Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article outlines how to use the Copy Activity in Azure Data Factory and Synapse Analytics pipelines to copy data from a MySQL database. It builds on the copy activity overview article that presents a general overview of copy activity.
Note
To copy data from or to Azure Database for MySQL service, use the specialized Azure Database for MySQL connector.
Important
The MySQL connector version 1.0 is at removal stage. You are recommended to upgrade the MySQL connector from version 1.0 to 2.0.
Supported capabilities
This MySQL connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR |
|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/-) | ① ② |
| Lookup activity | ① ② |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For a list of data stores that are supported as sources/sinks by the copy activity, see the Supported data stores table.
This connector supports MySQL version 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 8.0, 8.1 and 8.2 under the MySQL connector version 2.0 and 5.6, 5.7 and 8.0 for version 1.0.
Prerequisites
If your data store is located inside an on-premises network, an Azure virtual network, or Amazon Virtual Private Cloud, you need to configure a self-hosted integration runtime to connect to it.
If your data store is a managed cloud data service, you can use the Azure Integration Runtime. If the access is restricted to IPs that are approved in the firewall rules, you can add Azure Integration Runtime IPs to the allow list.
You can also use the managed virtual network integration runtime feature in Azure Data Factory to access the on-premises network without installing and configuring a self-hosted integration runtime.
For more information about the network security mechanisms and options supported by Data Factory, see Data access strategies.
The Integration Runtime provides a built-in MySQL driver starting from version 3.7, therefore you don't need to manually install any driver.
Getting started
To perform the copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- Copy Data tool
- Azure portal
- .NET SDK
- Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- REST API
- Azure Resource Manager template
Create a linked service to MySQL using UI
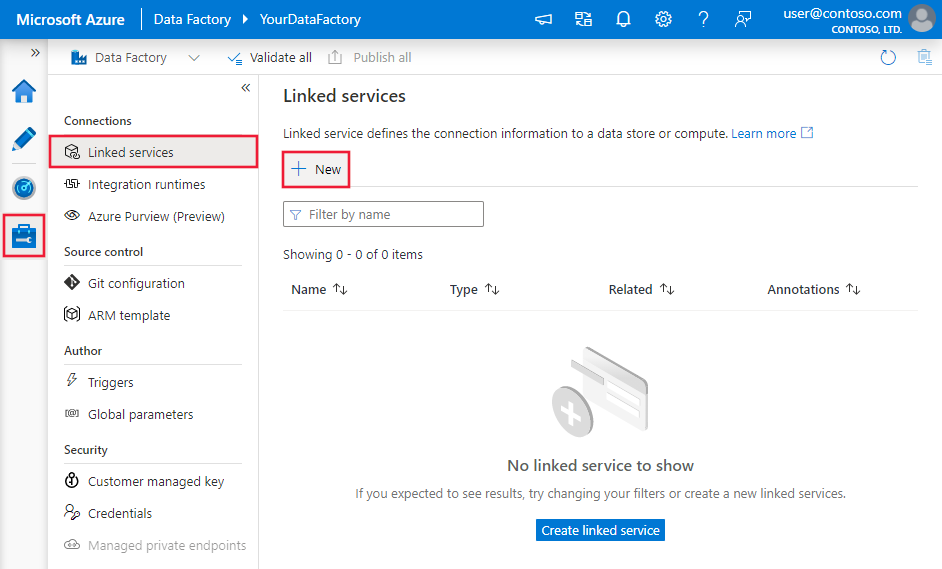
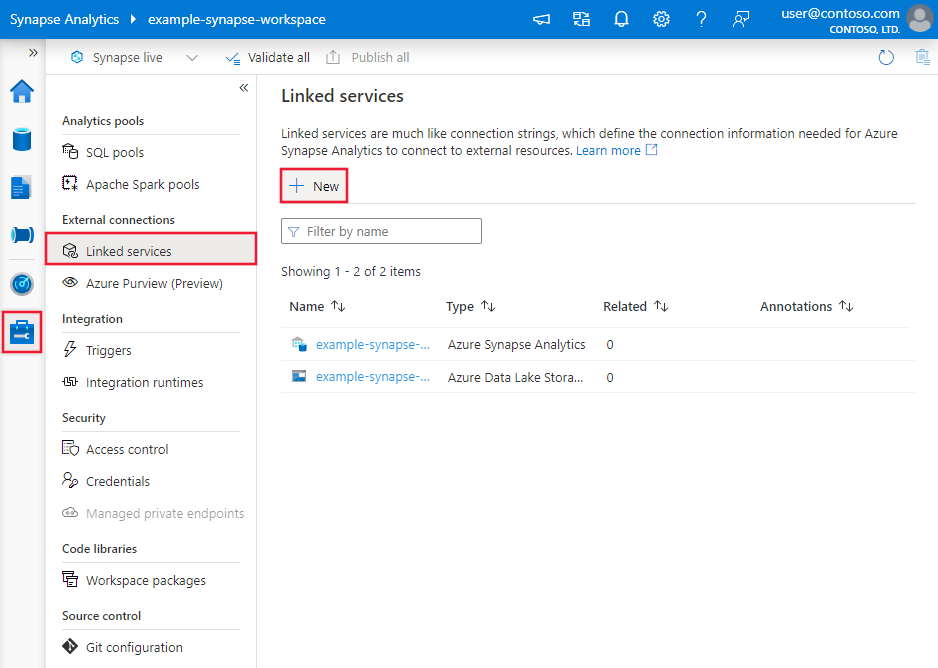
Use the following steps to create a linked service to MySQL in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
Search for MySQL and select the MySQL connector.

Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
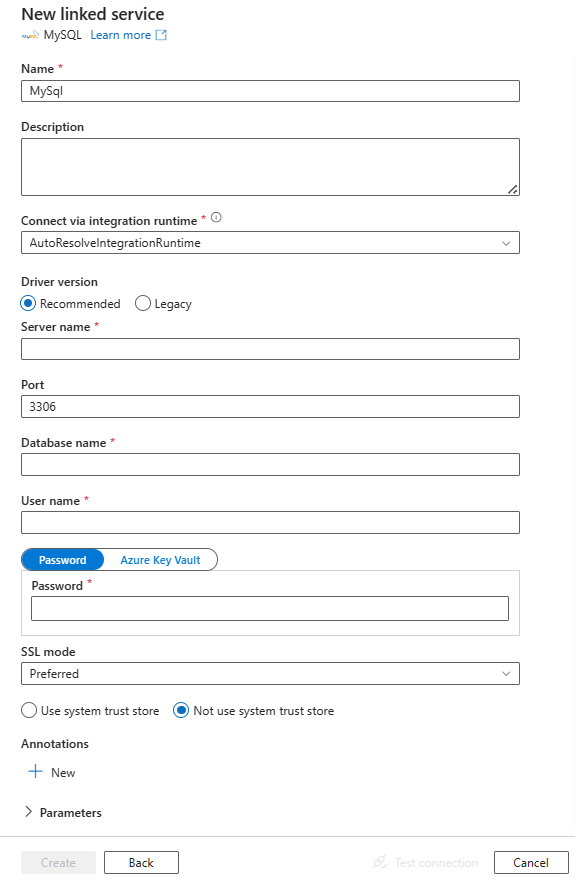
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that are used to define Data Factory entities specific to MySQL connector.
Linked service properties
If you use version 2.0, the following properties are supported for MySQL linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to: MySql | Yes |
| driverVersion | The driver version when you select version 2.0. The value is v2. | Yes |
| server | The name of your MySQL Server. | Yes |
| port | The port number to connect to the MySQL server. | No |
| database | Your MySQL database name. | Yes |
| username | Your user name. | Yes |
| password | The password for the user name. Mark this field as SecureString to store it securely. Or, you can reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. | Yes |
| sslMode | This option specifies whether the driver uses TLS encryption and verification when connecting to MySQL. E.g., SSLMode=<0/1/2/3/4>.Options: DISABLED (0) / PREFERRED (1) (Default) / REQUIRED (2) / VERIFY_CA (3) / VERIFY_IDENTITY (4) |
Yes |
| useSystemTrustStore | This option specifies whether to use a CA certificate from the system trust store, or from a specified PEM file. E.g. UseSystemTrustStore=<0/1>;Options: Enabled (1) / Disabled (0) (Default) |
No |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to be used to connect to the data store. Learn more from Prerequisites section. If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
| Additional connection properties | ||
| allowZeroDateTime | Specifying this property value to true allows the special "zero" date value of 0000-00-00 to be retrieved from the database. If set to false (the default), date columns are returned as DateTime values, which means 0000-00-00 cannot be retrieved. MySQL permits you to store a "zero" value of 0000-00-00 as a "dummy date". In some cases, this feature is more convenient than using NULL values, and uses less data and index space. To disallow 0000-00-00 in MySQL, enable the NO_ZERO_DATE mode. For more information, see this article. |
No |
| connectionTimeout | The length of time (in seconds) to wait for a connection to the server before terminating the attempt and generating an error. | No |
| convertZeroDateTime | Set it to true to return DateTime.MinValue for date or datetime columns that have disallowed values. |
No |
| guidFormat | Determines which column type (if any) should be read as a GUID. Go to this article for the description of each column type by searching this property. Version 2.0 treats Char(36) as GUID type by default for better performance. The connector treats Char(36) fields as GUIDs for easier database handling. This treatment simplifies operations such as inserting, updating, and retrieving GUID values, ensuring they are consistently managed as GUID objects in the application code instead of plain strings. This behavior is particularly useful in scenarios where GUIDs are used as primary keys or unique identifiers and provides better performance. If you don't need this default setting, you can configure guidFormat=none in connection property. |
No |
| sslCert | The path to the client's SSL certificate file in PEM format. SslKey must also be specified. | No |
| sslKey | The path to the client's SSL private key in PEM format. SslCert must also be specified. | No |
| treatTinyAsBoolean | When set to true, tinyint(1) values are returned as Boolean. Setting this property to false causes tinyint(1) to be returned as SByte/Byte. Version 2.0 treats tinyint(1) as Boolean type by default. For more information, see this article. To let the connector return tiny as numeric, set treatTinyAsBoolean=false in the connection properties. |
No |
Example:
{
"name": "MySQLLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "MySql",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<server>",
"port": 3306,
"database": "<database>",
"username": "<username>",
"password": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<password>"
},
"sslmode": <sslmode>,
"usesystemtruststore": <UseSystemTrustStore>,
"driverVersion": "v2"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: store password in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "MySQLLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "MySql",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<server>",
"port": 3306,
"database": "<database>",
"username": "<username>",
"sslmode": <sslmode>,
"usesystemtruststore": <UseSystemTrustStore>,
"password": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName>"
},
"driverVersion": "v2"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
If you use version 1.0, the following properties are supported:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to: MySql | Yes |
| connectionString | Specify information needed to connect to the Azure Database for MySQL instance. You can also put password in Azure Key Vault and pull the password configuration out of the connection string. Refer to the following samples and Store credentials in Azure Key Vault article with more details. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to be used to connect to the data store. Learn more from Prerequisites section. If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
A typical connection string is Server=<server>;Port=<port>;Database=<database>;UID=<username>;PWD=<password>. More properties you can set per your case:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| sslMode | This option specifies whether the driver uses TLS encryption and verification when connecting to MySQL. E.g., SSLMode=<0/1/2/3/4>.Options: DISABLED (0) / PREFERRED (1) (Default) / REQUIRED (2) / VERIFY_CA (3) / VERIFY_IDENTITY (4) |
Yes |
| SSLCert | The full path and name of a .pem file containing the SSL certificate used for proving the identity of the client. To specify a private key for encrypting this certificate before sending it to the server, use the SSLKey property. |
Yes, if using two-way SSL verification. |
| SSLKey | The full path and name of a file containing the private key used for encrypting the client-side certificate during two-way SSL verification. | Yes, if using two-way SSL verification. |
| useSystemTrustStore | This option specifies whether to use a CA certificate from the system trust store, or from a specified PEM file. E.g. UseSystemTrustStore=<0/1>;Options: Enabled (1) / Disabled (0) (Default) |
No |
Example:
{
"name": "MySQLLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "MySql",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "Server=<server>;Port=<port>;Database=<database>;UID=<username>;PWD=<password>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see the datasets article. This section provides a list of properties supported by MySQL dataset.
To copy data from MySQL, the following properties are supported:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to: MySqlTable | Yes |
| tableName | Name of the table in the MySQL database. | No (if "query" in activity source is specified) |
Example
{
"name": "MySQLDataset",
"properties":
{
"type": "MySqlTable",
"typeProperties": {},
"schema": [],
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<MySQL linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
}
}
}
If you were using RelationalTable typed dataset, it is still supported as-is, while you are suggested to use the new one going forward.
Copy activity properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties supported by MySQL source.
MySQL as source
To copy data from MySQL, the following properties are supported in the copy activity source section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to: MySqlSource | Yes |
| query | Use the custom SQL query to read data. For example: "SELECT * FROM MyTable". |
No (if "tableName" in dataset is specified) |
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromMySQL",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<MySQL input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "MySqlSource",
"query": "SELECT * FROM MyTable"
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
If you were using RelationalSource typed source, it is still supported as-is, while you are suggested to use the new one going forward.
Data type mapping for MySQL
When copying data from MySQL, the following mappings are used from MySQL data types to interim data types used by the service internally. See Schema and data type mappings to learn about how copy activity maps the source schema and data type to the sink.
| MySQL data type | Interim service data type (for version 2.0) | Interim service data type (for version 1.0) |
|---|---|---|
| BIGINT | Int64 | Int64 |
| BIGINT UNSIGNED | UInt64 | Decimal |
| BIT(1) | UInt64 | Boolean |
| BIT(M), M>1 | UInt64 | Byte[] |
| BLOB | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| BOOL | Boolean (If TreatTinyAsBoolean=false, it is mapped as SByte. TreatTinyAsBoolean is true by default) |
Int16 |
| CHAR | String | String |
| DATE | Datetime | Datetime |
| DATETIME | Datetime | Datetime |
| DECIMAL | Decimal | Decimal, String |
| DOUBLE | Double | Double |
| DOUBLE PRECISION | Double | Double |
| ENUM | String | String |
| FLOAT | Single | Single |
| INT | Int32 | Int32 |
| INT UNSIGNED | Int64 | Int64 |
| INTEGER | Int32 | Int32 |
| INTEGER UNSIGNED | UInt32 | Int64 |
| JSON | String | Byte[] |
| LONG VARBINARY | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| LONG VARCHAR | String | String |
| LONGBLOB | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| LONGTEXT | String | String |
| MEDIUMBLOB | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| MEDIUMINT | Int32 | Int32 |
| MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED | UInt32 | Int64 |
| MEDIUMTEXT | String | String |
| NUMERIC | Decimal | Decimal |
| REAL | Double | Double |
| SET | String | String |
| SMALLINT | Int16 | Int16 |
| SMALLINT UNSIGNED | UInt16 | Int32 |
| TEXT | String | String |
| TIME | TimeSpan | TimeSpan |
| TIMESTAMP | Datetime | Datetime |
| TINYBLOB | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| TINYINT | SByte | Int16 |
| TINYINT unsigned | Int16 | Int16 |
| TINYTEXT | String | String |
| VARCHAR | String | String |
| YEAR | Int | Int |
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
Upgrade the MySQL connector
Here are steps that help you upgrade your MySQL connector:
In Edit linked service page, select 2.0 under Version and configure the linked service by referring to Linked service properties.
The data type mapping for version 2.0 is different from that for version 1.0. To learn the version 2.0 data type mapping, see Data type mapping for MySQL.
Version 2.0 supports more MySQL versions. For more information, see Supported capabilities.
Best practices for MySQL connector version 2.0
This section introduces best practices for MySQL connector version 2.0.
Cannot load SSL key
Symptoms: If you are using MySQL connector version 2.0 with SSL Key as a connection property, you may meet the following error message:
Could not load the client key from your_pem_file: Unrecognized PEM header: -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----Cause: Version 2.0 cannot decrypt the PCKS#8 format.
Recommendation: Convert the PEM format to PCKS#1.
Differences between MySQL version 2.0 and version 1.0
The table below shows the data type mapping differences between MySQL using version 2.0 and version 1.0.
| MySQL data type | Interim service data type (using version 2.0) | Interim service data type (using version 1.0) |
|---|---|---|
| BIGINT UNSIGNED | UInt64 | Decimal |
| BIT(1) | UInt64 | Boolean |
| BIT(M), M>1 | UInt64 | Byte[] |
| BOOL | Boolean | Int16 |
| DECIMAL | Decimal | Decimal, String |
| INTEGER UNSIGNED | UInt32 | Int64 |
| JSON | String | Byte[] |
| MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED | UInt32 | Int64 |
| SMALLINT UNSIGNED | UInt16 | Int32 |
| TINYINT | SByte | Int16 |
Related content
For a list of data stores supported as sources and sinks by the copy activity, see supported data stores.