Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
SQL MCP Server is in preview and this documentation and the engine implementation is subject to change during this evaluation period.
This quickstart uses Aspire to build a container-based solution. The solution includes:
- A SQL database with sample data
- A SQL Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server powered by Data API builder
- MCP Inspector for testing
Aspire runs everything for you, starts services and connects containers, and stops services when you close it.
Prerequisites
Install these tools before you start.
1. .NET 10
In this step, you prepare your machine with the prerequisites required for this quickstart.
Important
You may already have this tool installed. Test it by running dotnet --version and confirm it reports version 10 or later. If you run this installation and .NET is already present, it refreshes your system without causing any issues.
Windows
winget install Microsoft.DotNet.SDK.10
Or download
https://get.dot.net
2. Container runtime
In this step, you install Docker Desktop to support the Aspire project.
Important
You may already have this tool installed. Test it by running docker --version to confirm Docker is available. If you run this installation and Docker is already present, it refreshes your system without causing any issues.
Windows
winget install Docker.DockerDesktop
macOS
brew install --cask docker
Note
Podman also works, but setup varies. Developers who prefer Podman can adapt these steps.
3. Aspire and Data API builder tools
In this step, you create the default Aspire project files used later.
Run the following commands
dotnet new tool-manifest
dotnet tool install aspire.cli
dotnet tool install microsoft.dataapibuilder --prerelease
aspire init
Note
SQL MCP Server is currently in prerelease. Using the --prerelease flag ensures you get the latest version of Data API builder with all the features used in this quickstart.
When prompted, select all defaults.
This command installs the tooling and creates the following files
.
├── .config
│ └── dotnet-tools.json
├── AppHost.cs
└── apphost.run.json
4. Complete the AppHost.cs file
In this step, you update AppHost.cs with the correct code to run this quickstart.
Replace the contents of AppHost.cs with the following
#:sdk Aspire.AppHost.Sdk@13.0.2
#:package Aspire.Hosting.SqlServer@13.0.2
#:package CommunityToolkit.Aspire.Hosting.McpInspector@9.8.0
using System.ComponentModel;
using Aspire.Hosting;
using Aspire.Hosting.ApplicationModel;
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var db = AddSqlServer(builder);
WithSqlCommander(db);
var mcp = AddMcpServer(db);
WithMcpInspector(mcp);
await builder.Build().RunAsync();
IResourceBuilder<SqlServerDatabaseResource> AddSqlServer(IDistributedApplicationBuilder builder) => builder
.AddSqlServer("sql-server").WithDataVolume()
.AddDatabase("sql-database", "productsdb")
.WithCreationScript(SqlScript("productsdb"));
IResourceBuilder<ContainerResource> WithSqlCommander(IResourceBuilder<SqlServerDatabaseResource> db) => db
.ApplicationBuilder.AddContainer("sql-cmdr", "jerrynixon/sql-commander", "latest")
.WithImageRegistry("docker.io")
.WithHttpEndpoint(targetPort: 8080, name: "http")
.WithEnvironment("ConnectionStrings__db", db)
.WithParentRelationship(db)
.WaitFor(db)
.WithUrls(x =>
{
x.Urls.Clear();
x.Urls.Add(new() { Url = "/", DisplayText = "Commander", Endpoint = x.GetEndpoint("http") });
});
IResourceBuilder<ContainerResource> AddMcpServer(IResourceBuilder<SqlServerDatabaseResource> db) => db
.ApplicationBuilder.AddContainer("sql-mcp-server", "azure-databases/data-api-builder", "1.7.83-rc")
.WithImageRegistry("mcr.microsoft.com")
.WithHttpEndpoint(targetPort: 5000, name: "http")
.WithEnvironment("MSSQL_CONNECTION_STRING", db)
.WithBindMount("dab-config.json", "/App/dab-config.json", true)
.WaitFor(db)
.WithUrls(x =>
{
x.Urls.Clear();
x.Urls.Add(new() { Url = "/swagger", DisplayText = "Swagger", Endpoint = x.GetEndpoint("http") });
});
IResourceBuilder<McpInspectorResource> WithMcpInspector(IResourceBuilder<ContainerResource> mcp) => mcp
.ApplicationBuilder.AddMcpInspector("mcp-inspector")
.WithMcpServer(mcp)
.WithParentRelationship(mcp)
.WaitFor(mcp)
.WithUrls(x =>
{
x.Urls[0].DisplayText = "Inspector";
});
string SqlScript(string db) => $"""
CREATE DATABASE {db};
GO
SELECT *
INTO {db}.dbo.Products
FROM (VALUES
(1, 'Action Figure', 40, 14.99, 5.00),
(2, 'Building Blocks', 25, 29.99, 10.00),
(3, 'Puzzle 500 pcs', 30, 12.49, 4.00),
(4, 'Toy Car', 50, 7.99, 2.50),
(5, 'Board Game', 20, 34.99, 12.50),
(6, 'Doll House', 10, 79.99, 30.00),
(7, 'Stuffed Bear', 45, 15.99, 6.00),
(8, 'Water Blaster', 35, 19.99, 7.00),
(9, 'Art Kit', 28, 24.99, 8.00),
(10,'RC Helicopter', 12, 59.99, 22.00)
) AS x (Id, Name, Inventory, Price, Cost);
ALTER TABLE {db}.dbo.Products
ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Products PRIMARY KEY (Id);
""";
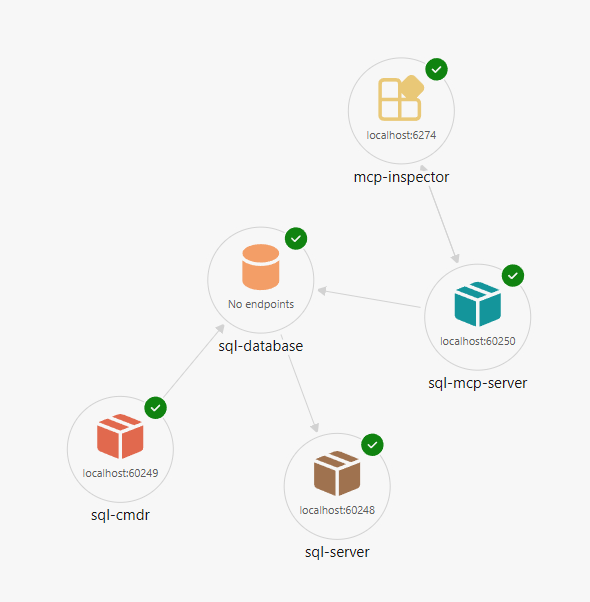
This code configures the following resources
.
├── SQL Server (sql)
│ └── SQL Database (productsdb)
└── SQL MCP Server (sql-mcp-server)
└── MCP Inspector (inspector)
5. Create your dab-config.json file
Run these commands in your project folder (the same folder where AppHost.cs is located).
The @env('MSSQL_CONNECTION_STRING') syntax tells Data API builder to read the connection string from an environment variable at runtime. Aspire sets this variable automatically when it starts the container, so you don't need to set it locally.
dab init --database-type mssql --connection-string "@env('MSSQL_CONNECTION_STRING')" --host-mode Development --config dab-config.json
dab add Products --source dbo.Products --permissions "anonymous:read" --description "Toy store products with inventory, price, and cost."
Note
The @env(...) expression is a DAB configuration feature that resolves environment variables at runtime, not during dab init. The generated dab-config.json contains the literal string @env('MSSQL_CONNECTION_STRING'), which DAB resolves when the container starts.
The dab-config.json file configures SQL MCP Server to connect to your database and identifies which objects to expose. In this case, Products is exposed.
This command adds a new file to your project
dab-config.json
Important
The dab-config.json file must be in the same directory where you run aspire run, because the bind mount uses a relative path (./dab-config.json).
Optionally, add field descriptions
This metadata can help language models understand your schema.
dab update Products --fields.name Id --fields.primary-key true --fields.description "Product Id"
dab update Products --fields.name Name --fields.description "Product name"
dab update Products --fields.name Inventory --fields.description "Units in stock"
dab update Products --fields.name Price --fields.description "Retail price"
dab update Products --fields.name Cost --fields.description "Store cost"
Test your solution
In this step, you run your Aspire environment and confirm that SQL Server, SQL MCP Server, and MCP Inspector are working together.
1. Start Aspire
aspire run
Important
Ensure Docker is running. Aspire requires your container host to work properly.
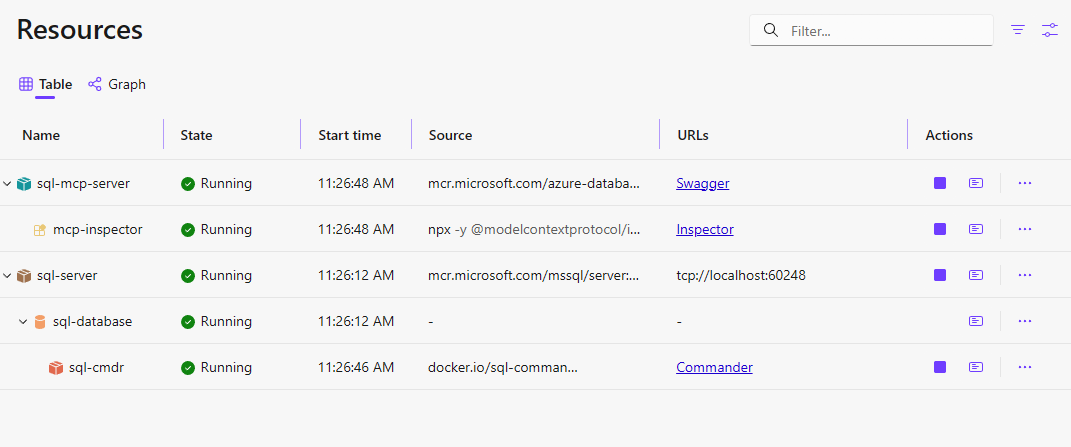
When the dashboard opens, you see links for Swagger, MCP, and Inspector.
Expected URLs
The Aspire dashboard displays these links (ports are assigned dynamically):
| Resource | Link | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sql-mcp-server | Swagger | REST API documentation |
| sql-mcp-server | MCP | MCP endpoint (/mcp) |
| inspector | Inspector | MCP Inspector UI |
2. Test the REST API with Swagger
Select Swagger from the dashboard.
Try the GET operation for Products. This test confirms SQL MCP Server is running and can connect to the database.
3. Explore the MCP tools
Select Inspector from the dashboard.
Try:
list_toolsto see available MCP toolsread_recordsfor theProductsentity
Try a filter (example syntax):
{ "filter": "Price gt 20" }
This test confirms MCP is working.
4. Stop Aspire
To stop Aspire, press Ctrl+C.
Aspire stops all services. SQL Server data persists between runs because the code uses .WithDataVolume() and .WithLifetime(ContainerLifetime.Persistent).
Troubleshooting
SQL MCP Server container fails to start
- Check the container logs in the Aspire dashboard for error details
- Verify the
--configargument matches the DAB container's expected syntax (some versions may use--ConfigFileNameinstead) - Ensure
dab-config.jsonexists in the same directory where you runaspire run
Database initialization script not found
- Verify
init-db.sqlis in the AppHost project directory - Check that the file is included in the project and copies to output if required
MCP Inspector can't connect
- Confirm the SQL MCP Server container is running and healthy
- Verify the MCP endpoint path (
/mcp) matches the DAB configuration