Using Kusto.Explorer
Kusto.Explorer is a desktop application that enables you to explore your data using the Kusto Query Language in an easy-to-use user interface. This article shows you how to use search and query modes, share your queries, and manage clusters, databases, and tables.
Search++ mode
Search++ mode enables you to search for a term using search syntax across one or more tables.
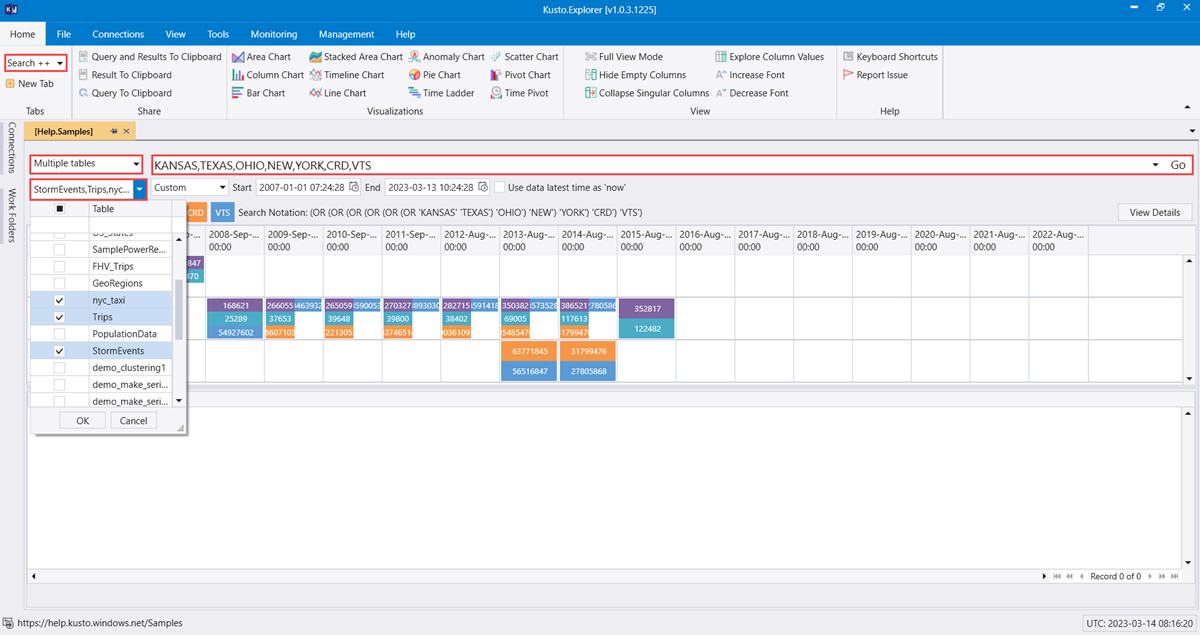
In the Query dropdown on the Home tab, select Search++.
Select Multiple tables.
Under Choose tables, define which tables to search, then select OK.
In the edit box, enter your search phrase and select Go.
A heat-map of the table/time-slot grid shows which terms appear and where they appear.
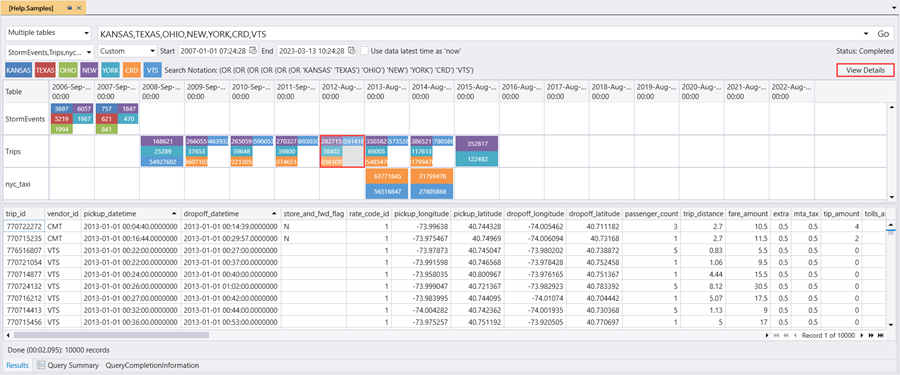
Select a cell in the grid and select View Details to show the relevant entries in the results pane.
Query mode
Kusto.Explorer includes a powerful query mode that enables you to write, edit, and run inline queries. The query mode comes with syntax highlighting and IntelliSense, so you can quickly ramp-up your knowledge of the Kusto Query Language.
This section describes how to run basic queries in Kusto.Explorer and how to add parameters to your queries.
Basic queries
If you have table Logs, you can start exploring them:
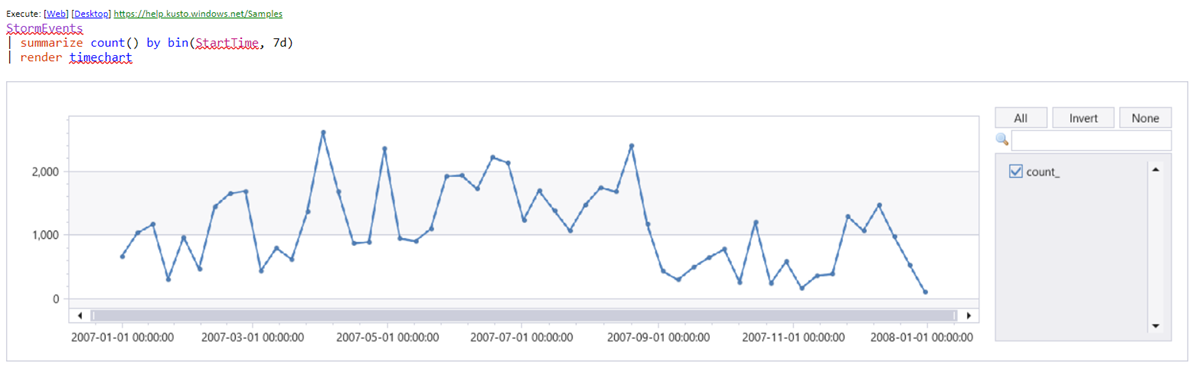
StormEvents | count
When your cursor is on this line, it's colored gray. Press F5 to run the query.
Here are some more example queries:
// Take 10 lines from the table. Useful to get familiar with the data
StormEvents | take 10
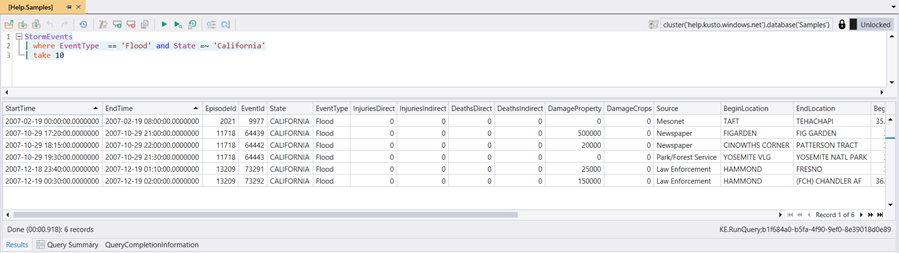
// Filter by EventType == 'Flood' and State == 'California' (=~ means case insensitive)
// and take sample of 10 lines
StormEvents
| where EventType == 'Flood' and State =~ 'California'
| take 10
To learn more about the Kusto Query Language, see Kusto Query Language.
Note
Blank lines in the query expression can affect which part of the query is executed.
If no text selected, it's assumed that the query or command is separated by empty lines. If text is selected, the selected text is run.
Client-side query parameterization
Note
There are two types of query parametrization techniques in Kusto:
Language-integrated query parametrization is implemented server-side and is meant to be used by applications that query the service programmatically. This method is not described in this document.
Client-side query parametrization, described below, is a feature of the Kusto.Explorer application only. It's equivalent to using string-replace operations on the queries before sending them to be executed by the service. The syntax described below is not part of the query language itself and can't be used when sending queries to the service by means other than Kusto.Explorer.
If you use the same value in multiple queries or in multiple tabs, it's highly inconvenient to change that value in every place it's used. That's why Kusto.Explorer supports query parameters. Query parameters are shared among tabs so that they can be easily reused. Parameters are denoted by {} brackets. For example, {parameter1}.
You can easily define and edit existing query parameters:
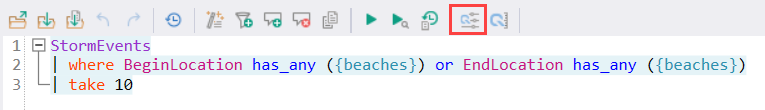
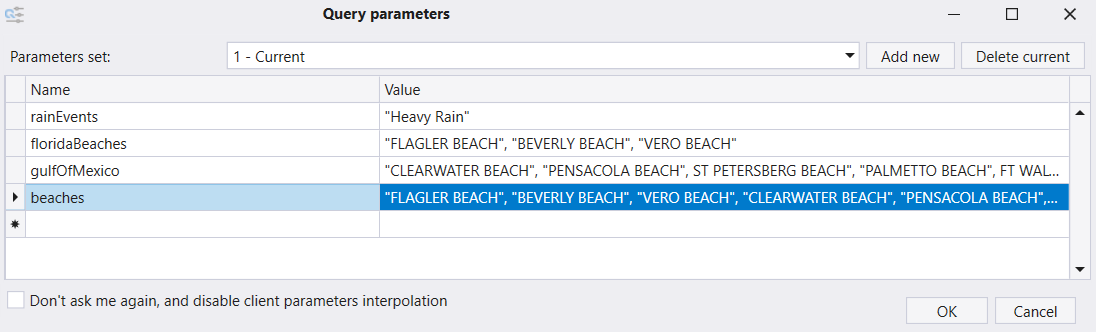
You can have multiple sets of parameters (listed in the Parameters Set combo box). Select Add new or Delete current to manipulate the list of parameter sets.
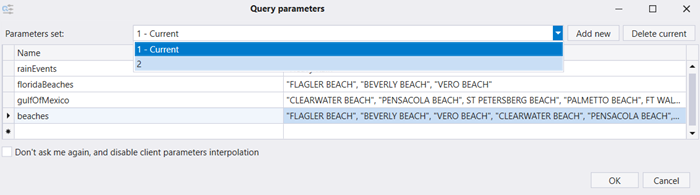
Share queries and results
In Kusto.Explorer, you can share queries and results by email. You can also create deep links that open and run a query in the browser.
Share queries and results by email
Kusto.Explorer provides a convenient way to share queries and query results by email.
Run your query in Kusto.Explorer.
In the Home tab, in the Share section, select Query and Results to Clipboard (or press Ctrl+Shift+C).
Kusto.Explorer copies the following to the clipboard:
- Your query
- The query results (table or chart)
- The connection details for the Kusto cluster and database
- A link that reruns the query automatically
Paste the contents of the clipboard into a new email message.
Deep-linking queries
You can create a URI that, when opened in a browser, opens Kusto.Explorer locally and runs a specific query on a specified Kusto database.
Note
For security reasons, deep-linking is disabled for management commands.
Creating a deep-link
The easiest way to create a deep-link is to author your query in Kusto.Explorer and then use
Export to Clipboard to copy the query (including the deep link and results) to the clipboard. You can then share it by email.
When copied to an email, the deep link is displayed in small font. For example:
https://help.kusto.windows.net/Samples [Run the query]
The first link opens Kusto.Explorer and sets the cluster and database context appropriately.
The second link (Run the query) is the deep link. If you move the link to an email message and press CTRL+K, you can see the actual URL:
https://help.kusto.windows.net/Samples?web=0&query=H4sIAAAAAAAEAAsuyS%2fKdS1LzSspVuDlqlEoLs3NTSzKrEpVSM4vzSvR0FRIqlRIyszTCC5JLCoJycxN1VEwT9EEKS1KzUtJLVIoAYolZwAlFQCB3oo%2bTAAAAA%3d%3d
Deep-links and parametrized queries
You can use parametrized queries with deep-linking.
Create a query to be formed as a parametrized query (for example,
KustoLogs | where Timestamp > ago({Period}) | count)Provide a parameter for every query parameter in the URI, such as:
https://<your_cluster>.kusto.windows.net/MyDatabase? web=0&query=KustoLogs+%7c+where+Timestamp+>+ago({Period})+%7c+count&Period=1hReplace <your_cluster> with your Azure Data Explorer cluster name.
Limitations
The queries are limited to ~2000 characters because of browser limitations, HTTP proxies, and tools that validate links, such as Microsoft Outlook. The limitation is approximate because it's dependent on the cluster and Database name length. For more information, see https://support.microsoft.com/kb/208427.
To reduce the chances of reaching the character limit, see Getting Shorter Links.
The format of the URI is:
https://<ClusterCname>.kusto.windows.net/<DatabaseName>web=0?query=<QueryToExecute>
For example: https://help.kusto.windows.net/Samples?web=0query=StormEvents+%7c+limit+10
This URI will open Kusto.Explorer, connect to the Help Kusto cluster, and run the specified query on the Samples database. If there's an instance of Kusto.Explorer already running, the running instance will open a new tab and run the query in it.
Getting shorter links
Queries can become long. To reduce the chance the query exceeds the maximum length, use the String Kusto.Data.Common.CslCommandGenerator.EncodeQueryAsBase64Url(string query) method available in Kusto Client Library. This method produces a more compact version of the query. The shorter format is also recognized by Kusto.Explorer.
The query is made more compact by applying next transformation:
UrlEncode(Base64Encode(GZip(original query)))
Kusto.Explorer command-line arguments
Command-line arguments are used to configure the tool to perform additional functions on start-up. For example, load a script and connect to a cluster. As such, command-line arguments aren't a replacement for any Kusto.Explorer functionality.
Command-line arguments are passed as part of the URL that's used to open the application, in a similar way to query deep-linking.
Command-line argument syntax
Kusto.Explorer supports several command-line arguments in the following syntax (the order matters):
[LocalScriptFile] [QueryString]
- LocalScriptFile is the name of a script file on your local machine, which must have the extension
.kql. If such a file exists, Kusto.Explorer automatically loads this file when it starts up. - QueryString is a string that uses HTTP query string formatting. This method provides additional properties, as described in the table below.
For example, to start Kusto.Explorer with a script file called c:\temp\script.kql
and configured to communicate with cluster help, database Samples, use the
following command:
Kusto.Explorer.exe c:\temp\script.kql "uri=https://help.kusto.windows.net/Samples;Fed=true&name=Samples"
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| Query to execute | |
query |
The query to execute (gzipped, then base64-encoded; see "Getting shorter links" above). If empty, use querysrc. |
querysrc |
The HTTP URL of a file/blob holding the query to execute (if query is empty). |
| Connection to the Kusto cluster | |
uri |
The connection string of the Kusto cluster to connect to. |
name |
The display name of the connection to the Kusto cluster. |
| Connection group | |
path |
The URL of a connection group file to download (URL-encoded). |
group |
The name of the connection group. |
filename |
The local file holding the connection group. |
Manage databases, tables, or function authorized principals
Important
Only admins can add or drop authorized principals in their own scope.
To view the list of authorized principals, right-click the target entity in the Connections panel, and select Manage Database Authorized Principals. (You can also select this option from the Management Menu.)
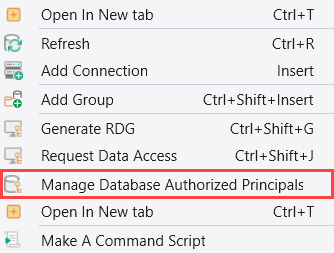
Select Add principal to add an authorized principal.
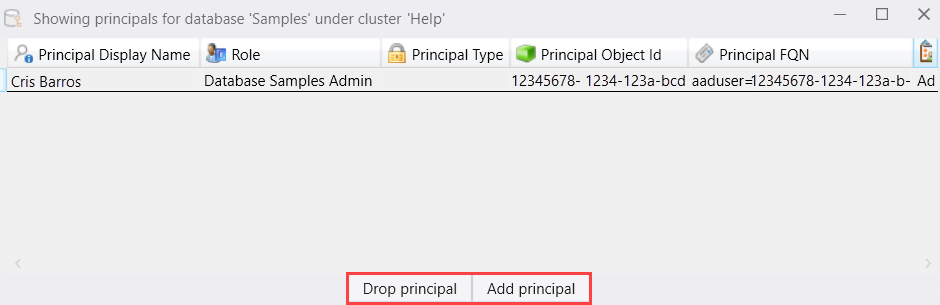
Provide the principal details, then select Add principal.
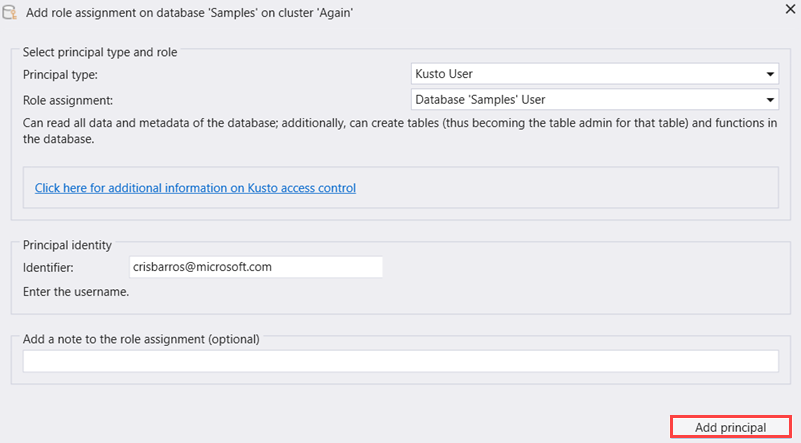
Confirm that you want to add the authorized principal.
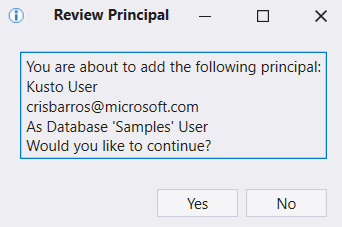
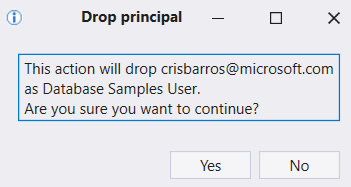
To drop an existing authorized principal, select Drop principal and confirm the action.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for