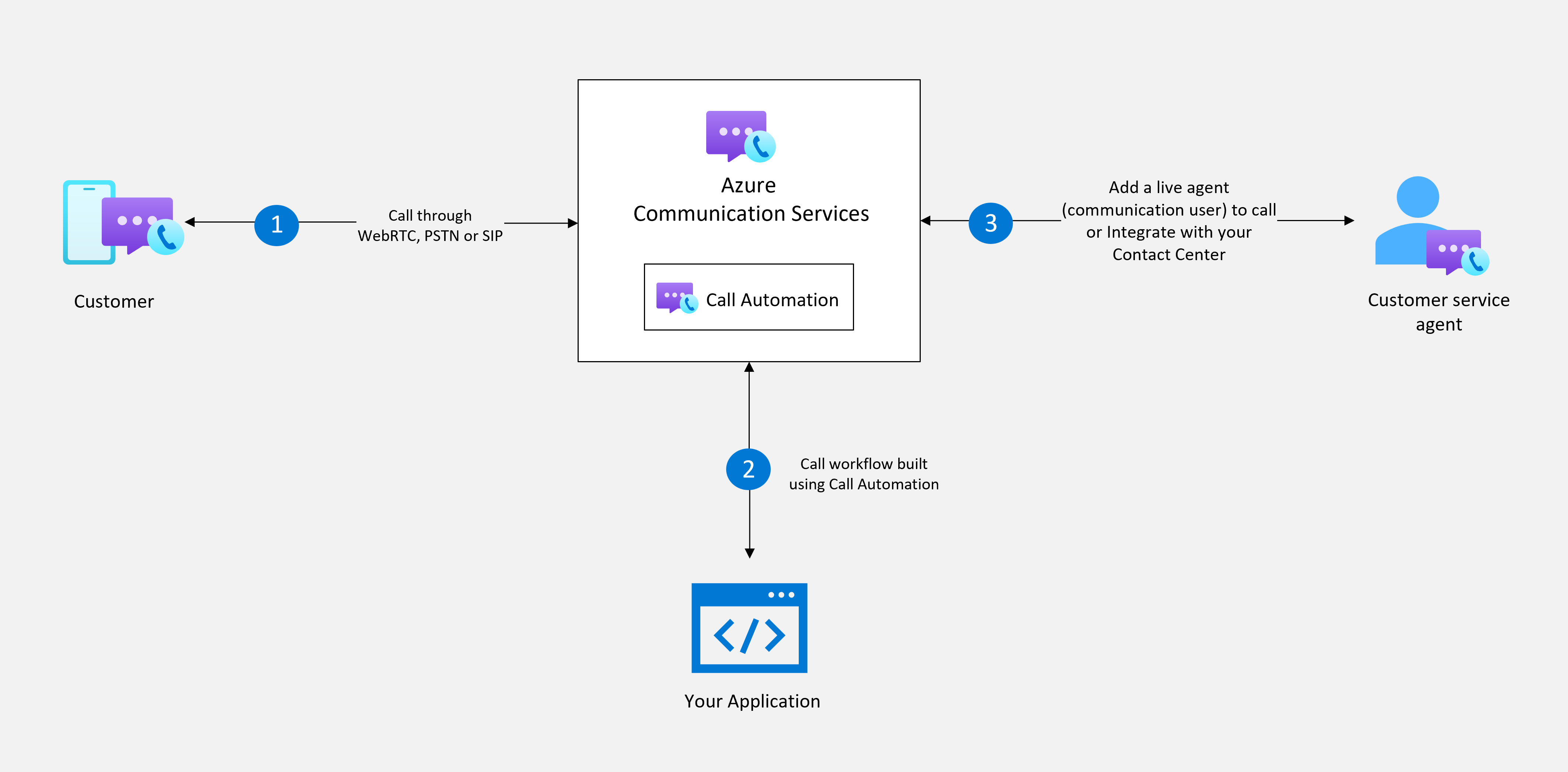
Capabilities
The following features are currently available in the Azure Communication Services Call Automation SDKs.
| Feature Area | Capability | .NET | Java | JavaScript | Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-call scenarios | Answer a one-to-one call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Answer a group call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Place new outbound call to one or more endpoints | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Redirect* (forward) a call to one or more endpoints | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Reject an incoming call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Connect to an ongoing call or Room | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Mid-call scenarios | Add one or more endpoints to an existing call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Cancel adding an endpoint to an existing call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Play Audio from an audio file | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Play Audio using Text-to-Speech | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Recognize user input through DTMF | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Recognize user voice inputs | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Start continuous DTMF recognition | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Stop continuous DTMF recognition | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Send DTMF | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Mute participant | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Hold participant | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Unhold participant | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Start/Stop audio streaming (public preview) | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Start/Stop real-time transcription (public preview) | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Remove one or more endpoints from an existing call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Blind Transfer a 1:1 call to another endpoint | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Blind Transfer a participant from group call to another endpoint | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Hang up a call (remove the call leg) | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Terminate a call (remove all participants and end call) | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Cancel media operations | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Share custom info (via VOIP or SIP headers) with endpoints when adding them to a call or transferring a call to them | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Query scenarios | Get the call state | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Get a participant in a call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| List all participants in a call | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Call Recording | Start/pause/resume/stop recording | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
* Redirect of a VoIP call to a phone number is not supported.
Architecture
Call Automation uses a REST API interface to receive requests and provide responses to all actions performed within the service. Due to the asynchronous nature of calling, most actions have corresponding events that are triggered when the action completes successfully or fails.
Azure Communication Services uses Event Grid to deliver the IncomingCall event and HTTPS Webhooks for all mid-call action callbacks.
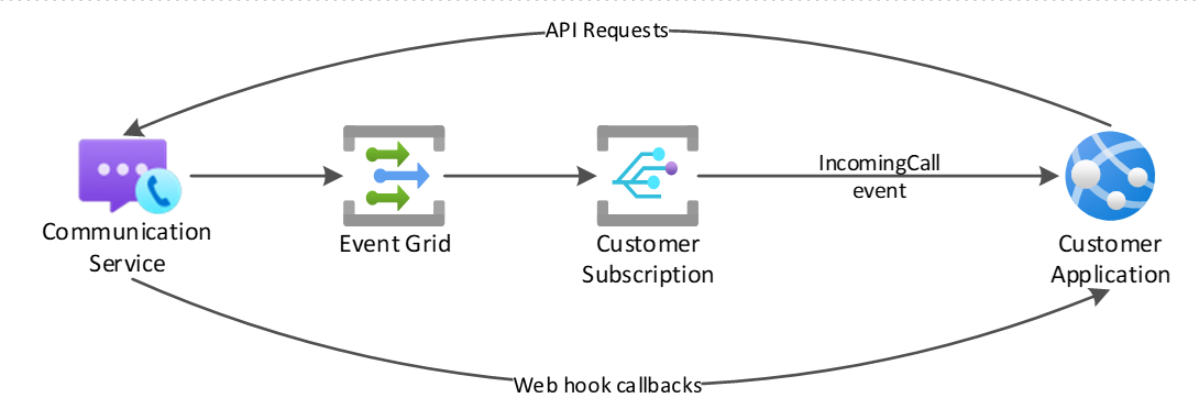
Call actions
Pre-call actions
These actions are performed before the destination endpoint listed in the IncomingCall event notification is connected. Web hook callback events only communicate the answer pre-call action, not for reject or redirect actions.
Answer – Using the IncomingCall event from Event Grid and Call Automation SDK, your application can answer a call. Use this action in IVR scenarios where your application can programmatically answer inbound PSTN calls. Other scenarios include answering a call on behalf of a user.
Reject – To reject a call means your application can receive the IncomingCall event and prevent the call from being connected to the destination endpoint.
Redirect – Using the IncomingCall event from Event Grid, you can redirect a call to another endpoint. Redirect action doesn't answer the call. The call is redirected or forwarded to another destination endpoint to be answered.
Create Call - Use the Create Call action to place outbound calls to phone numbers and to other communication users. Use cases include your application placing outbound calls to proactively inform users about an outage or notify about an order update.
Connect Call - Use the Connect Call action to connect to an ongoing call and take call actions on it. You can also use this action to connect and manage a Rooms call programmatically, like performing PSTN dial outs for Room using your service.
Mid-call actions
Your application can perform these actions on calls that are answered or placed using Call Automation SDKs. Each mid-call action has a corresponding success or failure web hook callback event.
Add/Remove participant(s) – You can add one or more participants in a single request with each participant being a variation of supported destination endpoints. A web hook callback is sent for every participant successfully added to the call.
Play – When your application answers a call or places an outbound call, you can play an audio prompt for the caller. This audio can be looped if needed in scenarios like playing hold music. To learn more, see Playing audio in call and Customizing voice prompts to users with Play action.
Recognize input – After your application plays an audio prompt, you can request user input to drive business logic and navigation in your application. To learn more, see Gathering user input and the how-to guide Gather user input with Recognize action.
Continuous DTMF recognition – When your application needs to be able to receive DTMF tones at any point in the call without the application needing to trigger a specific recognize action. This ability can be useful in scenarios where an agent is on a call and needs the user to enter in some kind of ID or tracking number. To learn more, see How to control mid-call media actions.
Send DTMF – When your application needs to send DTMF tones to an external participant. Use this action for dialing out to an external agent and providing the extension number, or navigating an external IVR menu.
Mute – Your application can mute certain users based on your business logic. The user would then need to unmute themselves manually if they want to speak.
Transfer – When your application answers a call or places an outbound call to an endpoint, that call can be transferred to another destination endpoint. Transferring a 1:1 call removes your application's ability to control the call using the Call Automation SDKs.
Record – You decide when to start/pause/resume/stop recording based on your application business logic, or you can grant control to the end user to trigger those actions. To learn more, view our concepts and quickstart.
Hang-up – When your application answers a one-to-one call, the hang-up action removes the call leg and terminates the call with the other endpoint. If there are more than two participants in the call (group call), performing a ‘hang-up’ action removes your application’s endpoint from the group call.
Terminate – Whether your application answers a one-to-one or group call, or places an outbound call with one or more participants, this action removes all participants and ends the call. This operation is triggered by setting the forEveryOne property to true in Hang-Up call action.
Cancel media operations – Based on business logic your application might need to cancel ongoing and queued media operations. Depending on the media operation canceled and the ones in queue, your application might receive a webhook event indicating that the action was canceled.
Start/Stop audio streaming (public preview) - Audio streaming allows you to subscribe to real-time audio streams from an ongoing call. For more detailed guidance on how to get started with audio streaming and information about audio streaming callback events, see our concept and our quickstart.
Start/Stop real-time transcription (public preview) - Real-time transcription allows you to access live transcriptions for the audio of an ongoing call. For more detailed guidance on how to get started with real-time transcription and information about real-time transcription callback events, see our concept and our quickstart.
Query scenarios
List participants – Returns a list of all the participants in a call. Recording and transcription bots are omitted from this list.
Events
The following table outlines the current events emitted by Azure Communication Services. The following two tables describe the events emitted by Event Grid and from the Call Automation as webhook events.
Event Grid events
Most of the events sent by Event Grid are platform agnostic. They're sent regardless of the SDK (Calling or Call Automation). While you can create a subscription for any event, we recommend using the IncomingCall event for all Call Automation use cases where you want to control the call programmatically. Use the other events for reporting/telemetry purposes.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
IncomingCall |
Notification of a call to a communication user or phone number. |
CallStarted |
Established a call (inbound or outbound). |
CallEnded |
Terminated a call and removed all participants. |
ParticipantAdded |
Added a participant to a call. |
ParticipantRemoved |
Removed a participant from a call. |
RecordingFileStatusUpdated |
A recording file is available. |
Read more about these events and payload schema in Azure Communication Services - Voice and video calling events
Call Automation webhook events
The Call Automation events are sent to the web hook callback URI specified when you answer or place a new outbound call.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
CallConnected |
The call successfully started (when using Answer or Create action) or your application successfully connected to an ongoing call (when using Connect action). |
CallDisconnected |
Your application has been disconnected from the call. |
CreateCallFailed |
Your application has failed to create the call. |
AnswerFailed |
Your application has failed to answer the call. |
ConnectFailed |
Your application failed to connect to a call (for Connect call action only). |
CallTransferAccepted |
Transfer action successfully completed and the transferee is connected to the target participant. |
CallTransferFailed |
The transfer action failed. |
AddParticipantSucceeded |
Your application successfully added a participant to the call. |
AddParticipantFailed |
Your application was unable to add a participant to the call (due to an error or the participant didn't accept the invite) |
CancelAddParticipantSucceeded |
Your application canceled an AddParticipant request successfully (the participant wasn't added to the call). |
CancelAddParticipantFailed |
Your application was unable to cancel an AddParticipant request (this could be because the request has already been processed). |
RemoveParticipantSucceeded |
Your application successfully removed a participant from the call. |
RemoveParticipantFailed |
Your application was unable to remove a participant from the call. |
ParticipantsUpdated |
The status of a participant changed while your application was connected to a call. |
PlayCompleted |
Your application successfully played the audio file provided. |
PlayFailed |
Your application failed to play audio. |
PlayCanceled |
The requested play action has been canceled. |
RecognizeCompleted |
Recognition of user input successfully completed. |
RecognizeCanceled |
The requested Recognize action has been canceled. |
RecognizeFailed |
Recognition of user input was unsuccessful. For more information about recognize action events, see the how-to guide for gathering user input. |
RecordingStateChanged |
Status of recording action has changed from active to inactive or vice versa. |
ContinuousDtmfRecognitionToneReceived |
StartContinuousDtmfRecognition completed successfully and a DTMF tone was received from the participant. |
ContinuousDtmfRecognitionToneFailed |
StartContinuousDtmfRecognition completed but an error occurred while handling a DTMF tone from the participant. |
ContinuousDtmfRecognitionStopped |
Successfully executed StopContinuousRecognition. |
SendDtmfCompleted |
SendDTMF completed successfully and sent DTMF tones to the target participant. |
SendDtmfFailed |
An error occurred while sending the DTMF tones. |
To understand which events are published for different actions, see Actions for call control. The article provides code samples and sequence diagrams for various call control flows.
As best practice when acknowledging callback events, respond with standard HTTP status codes like 200 OK. Detailed information is unnecessary and is more suitable for your debugging processes.
To learn how to secure the callback event delivery, see How to secure webhook endpoint.
Operation Callback URI
Operation Callback URI is an optional parameter in some mid-call APIs that use events as their async responses. By default, all events are sent to the default callback URI set by CreateCall / AnswerCall API events when the user establishes a call. Using the Operation Callback URI, the API sends corresponding events for this individual (one-time only) request to the new URI.
| Supported API | Corresponding event |
|---|---|
AddParticipant |
AddParticipantSucceed / AddParticipantFailed |
RemoveParticipant |
RemoveParticipantSucceed / RemoveParticipantFailed |
TransferCall |
CallTransferAccepted / CallTransferFailed |
CancelAddParticipant |
CancelAddParticipantSucceeded / CancelAddParticipantFailed |
Play |
PlayCompleted / PlayFailed / PlayCanceled |
PlayToAll |
PlayCompleted / PlayFailed / PlayCanceled |
Recognize |
RecognizeCompleted / RecognizeFailed / RecognizeCanceled |
StopContinuousDTMFRecognition |
ContinuousDtmfRecognitionStopped |
SendDTMF |
ContinuousDtmfRecognitionToneReceived / ContinuousDtmfRecognitionToneFailed |
Hold |
HoldFailed |
StartMediaStreaming |
MediaStreamingStarted / MediaStreamingFailed |
StopMediaStreaming |
MediaStreamingStopped / MediaStreamingFailed |
StartTranscription |
TranscriptionStarted / TranscriptionFailed |
UpdateTranscription |
TranscriptionUpdated / TranscriptionFailed |
StopTranscription |
TranscriptionStopped / TranscriptionFailed |
Next steps
Related articles
- Understand how your resource is charged for various calling use cases with examples.
- See quickstart to place an outbound call.
- Learn about usage and operational logs published by call automation.