Errors and Conditional execution
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
Conditional paths
Azure Data Factory and Synapse Pipeline orchestration allows conditional logic and enables the user to take a different path based upon outcomes of a previous activity. Using different paths allow users to build robust pipelines and incorporates error handling in ETL/ELT logic. In total, we allow four conditional paths,
| Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Upon Success | (Default Pass) Execute this path if the current activity succeeded |
| Upon Failure | Execute this path if the current activity failed |
| Upon Completion | Execute this path after the current activity completed, regardless if it succeeded or not |
| Upon Skip | Execute this path if the activity itself didn't run |
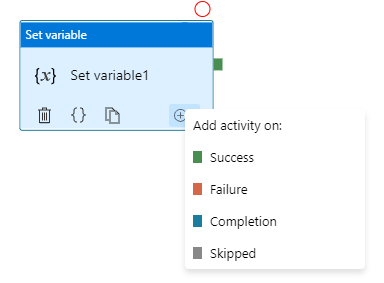
You may add multiple branches following an activity, with one exception: Upon Completion path can't coexist with either Upon Success or Upon Failure path. For each pipeline run, at most one path is activated, based on the execution outcome of the activity.
Error Handling
Common error handling mechanism
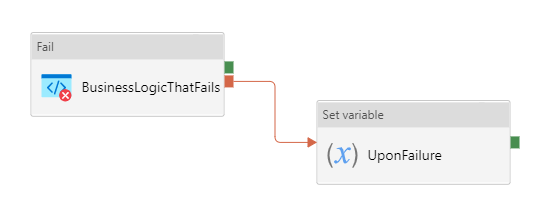
Try Catch block
In this approach, customer defines the business logic, and only defines the Upon Failure path to catch any error from previous activity. This approach renders pipeline succeeds, if Upon Failure path succeeds.
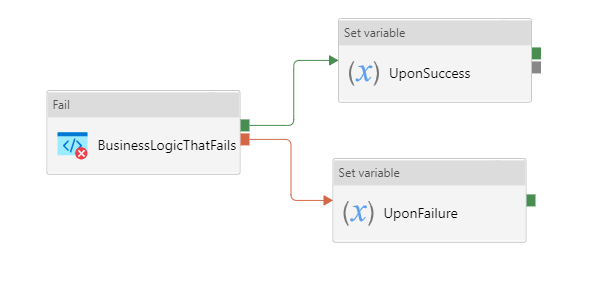
Do If Else block
In this approach, customer defines the business logic, and defines both the Upon Failure and Upon Success paths. This approach renders pipeline fails, even if Upon Failure path succeeds.
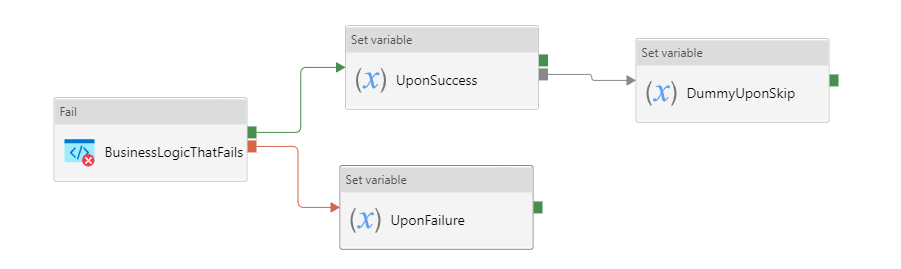
Do If Skip Else block
In this approach, customer defines the business logic, and defines both the Upon Failure path, and Upon Success path, with a dummy Upon Skipped activity attached. This approach renders pipeline succeeds, if Upon Failure path succeeds.
Summary table
| Approach | Defines | When activity succeeds, overall pipeline shows | When activity fails, overall pipeline shows |
|---|---|---|---|
| Try-Catch | Only Upon Failure path | Success | Success |
| Do-If-Else | Upon Failure path + Upon Success paths | Success | Failure |
| Do-If-Skip-Else | Upon Failure path + Upon Success path (with a Dummy Upon Skip at the end) | Success | Success |
How pipeline failure are determined
Different error handling mechanisms lead to different status for the pipeline: while some pipelines fail, others succeed. We determine pipeline success and failures as follows:
- Evaluate outcome for all leaves activities. If a leaf activity was skipped, we evaluate its parent activity instead
- Pipeline result is success if and only if all nodes evaluated succeed
Assuming Upon Failure activity and Dummy Upon Failure activity succeed,
In Try-Catch approach,
- When previous activity succeeds: node Upon Failure is skipped and its parent node succeeds; overall pipeline succeeds
- When previous activity fails: node Upon Failure is enacted; overall pipeline succeeds
In Do-If-Else approach,
- When previous activity succeeds: node Upon Success succeeds and node Upon Failure is skipped (and its parent node succeeds); overall pipeline succeeds
- When previous activity fails: node Upon Success is skipped and its parent node failed; overall pipeline fails
In Do-If-Skip-Else approach,
- When previous activity succeeds: node Dummy Upon Skip is skipped and its parent node Upon Success succeeds; the other node activity, Upon Failure, is skipped and its parent node succeeds; overall pipeline succeeds
- When previous activity fails: node Upon Failure succeeds and Dummy Upon Skip succeeds; overall pipeline succeeds
Conditional execution
As we develop more complicated and resilient pipelines, it's sometimes required to introduced conditional executions to our logic: execute a certain activity only if certain conditions are met. The use cases are plenty, for instance:
- run a follow-up activity, such as sending an email notification, if previous copy jobs succeeded
- run an error handling job, if any of the previous activities failed
- proceed to the next step if either the activity itself or its corresponding error handling activity succeeds
- etc.
Here we explain some common logics and how to implement them in ADF.
Single activity
Here are some common patterns following a single activity. We can use these patterns as building blocks to construct complicated work flows.
Error handling
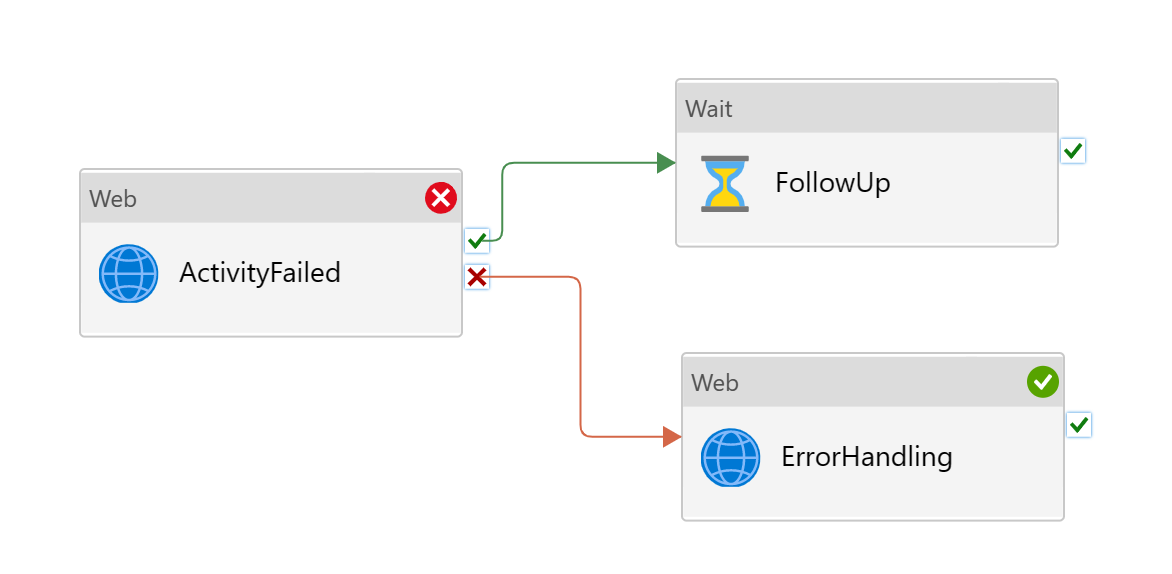
The pattern is the most common condition logic in ADF. An error handling activity is defined for the "Upon Failure" path, and will be invoked if the main activity fails. It should be incorporated as best practice for all mission critical steps that needs fall-back alternatives or logging.
Best effort steps
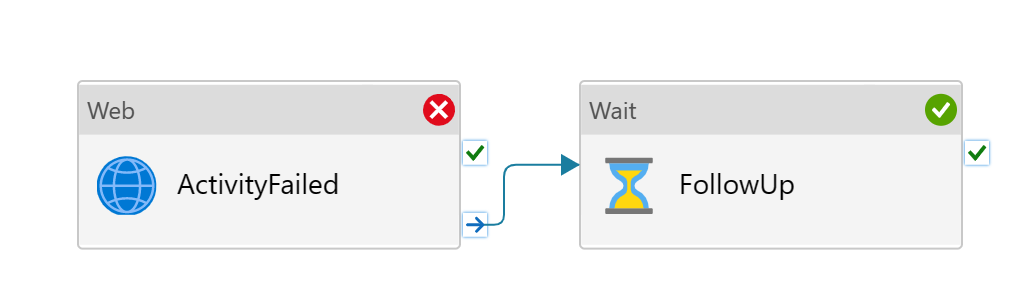
Certain steps, such as informational logging, are less critical, and their failures shouldn't block the whole pipeline. In such cases, we should adopt the best effort strategies: adding next steps to the "Upon Completion" path, to unblock the work flow.
And
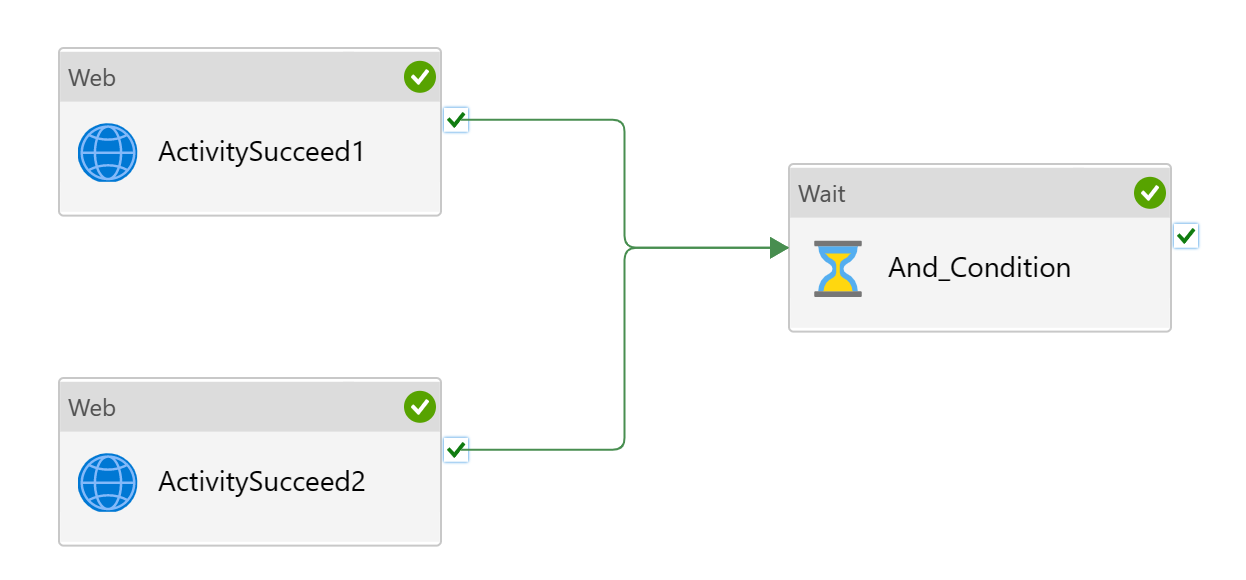
First and most common scenarios are conditional "and": continue the pipeline if and only if the previous activities succeed. For instance, you may have multiple copy activities that need to succeed first before moving onto next stage of data processing. In ADF, the behavior can be achieved easily: declare multiple dependencies for the next step. Graphically, that means multiple lines pointing into the next activity. You can choose either "Upon Success" path to ensure the dependency have succeeded, or "Upon Completion" path to allow best effort execution.
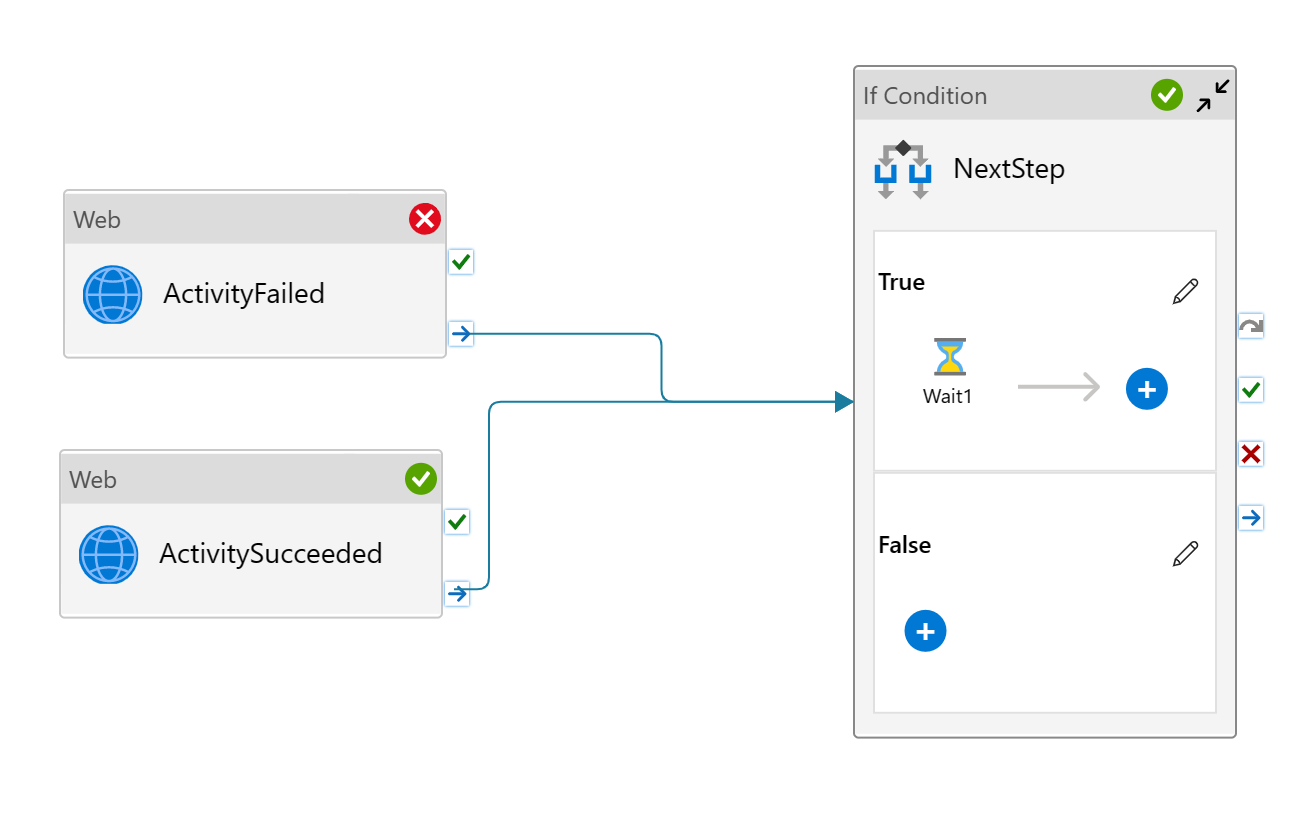
Here, the follow-up wait activity will only execute when both web activities were successful.
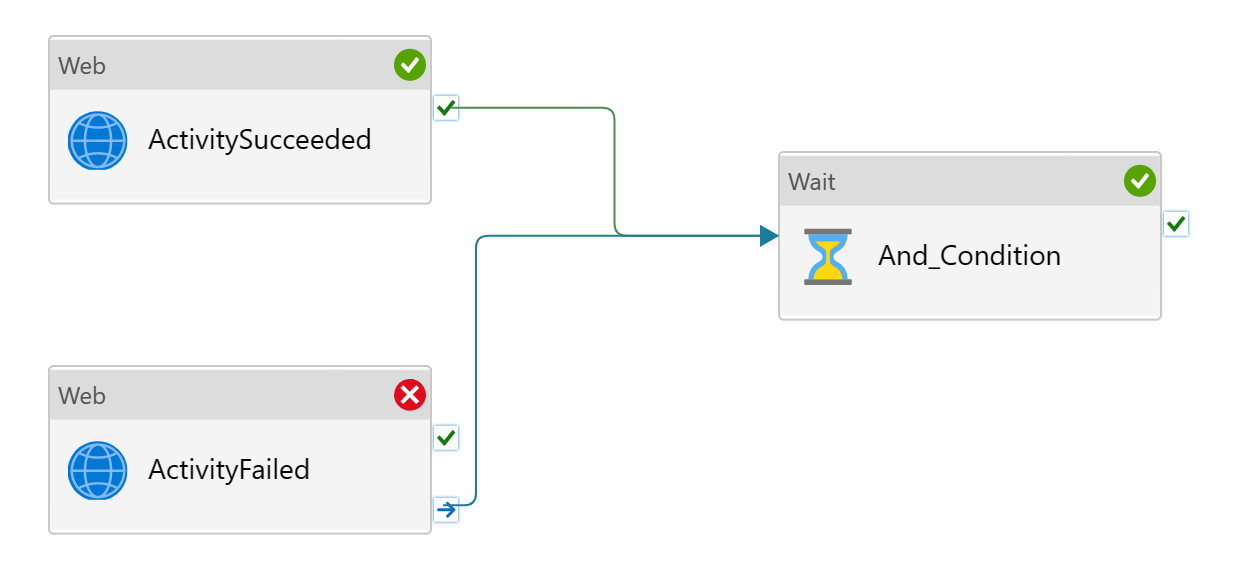
And here, the follow-up wait activity executes when ActivitySucceeded passes and ActivityFailed completed. Note, with "Upon Success" path ActivitySucceeded has to succeed, whereas ActivityFailed on the "Upon Completion" path runs with best effort, that is, may fail.
Or
Second common scenarios are conditional "or": run an activity if any of the dependencies succeeds or fails. Here we need to use "Upon Completion" paths, If Condition activity and expression language.
Before we dive deep into code, we need to understand one more thing. After an activity ran and completed, you may reference its status with @activity('ActivityName').Status. It's either "Succeeded"_ or "Failed". We use this property to build conditional or logic.
Shared error handling logging step
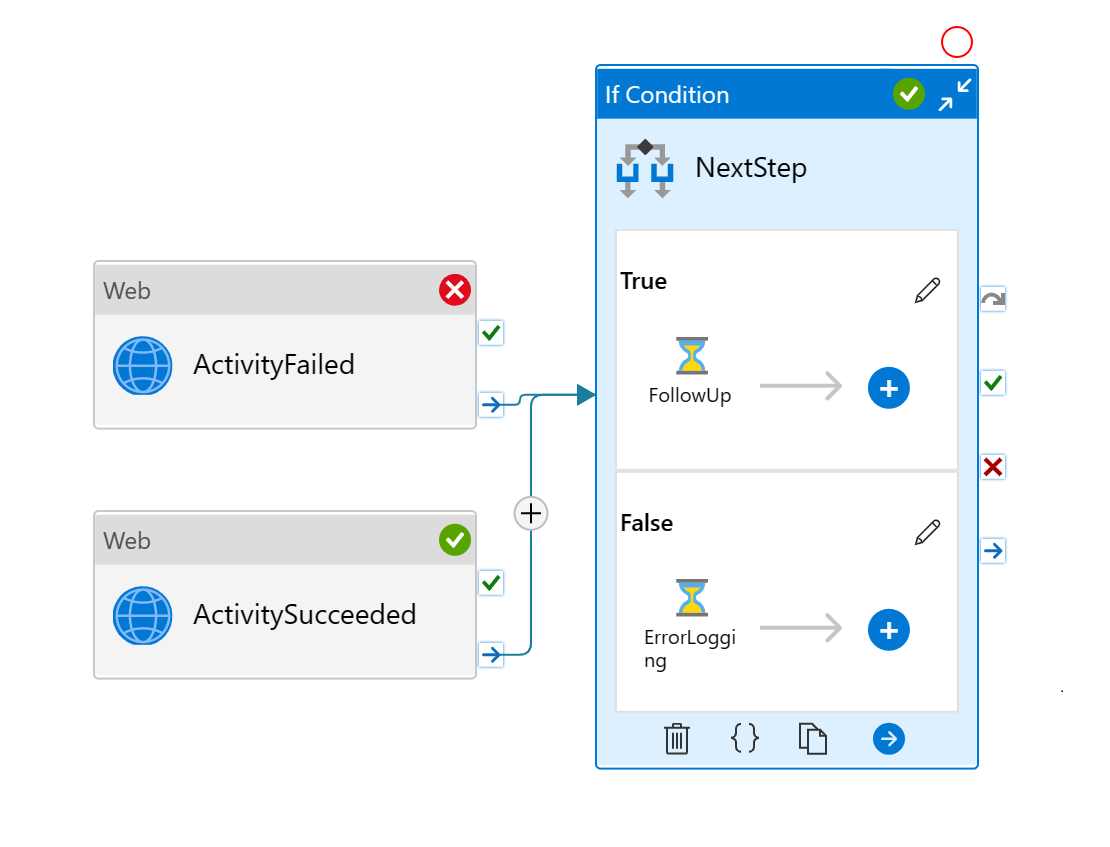
In some cases, you may want to invoke a shared error handling or logging step, if any of the previous activities failed. You can build your pipeline like this:
- run multiple activities in parallel
- add an if condition to contain the error handling steps, in True branch
- connect activities to the condition activity using "Upon Completion" path
- logical expression for condition activity reads
@or(equals(activity('ActivityFailed').Status, 'Failed'), equals(activity('ActivitySucceeded').Status, 'Failed'))
- Note: you need concatenated or if you have more than two dependency activities, for instance,
@or(or(equals(activity('ActivityFailed').Status, 'Failed'), equals(activity('ActivitySucceeded1').Status, 'Failed')),equals(activity('ActivitySucceeded1').Status, 'Failed'))

Greenlight if any activity succeeded
When all your activities are best effort, you may want to proceed to next step if any of the previous activities succeeded. You can build your pipeline like this:
- run multiple activities in parallel
- add an if condition to contain next steps, in True branch
- connect activities to the condition activity using "Upon Completion" path
- logical expression for condition activity reads
@or(equals(activity('ActivityFailed').Status, 'Succeeded'), equals(activity('ActivitySucceeded').Status, 'Succeeded'))
- Note: the graph looks exactly like the previous scenario. The only difference is the expression language used
Complex scenarios
All activities need to succeed to proceed
The pattern is a combination of two: conditional and + error handling. The pipeline proceeds to next steps if all proceeding activities succeed, or else it runs a shared error logging step. You can build the pipeline like this:
- run multiple activities in parallel
- add an if condition. Add next steps in True branch, and add error handling code in False branch
- connect activities to the condition activity using "Upon Completion" path
- logical expression for condition activity reads
@and(equals(activity('ActivityFailed').Status, 'Succeeded'), equals(activity('ActivitySucceeded').Status, 'Succeeded'))
Common patterns
Try-Catch-Proceed
The pattern is equivalent to try catch block in coding. An activity might fail in a pipeline. When it fails, customer needs to run an error handling job to deal with it. However, the single activity failure shouldn't block next activities in the pipeline. For instance, I attempt to run a copy job, moving files into storage. However it might fail half way through. And in that case, I want to delete the partially copied, unreliable files from the storage account (my error handling step). But I'm OK to proceed with other activities afterwards.
To set up the pattern:
- Add first activity
- Add error handling to the UponFailure path
- Add second activity, but don't connect to the first activity
- Connect both UponFailure and UponSkip paths from the error handling activity to the second activity
Note
Each path (UponSuccess, UponFailure, and UponSkip) can point to any activity. Multiple paths can point to the same activity. For example, UponSuccess and UponSkip can both point to one activity while UponFailure points to a different one.
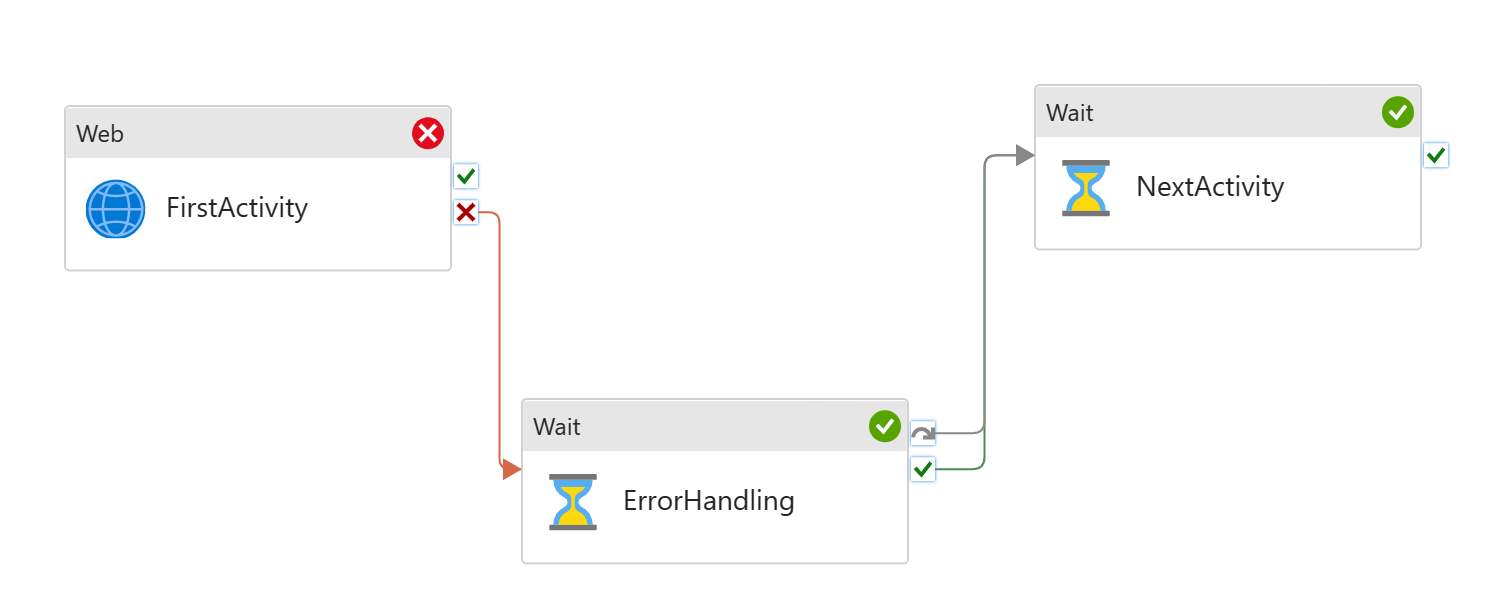
Error Handling job runs only when First Activity fails. Next Activity will run regardless if First Activity succeeds or not.
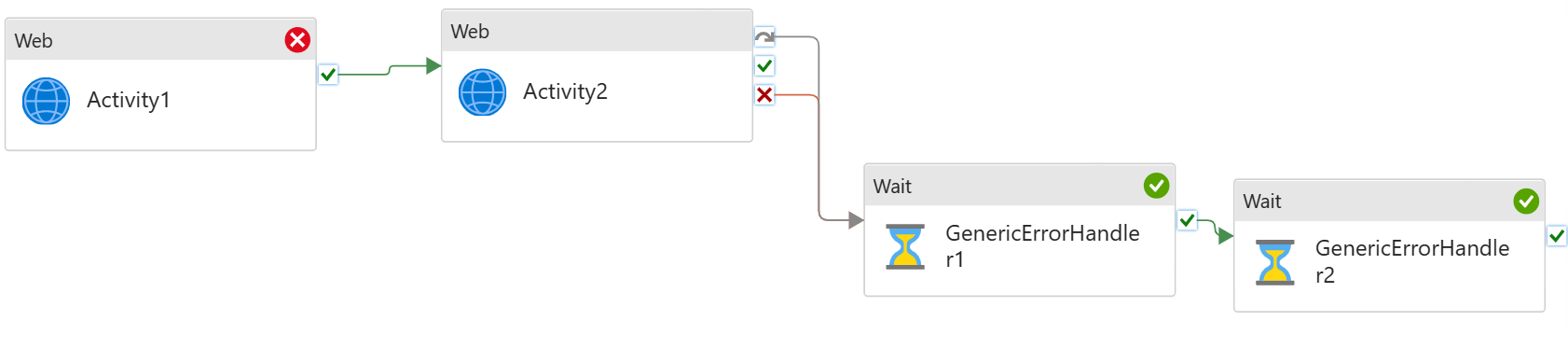
Generic error handling
Commonly, we have multiple activities running sequentially in the pipeline. If any fails, I need to run an error handling job to clear the state, and/or log the error. For instance, I have sequential copy activities in the pipeline. If any of these fails, I need to run a script job to log the pipeline failure.
To set up the pattern:
- Build sequential data processing pipeline
- Add generic error handling step to the end of the pipeline
- Connect both UponFailure and UponSkip paths from the last activity to the error handling activity
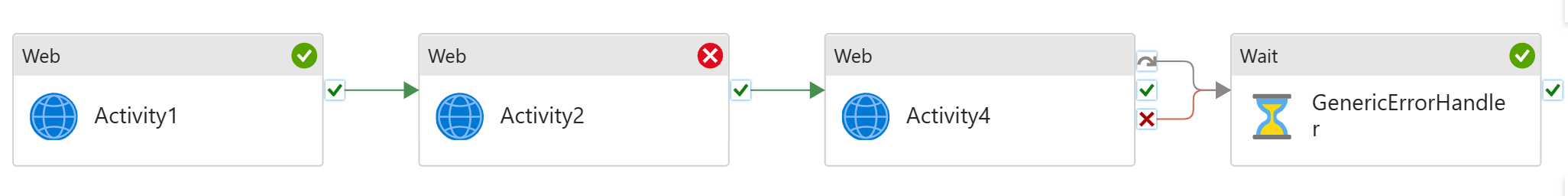
The last step, Generic Error Handling, will only run if any of the previous activities fails. It will not run if they all succeed.
You can add multiple activities for error handling.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for