Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Call Recording enables you to record multiple calling scenarios available in Azure Communication Services by providing you with a set of APIs to start, stop, pause, and resume recording. Whether it's a PSTN, WebRTC, or SIP call, these APIs can be accessed from your server-side business logic. Also, recordings can be triggered by a user action that tells the server application to start recording.
Depending on your business needs, you can use Call Recording for different Azure Communication Services calling implementations.
For example, you can record 1:1 or 1:N audio and video calls:
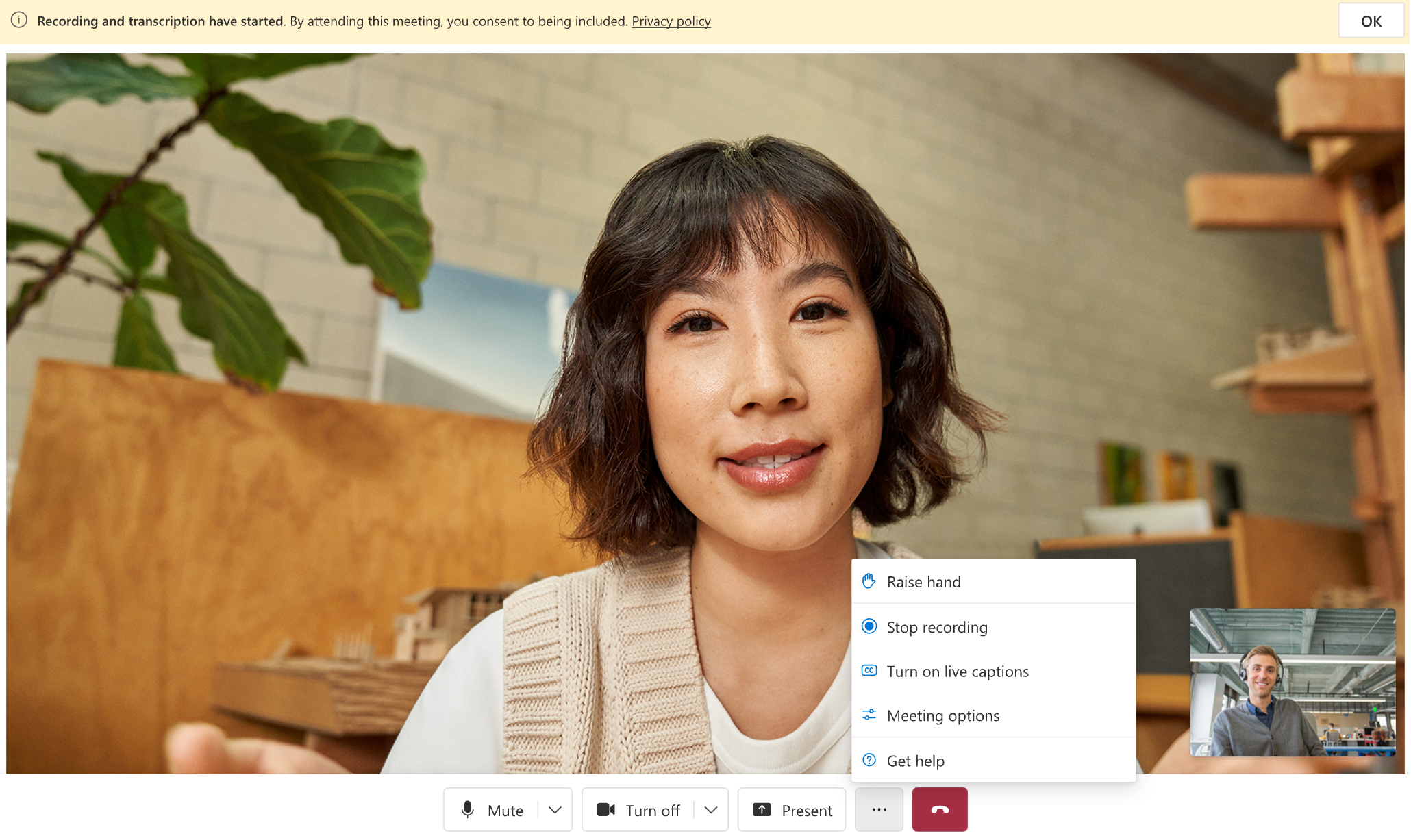
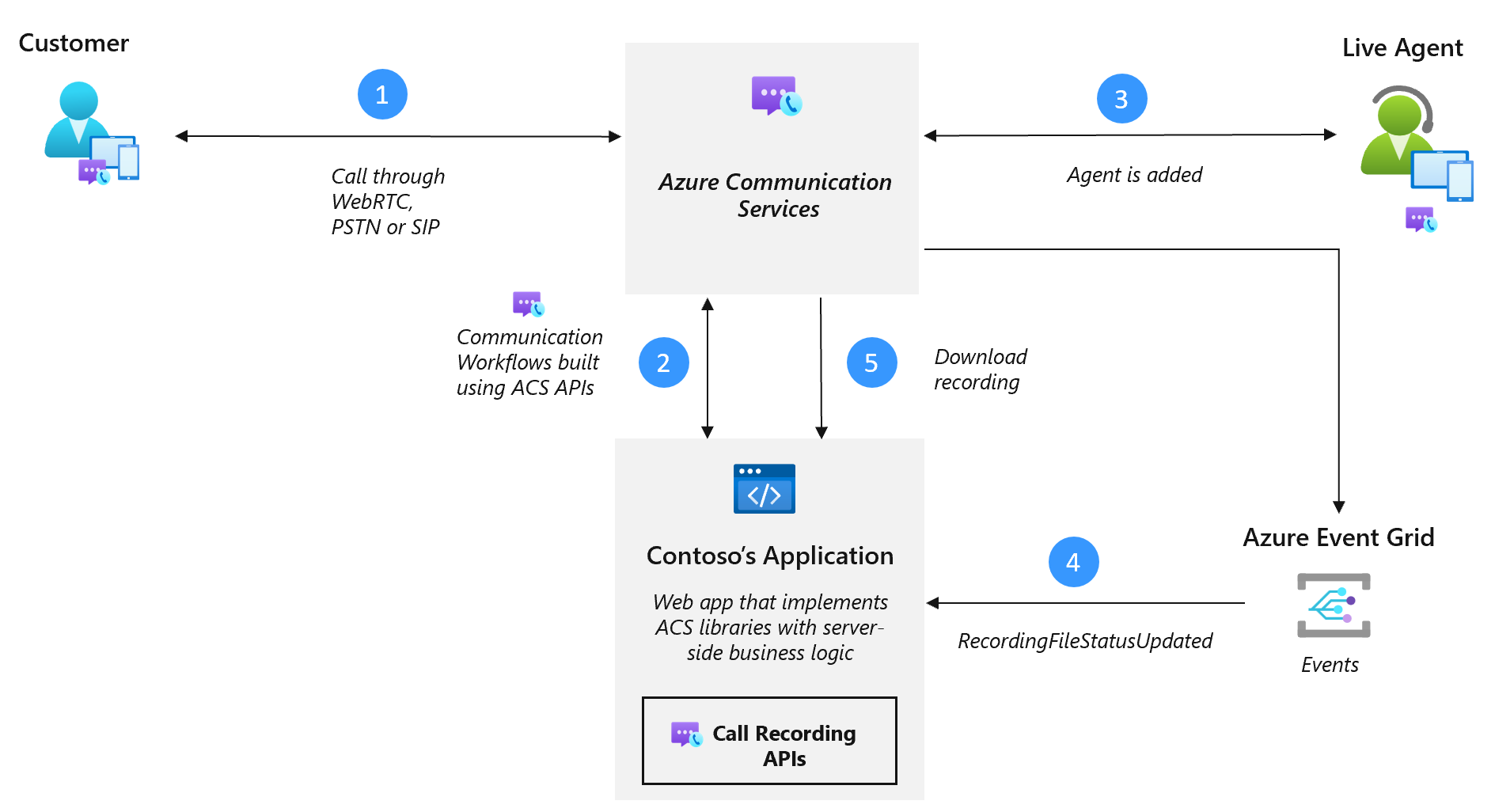
You can also use Call Recording to record complex PSTN or VoIP inbound and outbound calling workflows managed by Call Automation.
Regardless of how you established the call, Call Recording enables you to produce mixed or unmixed media files that are stored for 24 hours on a built-in temporary storage. You can retrieve the files, move them in your own Azure Blob Store Bring Your Own Storage, or a storage solution of your choice. Call Recording supports all Azure Communication Services data regions.
Call Recording that supports your business needs
Call Recording supports multiple media outputs and content types to address your business needs and use cases. You might use mixed formats for scenarios such as keeping records, meeting notes, coaching and training, or even compliance and adherence. Or, you can use unmixed audio format to address quality assurance use cases or even more complex scenarios like advanced analytics or AI-based (Artificial Intelligence) sophisticated post-call processes.
Video
| Channel Type | Content Format | Resolution | Sampling Rate | Bit rate | Data rate | Output | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mixed | mp4 | 1920x1080, 16 FPS (frames per second) | 16 kHz | 1 mbps | 7.5 MB/min* | single file, single channel | mixed video in a default 3x3 (most active speakers) tile arrangement with display name support |
Audio
| Channel Type | Content Format | Sampling Rate | Bit rate | Data rate | Output | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mixed | mp3 | 16 kHz | 48 kbps | 0.36 MB/min* | single file, single channel | mixed audio of all participants |
| mixed | wav | 16 kHz | 256 kbps | 1.92 MB/min | single file, single channel | mixed audio of all participants |
| unmixed | wav | 16 kHz | 256 kbps | 1.92 MB/min* per channel | single file, up to 5 wav channels | unmixed audio, one participant per channel, up to five channels |
[*NOTE] Mp3 and Mp4 formats use lossy compression that results in variable bitrate; therefore, data rate values in the preceding tables reflect the theoretical maximum. WAV format is uncompressed and bitrate is fixed, so the data rate calculations are exact.
Get full control over your recordings with our Call Recording APIs
You can use Call Recording APIs to manage recording via internal business logic triggers, such as an application creating a group call and recording the conversation. Also, recordings can be triggered by a user action that tells the server application to start recording. Call Recording APIs use exclusively the serverCallId to initiate recording. To learn how to get the serverCallId, check our Call Recording Quickstart.
A recordingId is returned when recording is started, which can then be used for follow-on operations like pause and resume.
| Operation | Operates On | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Start Recording | serverCallId |
Returns recordingId |
| Get Recording State | recordingId |
Returns RecordingStateResult |
| Pause Recording | recordingId |
Pausing and resuming call recording enables you to skip recording a portion of a call or meeting, and resume recording to a single file. |
| Resume Recording | recordingId |
Resumes a Paused recording operation. Content is included in the same file as content from prior to pausing. |
| Stop Recording | recordingId |
Stops recording, and initiates final media processing for file download. |
Event Grid notifications
Call Recording use Azure Event Grid to provide you with notifications related to media and metadata.
Note
Azure Communication Services provides short term media storage for recordings. Recordings are available to download for 24 hours. After 24 hours, recordings are no longer available.
An Event Grid notification Microsoft.Communication.RecordingFileStatusUpdated is published when a recording is ready for retrieval, typically a few minutes after the recording process completes, such as meeting ended, or recording stopped. Recording event notifications include contentLocation and metadataLocation, which are used to retrieve both recorded media and a recording metadata file.
Notification Schema Reference
{
"id": string, // Unique guid for event
"topic": string, // /subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourceGroups/{group-name}/providers/Microsoft.Communication/communicationServices/{communication-services-resource-name}
"subject": string, // /recording/call/{call-id}/serverCallId/{serverCallId}/recordingId/{recordingId}
"data": {
"recordingStorageInfo": {
"recordingChunks": [
{
"documentId": string, // Document id for retrieving from storage
"index": int, // Index providing ordering for this chunk in the entire recording
"endReason": string, // Reason for chunk ending: "SessionEnded", "ChunkMaximumSizeExceeded”, etc.
"metadataLocation": <string>, // url of the metadata for this chunk
"contentLocation": <string>, // url of the mp4, mp3, or wav for this chunk
"deleteLocation": <string> // url of the mp4, mp3, or wav to delete this chunk
}
]
},
"recordingStartTime": string, // ISO 8601 date time for the start of the recording
"recordingDurationMs": int, // Duration of recording in milliseconds
"sessionEndReason": string // Reason for call ending: "CallEnded", "InitiatorLeft", etc.
},
"eventType": string, // "Microsoft.Communication.RecordingFileStatusUpdated"
"dataVersion": string, // "1.0"
"metadataVersion": string, // "1"
"eventTime": string // ISO 8601 date time for when the event was created
}
Metadata Schema Reference
{
"resourceId": <string>, // stable resource id of the Azure Communication Services resource recording
"callId": <string>, // id of the call
"chunkDocumentId": <string>, // object identifier for the chunk this metadata corresponds to
"chunkIndex": <number>, // index of this chunk with respect to all chunks in the recording
"chunkStartTime": <string>, // ISO 8601 datetime for the start time of the chunk this metadata corresponds to
"chunkDuration": <number>, // [Chunk duration has a maximum of 4 hours] duration of the chunk this metadata corresponds to in milliseconds
"pauseResumeIntervals": [
"startTime": <string>, // ISO 8601 datetime for the time at which the recording was paused
"duration": <number> // duration of the pause in the recording in milliseconds
],
"recordingInfo": {
"contentType": <string>, // content type of recording, e.g. audio/audioVideo
"channelType": <string>, // channel type of recording, e.g. mixed/unmixed
"format": <string>, // format of the recording, e.g. mp4/mp3/wav
"audioConfiguration": {
"sampleRate": <number>, // sample rate for audio recording
"bitRate": <number>, // bitrate for audio recording
"channels": <number> // number of audio channels in output recording
},
"videoConfiguration": {
"longerSideLength": <number>, // longerSideLength for video recording
"shorterSideLength": <number>, // shorterSideLength for video recording
"frameRate": <number>, // frameRate for video recording
"bitRate": <number> // bitrate for video recording
}
},
"participants": [
{
"participantId": <string>, // participant identifier of a participant captured in the recording
"channel": <number> // channel the participant was assigned to if the recording is unmixed
}
]
}
Regulatory and privacy concerns
Many countries/regions and states have laws and regulations that apply to call recording. PSTN, voice, and video calls often require that users consent to the recording of their communications. It is your responsibility to use the call recording capabilities in compliance with the law. You must obtain consent from the parties of recorded communications in a manner that complies with the laws applicable to each participant.
Regulations around the maintenance of personal data require the ability to export user data. In order to support these requirements, recording metadata files include the participantId for each call participant in the participants array. You can cross-reference the Azure Communication Services User Identity in the participants array with your internal user identities to identify participants in a call.
Next steps
Here are some articles of interest to you:
- Learn more about call recording Insights and Logs
- Learn more about Call Automation.
- Learn more about Video Calling.