Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Push notifications send information from your application to users' devices. You can use push notifications to show a dialog, play a sound, or display incoming call into the app's UI layer.
In this article, you learn how to enable push notifications for Azure Communication Services calls. Communication Services provides integrations with Azure Event Grid and Azure Notification Hubs that enable you to add push notifications to your apps.
Overview of TTL tokens
The time-to-live (TTL) token is a setting that determines the length of time that a notification token stays valid before becoming invalid. This setting is useful for applications where user engagement doesn't require daily interaction but remains critical over longer periods.
The TTL configuration enables the management of push notifications' life cycle. It reduces the need for frequent token renewals while helping to ensure that the communication channel between the application and its users remains open and reliable for extended durations.
Currently, the maximum value for TTL is 180 days (15,552,000 seconds), and the minimum value is 5 minutes (300 seconds). You can enter this value and adjust it to fit your needs. If you don't provide a value, the default value is 24 hours (86,400 seconds).
After the Register Push Notification API is called, the device token information is saved in the registrar. After the TTL duration ends, the device endpoint information is deleted. Any incoming calls on those devices can't be delivered to the devices if those devices don't call the Register Push Notification API again.
If you want to revoke an identity, follow this process. After the identity is revoked, the registrar entry should be deleted.
Note
For a Microsoft Teams user, the maximum TTL value is 24 hrs (86,400 seconds). There's no way to increase this value. You should wake up the application every 24 hours in the background and register the device token.
To wake up the application, fetch the new token, and perform the registration, follow the instructions for the iOS platform or the instructions for the Android platform.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
A deployed Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource.
A user access token to enable the calling client. For more information, see Create and manage access tokens.
Optional: Completion of the quickstart to add voice calling to your application.
Follow the quickstart
Web push notifications via the Azure Communication Services Web Calling SDK are in preview and are available as part of version 1.12.0-beta.2+.
Important
This feature of Azure Communication Services is currently in preview. Features in preview are publicly available and can be used by all new and existing Microsoft customers.
Preview APIs and SDKs are provided without a service-level agreement. We recommend that you don't use them for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or capabilities might be constrained.
For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
For step-by-step instructions, see the quickstart on GitHub.
A Firebase account with Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) enabled and with your FCM service connected to an Azure Notification Hubs instance. For more information, see Communication Services notifications.
Android Studio version 3.6 or later to build your application.
A set of permissions to enable the Android application to receive notification messages from FCM. In your
AndroidManifest.xmlfile, add the following permissions right after<manifest ...>or below the</application>tag:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS"/> <uses-permission android:name="com.google.android.c2dm.permission.RECEIVE" />
Important
On June 20, 2023, Google announced that it deprecated sending messages by using the FCM legacy APIs and would start removing the legacy FCM from service in June 2024. Google recommends migrating from legacy FCM APIs to FCM HTTP v1.
If your Communication Services resource is still using the FCM legacy APIs, follow this migration guide.
Considerations for mobile push notifications
Mobile push notifications are the pop-up notifications that appear on mobile devices. For calling, this article focuses on voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) push notifications.
Note
When the application registers for push notifications and handles the incoming push notifications for a Teams user, the APIs are the same. The APIs that this article describes can also be invoked on the CommonCallAgent or TeamsCallAgent class.
Install the SDK
Locate your project-level build.gradle file and add mavenCentral() to the list of repositories under buildscript and allprojects:
buildscript {
repositories {
...
mavenCentral()
...
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
...
mavenCentral()
...
}
}
Then, in your module-level build.gradle file, add the following lines to the dependencies section:
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.azure.android:azure-communication-calling:1.0.0'
...
}
Initialize the required objects
To create a CallAgent instance, you have to call the createCallAgent method on a CallClient instance. This call asynchronously returns a CallAgent instance object.
The createCallAgent method takes CommunicationUserCredential as an argument, which encapsulates an access token.
To access DeviceManager, you must create a callAgent instance first. Then you can use the CallClient.getDeviceManager method to get DeviceManager.
String userToken = '<user token>';
CallClient callClient = new CallClient();
CommunicationTokenCredential tokenCredential = new CommunicationTokenCredential(userToken);
android.content.Context appContext = this.getApplicationContext(); // From within an activity, for instance
CallAgent callAgent = callClient.createCallAgent(appContext, tokenCredential).get();
DeviceManager deviceManager = callClient.getDeviceManager(appContext).get();
To set a display name for the caller, use this alternative method:
String userToken = '<user token>';
CallClient callClient = new CallClient();
CommunicationTokenCredential tokenCredential = new CommunicationTokenCredential(userToken);
android.content.Context appContext = this.getApplicationContext(); // From within an activity, for instance
CallAgentOptions callAgentOptions = new CallAgentOptions();
callAgentOptions.setDisplayName("Alice Bob");
DeviceManager deviceManager = callClient.getDeviceManager(appContext).get();
CallAgent callAgent = callClient.createCallAgent(appContext, tokenCredential, callAgentOptions).get();
Register for push notifications
To register for push notifications, the application needs to call registerPushNotification() on a CallAgent instance by using a device registration token.
To obtain the device registration token, add the Firebase SDK to your application module's build.gradle file by adding the following lines in the dependencies section (if the lines aren't already there):
// Add the SDK for Firebase Cloud Messaging
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-core:16.0.8'
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-messaging:20.2.4'
In your project level's build.gradle file, add the following line in the dependencies section if it's not already there:
classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.3.3'
Add the following plug-in to the beginning of the file if it's not already there:
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'
On the toolbar, select Sync Now. Add the following code snippet to get the device registration token that the Firebase Cloud Messaging SDK generated for the client application instance. Be sure to add the following imports to the header of the main activity for the instance to retrieve the token.
import com.google.android.gms.tasks.OnCompleteListener;
import com.google.android.gms.tasks.Task;
import com.google.firebase.iid.FirebaseInstanceId;
import com.google.firebase.iid.InstanceIdResult;
Add this snippet to retrieve the token:
FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getInstanceId()
.addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<InstanceIdResult>() {
@Override
public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<InstanceIdResult> task) {
if (!task.isSuccessful()) {
Log.w("PushNotification", "getInstanceId failed", task.getException());
return;
}
// Get the new instance ID token
String deviceToken = task.getResult().getToken();
// Log
Log.d("PushNotification", "Device Registration token retrieved successfully");
}
});
Register the device registration token with the Calling Services SDK for incoming call push notifications:
String deviceRegistrationToken = "<Device Token from previous section>";
try {
callAgent.registerPushNotification(deviceRegistrationToken).get();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something went wrong while registering for Incoming Calls Push Notifications.")
}
Handle push notifications
To receive incoming call push notifications, call handlePushNotification() on a CallAgent instance with a payload.
To obtain the payload from Firebase Cloud Messaging, begin by creating a new service (select File > New > Service > Service) that extends the FirebaseMessagingService Firebase SDK class and overrides the onMessageReceived method. This method is the event handler called when Firebase Cloud Messaging delivers the push notification to the application.
public class MyFirebaseMessagingService extends FirebaseMessagingService {
private java.util.Map<String, String> pushNotificationMessageDataFromFCM;
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage remoteMessage) {
// Check if the message contains a notification payload.
if (remoteMessage.getNotification() != null) {
Log.d("PushNotification", "Message Notification Body: " + remoteMessage.getNotification().getBody());
}
else {
pushNotificationMessageDataFromFCM = remoteMessage.getData();
}
}
}
Add the following service definition to the AndroidManifest.xml file, inside the <application> tag:
<service
android:name=".MyFirebaseMessagingService"
android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.google.firebase.MESSAGING_EVENT" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
After you retrieve the payload, you can pass it to the Communication Services SDK to be parsed into an internal IncomingCallInformation object. This object handles calling the handlePushNotification method on a CallAgent instance. You create a CallAgent instance by calling the createCallAgent(...) method on the CallClient class.
try {
IncomingCallInformation notification = IncomingCallInformation.fromMap(pushNotificationMessageDataFromFCM);
Future handlePushNotificationFuture = callAgent.handlePushNotification(notification).get();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something went wrong while handling the Incoming Calls Push Notifications.");
}
When the handling of the push notification message is successful, and the all event handlers are registered properly, the application rings.
Unregister push notifications
Applications can unregister push notification at any time. To unregister, call the unregisterPushNotification() method on callAgent:
try {
callAgent.unregisterPushNotification().get();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something went wrong while un-registering for all Incoming Calls Push Notifications.")
}
Disable internal push notifications for an incoming call
The push payload of an incoming call can be delivered to the callee in two ways:
- Using FCM and registering the device token with the API mentioned earlier,
registerPushNotificationonCallAgentorTeamsCallAgent - Registering the SDK with an internal service upon creation of
CallAgentorTeamsCallAgentto get the push payload delivered
By using the property setDisableInternalPushForIncomingCall in CallAgentOptions or TeamsCallAgentOptions, it's possible to instruct the SDK to disable the delivery of the push payload via the internal push service:
CallAgentOptions callAgentOptions = new CallAgentOptions();
callAgentOptions.setDisableInternalPushForIncomingCall(true);
Implement iOS mobile push notifications
Mobile push notifications are the pop-up notifications that appear on mobile devices. For calling, this article focuses on voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) push notifications. For a guide on CallKit integration in your iOS application, see Integrate with CallKit.
Note
When the application registers for push notifications and handles the incoming push notifications for a Teams user, the APIs are the same. The APIs that this article describes can also be invoked on the CommonCallAgent or TeamsCallAgent class.
Set up your system
Follow these steps to set up your system.
Create the Xcode project
In Xcode, create a new iOS project and select the Single View App template. This article uses the SwiftUI framework, so you should set Language to Swift and set Interface to SwiftUI.
You're not going to create tests in this article. Feel free to clear the Include Tests checkbox.
Install the package and dependencies by using CocoaPods
Create a Podfile for your application, like this example:
platform :ios, '13.0' use_frameworks! target 'AzureCommunicationCallingSample' do pod 'AzureCommunicationCalling', '~> 1.0.0' endRun
pod install.Open
.xcworkspaceby using Xcode.
Request access to the microphone
To access the device's microphone, you need to update your app's information property list by using NSMicrophoneUsageDescription. Set the associated value to a string that's included in the dialog that the system uses to request access from the user.
Right-click the Info.plist entry of the project tree, and then select Open As > Source Code. Add the following lines in the top-level <dict> section, and then save the file.
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need microphone access for VOIP calling.</string>
Set up the app framework
Open your project's ContentView.swift file. Add an import declaration to the top of the file to import the AzureCommunicationCalling library. In addition, import AVFoundation. You need it for audio permission requests in the code.
import AzureCommunicationCalling
import AVFoundation
Initialize CallAgent
To create a CallAgent instance from CallClient, you have to use a callClient.createCallAgent method that asynchronously returns a CallAgent object after it's initialized.
To create a call client, pass a CommunicationTokenCredential object:
import AzureCommunication
let tokenString = "token_string"
var userCredential: CommunicationTokenCredential?
do {
let options = CommunicationTokenRefreshOptions(initialToken: token, refreshProactively: true, tokenRefresher: self.fetchTokenSync)
userCredential = try CommunicationTokenCredential(withOptions: options)
} catch {
updates("Couldn't created Credential object", false)
initializationDispatchGroup!.leave()
return
}
// tokenProvider needs to be implemented by Contoso, which fetches a new token
public func fetchTokenSync(then onCompletion: TokenRefreshOnCompletion) {
let newToken = self.tokenProvider!.fetchNewToken()
onCompletion(newToken, nil)
}
Pass the CommunicationTokenCredential object that you created to CallClient, and set the display name:
self.callClient = CallClient()
let callAgentOptions = CallAgentOptions()
options.displayName = " iOS Azure Communication Services User"
self.callClient!.createCallAgent(userCredential: userCredential!,
options: callAgentOptions) { (callAgent, error) in
if error == nil {
print("Create agent succeeded")
self.callAgent = callAgent
} else {
print("Create agent failed")
}
})
Set up push notifications
Before you start the tasks of registering for, handling, and unregistering push notifications, complete this setup task:
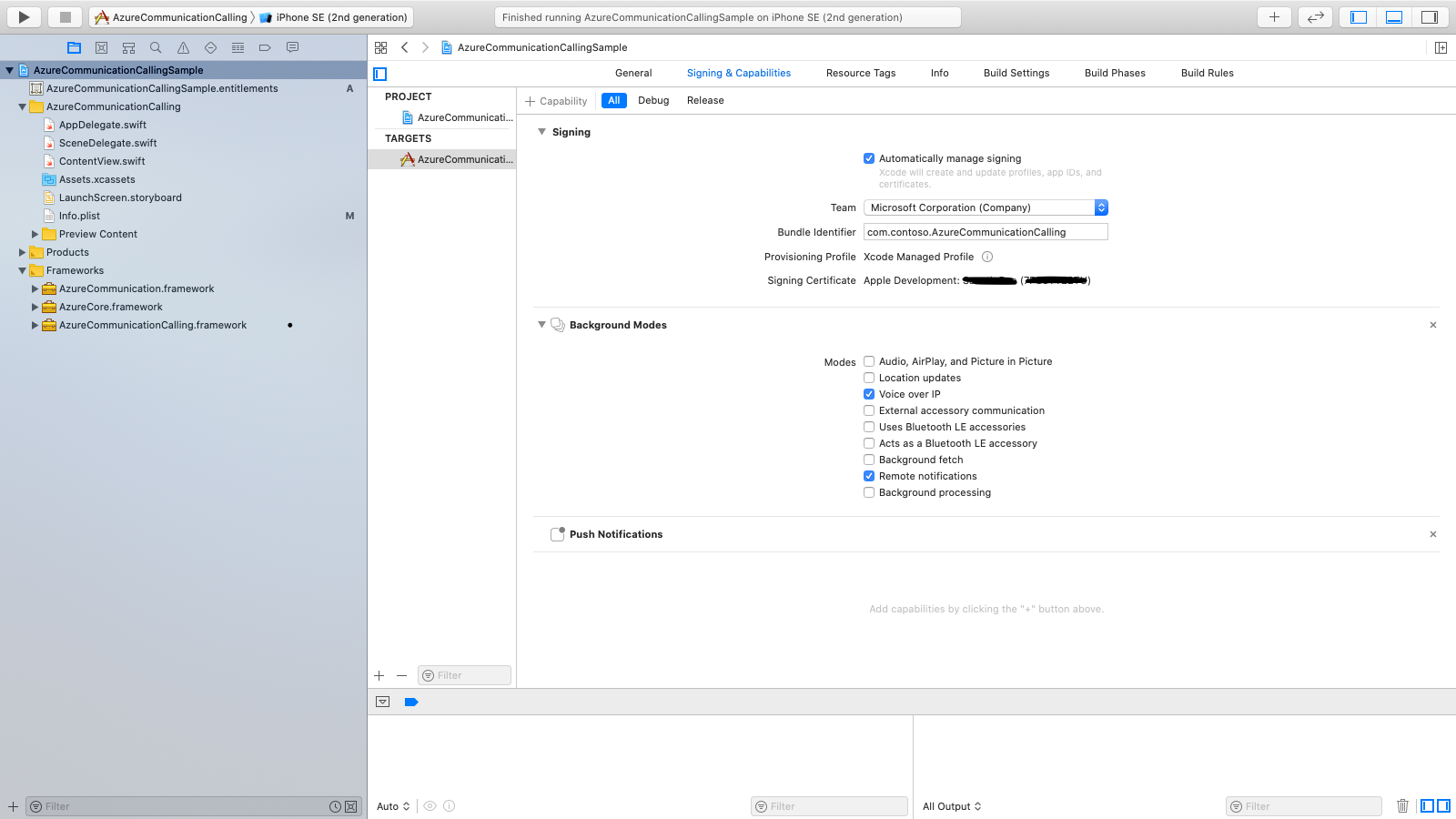
- In Xcode, go to Signing & Capabilities. Add a capability by selecting + Capability, and then select Push Notifications.
- Add another capability by selecting + Capability, and then select Background Modes.
- Under Background Modes, select the Voice over IP and Remote notifications checkboxes.
Register for push notifications
To register for push notifications, call registerPushNotification() on a CallAgent instance by using a device registration token.
Registration for push notifications needs to happen after successful initialization. When the callAgent object is destroyed, logout is called, which automatically unregisters push notifications.
let deviceToken: Data = pushRegistry?.pushToken(for: PKPushType.voIP)
callAgent.registerPushNotifications(deviceToken: deviceToken!) { (error) in
if(error == nil) {
print("Successfully registered to push notification.")
} else {
print("Failed to register push notification.")
}
}
Handle push notifications
To receive push notifications for incoming calls, call handlePushNotification() on a CallAgent instance with a dictionary payload:
let callNotification = PushNotificationInfo.fromDictionary(pushPayload.dictionaryPayload)
callAgent.handlePush(notification: callNotification) { (error) in
if (error == nil) {
print("Handling of push notification was successful")
} else {
print("Handling of push notification failed")
}
}
Unregister push notifications
Applications can unregister push notification at any time. To unregister, call the unregisterPushNotification method on CallAgent.
Note
Applications aren't automatically unregistered from push notifications on sign out.
callAgent.unregisterPushNotification { (error) in
if (error == nil) {
print("Unregister of push notification was successful")
} else {
print("Unregister of push notification failed, please try again")
}
}
Disable internal push notifications for an incoming call
The push payload of an incoming call can be delivered to the callee in two ways:
- Using Apple Push Notification service (APNS) and registering the device token with the API mentioned earlier,
registerPushNotificationonCallAgentorTeamsCallAgent - Registering the SDK with an internal service upon creation of
CallAgentorTeamsCallAgentto get the push payload delivered
By using the property disableInternalPushForIncomingCall in CallAgentOptions or TeamsCallAgentOptions, you can instruct the SDK to disable the delivery of the push payload via the internal push service:
let options = CallAgentOptions()
options.disableInternalPushForIncomingCall = true
Implement Windows push notifications
Mobile push notifications are the pop-up notifications that appear on mobile devices. For calling, this article focuses on voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) push notifications.
Push notifications on the Windows platform are delivered through the Windows Push Notification Service (WNS).
Note
When the application registers for push notifications and handles the push notifications for a Custom Teams Endpoint (CTE), the APIs are the same. The APIs that this article describes can also be invoked on the CommonCallAgent or TeamsCallAgent class for a CTE.
Set up your system
Follow these steps to set up your system.
Create the Visual Studio project
For a Universal Windows Platform app, in Visual Studio 2022, create a new Blank App (Universal Windows) project. After you enter the project name, feel free to choose any Windows SDK later than 10.0.17763.0.
For a WinUI 3 app, create a new project with the Blank App, Packaged (WinUI 3 in Desktop) template to set up a single-page WinUI 3 app. Windows App SDK version 1.3 or later is required.
Install the package and dependencies by using NuGet Package Manager
The Calling SDK APIs and libraries are publicly available via a NuGet package.
To find, download, and install the Calling SDK NuGet package:
- Open NuGet Package Manager by selecting Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Manage NuGet Packages for Solution.
- Select Browse, and then enter Azure.Communication.Calling.WindowsClient in the search box.
- Make sure that the Include prerelease checkbox is selected.
- Select the Azure.Communication.Calling.WindowsClient package, and then select Azure.Communication.Calling.WindowsClient 1.4.0-beta.1 or a newer version.
- Select the checkbox that corresponds to the Azure Communication Services project on the right pane.
- Select Install.
Set up push notifications
Before you start the tasks of registering for, handling, and showing a Windows notification to answer or decline an incoming call, complete this setup task:
Follow Tutorial: Send notifications to Universal Windows Platform apps using Azure Notification Hubs. After you follow the tutorial, you have:
- An application that has the
WindowsAzure.Messaging.ManagedandMicrosoft.Toolkit.Uwp.Notificationspackages. - An Azure Notifications Hub hub name referenced as
<AZURE_PNH_HUB_NAME>and an Azure Notifications Hub connection string referenced as<AZURE_PNH_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING>in this article.
- An application that has the
To register for a WNS channel on every application initialization, be sure to add the initialization code in your
App.xaml.csfile:// App.xaml.cs protected override async void OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs e) { await InitNotificationsAsync(); ... } private async Task InitNotificationsAsync() { if (AZURE_PNH_HUB_NAME != "<AZURE_PNH_HUB_NAME>" && AZURE_PNH_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING != "<AZURE_PNH_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING>") { var channel = await PushNotificationChannelManager.CreatePushNotificationChannelForApplicationAsync(); channel.PushNotificationReceived += Channel_PushNotificationReceived; var hub = new NotificationHub(AZURE_PNH_HUB_NAME, AZURE_PNH_HUB_CONNECTION_STRING); var result = await hub.RegisterNativeAsync(channel.Uri); if (result.ChannelUri != null) { PNHChannelUri = new Uri(result.ChannelUri); } else { Debug.WriteLine("Cannot register WNS channel"); } } }Register the event handler activated when a new push notification message arrives on
App.xaml.cs:// App.xaml.cs private void Channel_PushNotificationReceived(PushNotificationChannel sender, PushNotificationReceivedEventArgs args) { switch (args.NotificationType) { case PushNotificationType.Toast: case PushNotificationType.Tile: case PushNotificationType.TileFlyout: case PushNotificationType.Badge: break; case PushNotificationType.Raw: var frame = (Frame)Window.Current.Content; if (frame.Content is MainPage) { var mainPage = frame.Content as MainPage; await mainPage.HandlePushNotificationIncomingCallAsync(args.RawNotification.Content); } break; } }
Register for push notifications
To register for push notifications, call RegisterForPushNotificationAsync() on a CallAgent instance with the WNS registration channel obtained on application initialization.
Registration for push notifications needs to happen after successful initialization.
// MainPage.xaml.cs
this.callAgent = await this.callClient.CreateCallAgentAsync(tokenCredential, callAgentOptions);
if ((Application.Current as App).PNHChannelUri != null)
{
await this.callAgent.RegisterForPushNotificationAsync((Application.Current as App).PNHChannelUri.ToString());
}
this.callAgent.CallsUpdated += OnCallsUpdatedAsync;
this.callAgent.IncomingCallReceived += OnIncomingCallAsync;
Handle push notifications
To receive push notifications for incoming calls, call handlePushNotification() on a CallAgent instance with a dictionary payload:
// MainPage.xaml.cs
public async Task HandlePushNotificationIncomingCallAsync(string notificationContent)
{
if (this.callAgent != null)
{
PushNotificationDetails pnDetails = PushNotificationDetails.Parse(notificationContent);
await callAgent.HandlePushNotificationAsync(pnDetails);
}
}
This call triggers an incoming call event on CallAgent that shows the incoming call notification:
// MainPage.xaml.cs
private async void OnIncomingCallAsync(object sender, IncomingCallReceivedEventArgs args)
{
incomingCall = args.IncomingCall;
(Application.Current as App).ShowIncomingCallNotification(incomingCall);
}
// App.xaml.cs
public void ShowIncomingCallNotification(IncomingCall incomingCall)
{
string incomingCallType = incomingCall.IsVideoEnabled ? "Video" : "Audio";
string caller = incomingCall.CallerDetails.DisplayName != "" ? incomingCall.CallerDetails.DisplayName : incomingCall.CallerDetails.Identifier.RawId;
new ToastContentBuilder()
.SetToastScenario(ToastScenario.IncomingCall)
.AddText(caller + " is calling you.")
.AddText("New Incoming " + incomingCallType + " Call")
.AddButton(new ToastButton()
.SetContent("Decline")
.AddArgument("action", "decline"))
.AddButton(new ToastButton()
.SetContent("Accept")
.AddArgument("action", "accept"))
.Show();
}
Add the code to handle the button press for the notification in the OnActivated method:
// App.xaml.cs
protected override async void OnActivated(IActivatedEventArgs e)
{
// Handle notification activation
if (e is ToastNotificationActivatedEventArgs toastActivationArgs)
{
ToastArguments args = ToastArguments.Parse(toastActivationArgs.Argument);
string action = args?.Get("action");
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(action))
{
var frame = Window.Current.Content as Frame;
if (frame.Content is MainPage)
{
var mainPage = frame.Content as MainPage;
await mainPage.AnswerIncomingCall(action);
}
}
}
}
// MainPage.xaml.cs
public async Task AnswerIncomingCall(string action)
{
if (action == "accept")
{
var acceptCallOptions = new AcceptCallOptions()
{
IncomingVideoOptions = new IncomingVideoOptions()
{
StreamKind = VideoStreamKind.RemoteIncoming
}
};
call = await incomingCall?.AcceptAsync(acceptCallOptions);
call.StateChanged += OnStateChangedAsync;
call.RemoteParticipantsUpdated += OnRemoteParticipantsUpdatedAsync;
}
else if (action == "decline")
{
await incomingCall?.RejectAsync();
}
}