Dapr integration with Azure Container Apps
Distributed Application Runtime (Dapr) provides APIs that run as a sidecar process that helps you write and implement simple, portable, resilient, and secured microservices. Dapr works together with Azure Container Apps as an abstraction layer to provide a low-maintenance, serverless, and scalable platform. Enabling Dapr on your container app creates a secondary process alongside your application code that simplifies application intercommunication with Dapr via HTTP or gRPC.
Dapr in Azure Container Apps
Configure Dapr for your container apps environment with a Dapr-enabled container app, a Dapr component configured for your solution, and a Dapr sidecar invoking communication between them. The following diagram demonstrates these core concepts related to Dapr in Azure Container Apps.
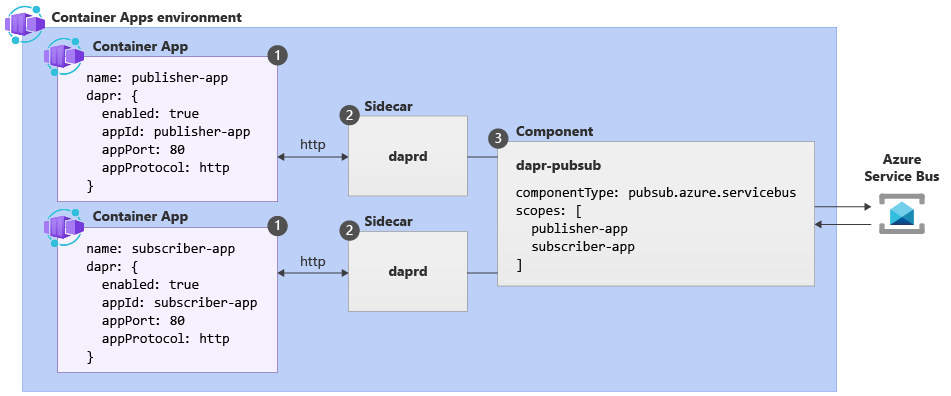
| Label | Dapr settings | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Container Apps with Dapr enabled | Dapr is enabled at the container app level by configuring a set of Dapr arguments. These values apply to all revisions of a given container app when running in multiple revisions mode. |
| 2 | Dapr | The fully managed Dapr APIs are exposed to each container app through a Dapr sidecar. The Dapr APIs can be invoked from your container app via HTTP or gRPC. The Dapr sidecar runs on HTTP port 3500 and gRPC port 50001. |
| 3 | Dapr component configuration | Dapr uses a modular design where functionality is delivered as a component. Dapr components can be shared across multiple container apps. The Dapr app identifiers provided in the scopes array dictate which dapr-enabled container apps load a given component at runtime. |
Supported Dapr APIs
Azure Container Apps offers fully managed versions of the following stable Dapr APIs (building blocks). To learn more about using alpha APIs and features, see the Dapr FAQ.
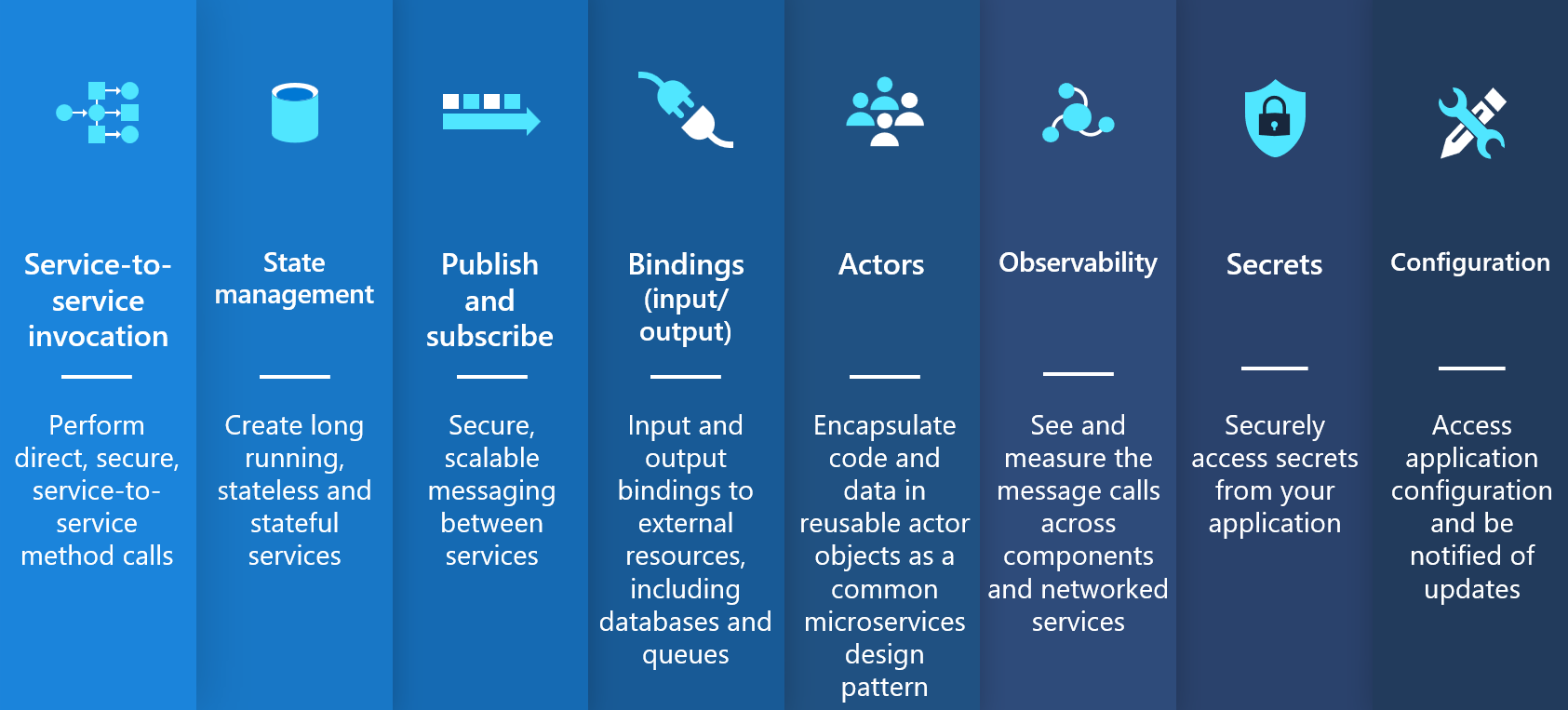
| Dapr API | Description |
|---|---|
| Service-to-service invocation | Discover services and perform reliable, direct service-to-service calls with automatic mTLS authentication and encryption. See known limitations for Dapr service invocation in Azure Container Apps. |
| State management | Provides state management capabilities for transactions and CRUD operations. |
| Pub/sub | Allows publisher and subscriber container apps to intercommunicate via an intermediary message broker. You can also create declarative subscriptions to a topic using an external component JSON file. Learn more about the declarative pub/sub API. |
| Bindings | Trigger your applications based on events |
| Actors | Dapr actors are message-driven, single-threaded, units of work designed to quickly scale. For example, in burst-heavy workload situations. |
| Observability | Send tracing information to an Application Insights backend. |
| Secrets | Access secrets from your application code or reference secure values in your Dapr components. |
| Configuration | Retrieve and subscribe to application configuration items for supported configuration stores. |
Limitations
- Dapr Configuration spec: Any capabilities that require use of the Dapr configuration spec.
- Any Dapr sidecar annotations not listed in the Dapr enablement guide
- Alpha APIs and components: Azure Container Apps doesn't guarantee the availability of Dapr alpha APIs and features. For more information, see the Dapr FAQ.
- Actor reminders: Require a minReplicas of 1+ to ensure reminders is always active and fires correctly.
- Jobs: Dapr isn't supported for jobs.
Next Steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for