Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud integrates natively with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to provide Defender for Endpoint and Defender Vulnerability Management capabilities in Defender for Cloud.
- When you enable the Defender for Servers plan in Defender for Cloud, Defender for Endpoint integration is enabled by default.
- The integration automatically deploys the Defender for Endpoint agent on machines.
This article explains how to manually enable Defender for Endpoint integration when necessary.
Prerequisites
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Windows support | Verify that Windows machines are supported by Defender for Endpoint. |
| Linux support | For Linux servers, you must have Python installed. Python 3 is recommended for all distros, but is required for RHEL 8.x and Ubuntu 20.04 or higher. Automatic deployment of the Defender for Endpoint sensor on Linux machines might not work as expected if machines run services that use fanotify. Manually install the Defender for Endpoint sensor on these machines. |
| Azure VMs | Check that VMs can connect to the Defender for Endpoint service. If machines don't have direct access, proxy settings or firewall rules need to allow access to Defender for Endpoint URLs. Review proxy settings for Windows and Linux machines. |
| On-premises VMs | We recommend that you onboard on-premises machines as Azure Arc-enabled VMs. If you onboard on-premises VMs directly, Defender Server Plan 1 features are available, but most Defender for Servers Plan 2 functionality doesn't work. |
| Azure tenant | If you moved your subscription between Azure tenants, some manual preparatory steps are also required. Contact Microsoft support for details. |
| Windows Server 2016, 2012 R2 | Unlike later versions of Windows Server, which come with the Defender for Endpoint sensor preinstalled, Defender for Cloud installs the sensor on machines running Windows Server 2016/2012 R2 using the unified Defender for Endpoint solution. |
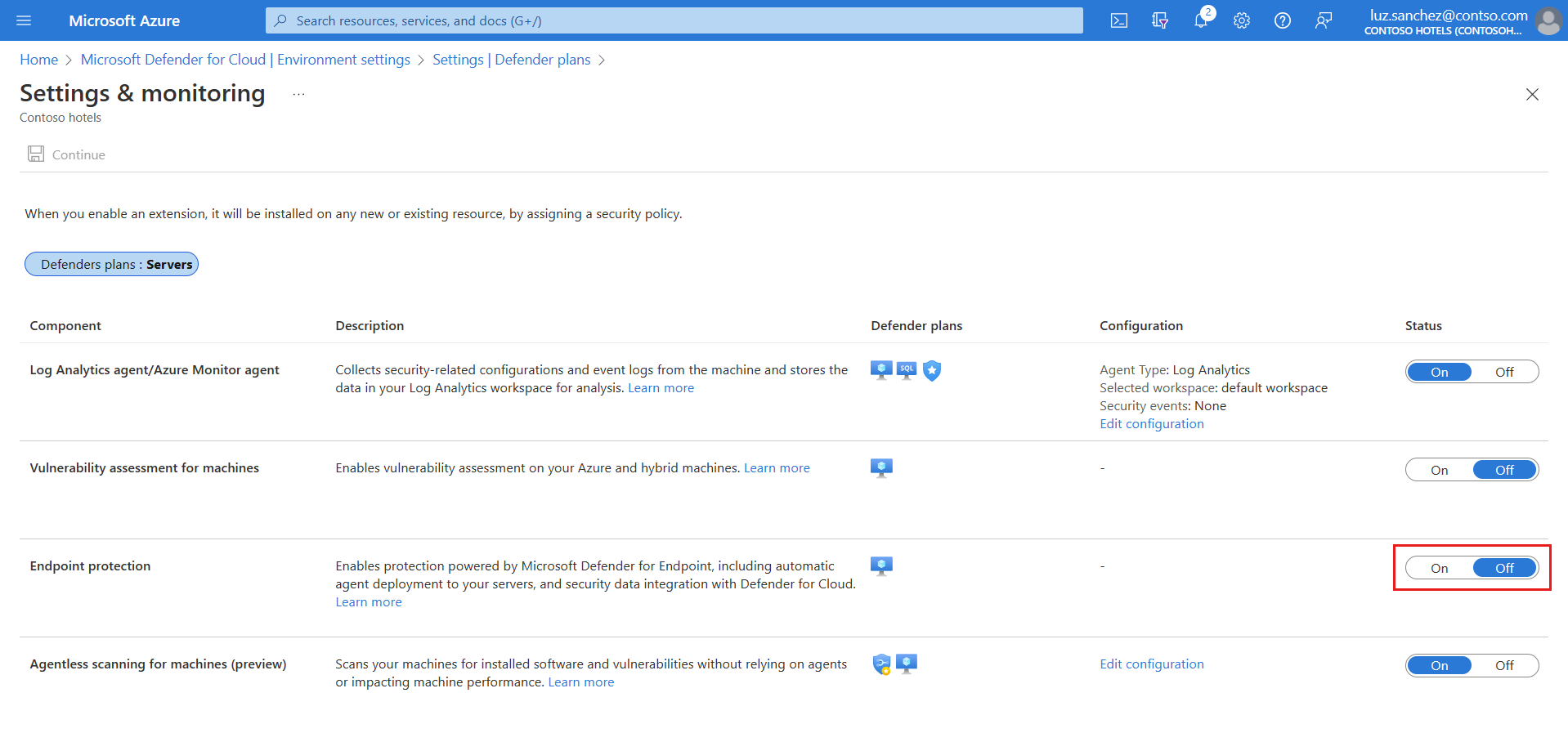
Enable on a subscription
Defender for Endpoint integration is enabled by default when you enable a Defender for Servers plan. If you turn off the Defender for Endpoint integration on a subscription, you can turn it on again manually when necessary using these instructions.
In Defender for Cloud, select Environment settings and select the subscription containing the machines on which you want to deploy the Defender for Endpoint integration.
In Settings and monitoring > Endpoint protection, toggle the Status column settings to On.
Select Continue and Save to save your settings.
The Defender for Endpoint sensor is deployed to all Windows and Linux machines in the selected subscription.
Onboarding might take up to an hour. Defender for Cloud detects any previous Defender for Endpoint installations and reconfigures them to integrate with Defender for Cloud.
Note
For Azure VMs created from generalized OS images, MDE will not be automatically provisioned via this setting; however, you can manually enable the MDE agent and extension using Azure CLI, REST API, or Azure Policy.
Verify installation on Linux machines
Verify Defender for Endpoint sensor installation on a Linux machine by following these steps:
Run the following shell command on each machine:
mdatp health. If Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is installed, you see its health status:healthy : truelicensed: trueAdditionally, in the Azure portal, you can check that Linux machines have a new Azure extension called
MDE.Linux.
Note
On new subscriptions, Defender for Endpoint integration is automatically enabled and covers machines running a supported Windows Server or Linux operating system. The following sections cover a one-time opt-in that might be required in some scenarios only.
Enable Defender for Endpoint unified solution on Windows Server 2016/2012 R2
If Defender for Servers is enabled and Defender for Endpoint integration is on in a subscription that existed before spring 2022, you might need to manually enable integration of the unified solution for machines running Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2012 R2 in the subscription.
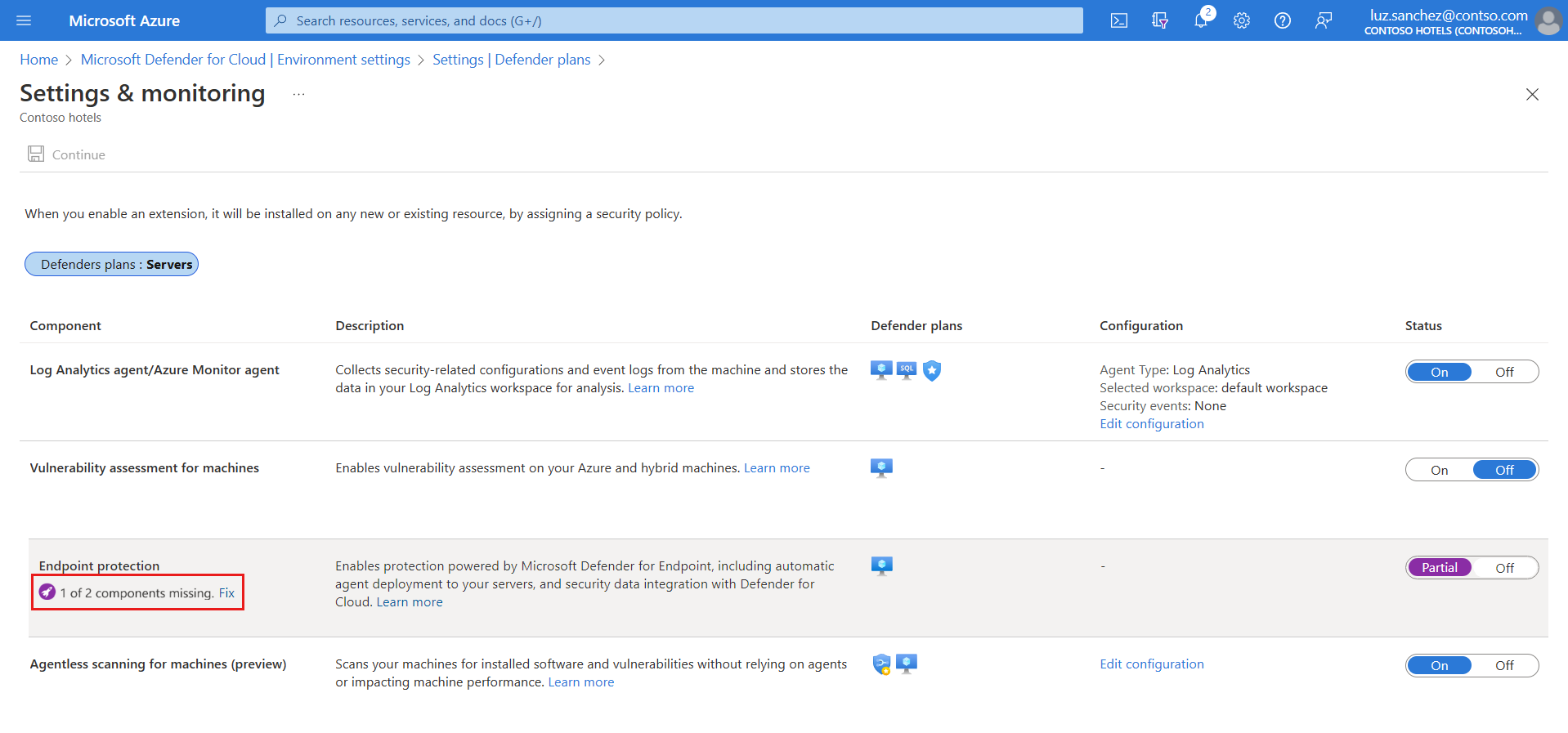
In Defender for Cloud, select Environment settings and select the subscription with the Windows machines that you want to receive Defender for Endpoint.
In the Monitoring coverage column of the Defender for Servers plan, select Settings.
The status of the Endpoint protections component is Partial, meaning that not all parts of the component are enabled.
Select Fix to see the components that aren't enabled.
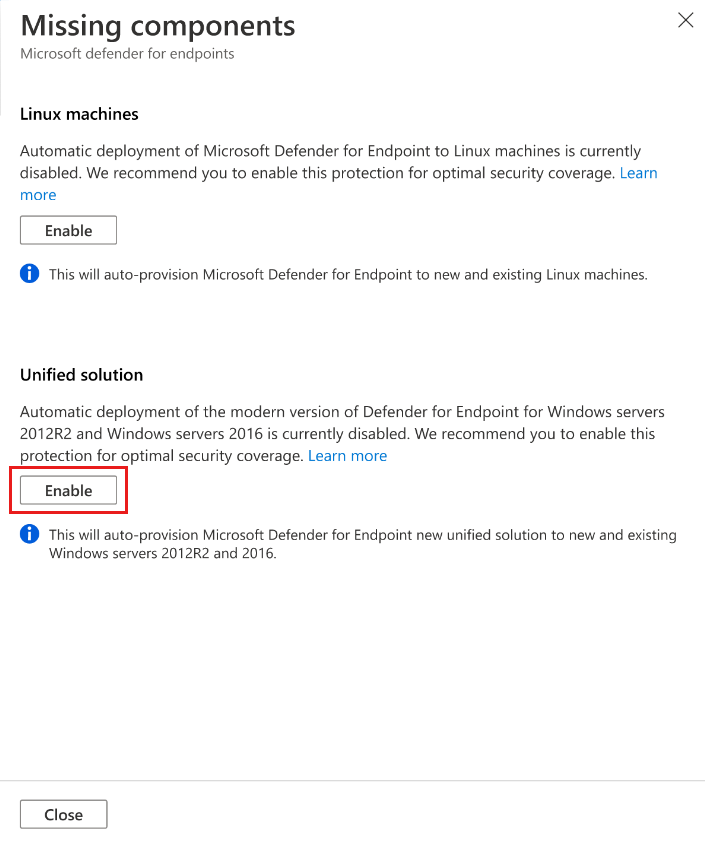
In Missing components > Unified solution, select Enable to automatically install the Defender for Endpoint agent on Windows Server 2012 R2 and 2016 machines connected to Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
To save the changes, select Save at the top of the page. In the Settings and monitoring page, select Continue.
Defender for Cloud onboards existing and new machines to Defender for Endpoint.
In case you are configuring Defender for Endpoint on the first subscription in your tenant, onboarding might take up to 12 hours. For new machines and subscriptions created after the integration has been enabled for the first time, onboarding takes up to an hour.
Note
Enabling Defender for Endpoint integration on Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016 machines is a one-time action. If you disable the plan and re-enable it, integration remains enabled.
Enable on Linux machines (plan/integration enabled)
If Defender for Servers is already enabled and Defender for Endpoint integration is on in a subscription that existed before summer 2021, you might need to manually enable the integration for Linux machines.
In Defender for Cloud, select Environment settings and select the subscription with the Linux machines that you want to receive Defender for Endpoint.
In the Monitoring coverage column of the Defender for Server plan, select Settings.
The status of the Endpoint protections component is Partial, meaning that not all parts of the component are enabled.
Select Fix to see the components that aren't enabled.

In Missing components > Linux machines, select Enable.
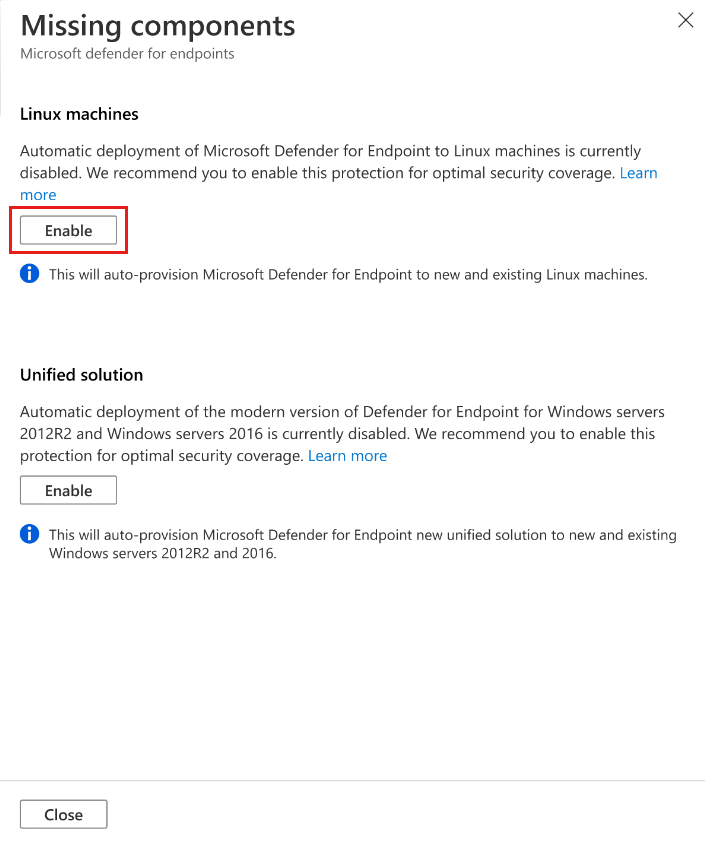
To save the changes, select Save at the top of the page. In the Settings and monitoring page, select Continue.
- Defender for Cloud onboards Linux machines to Defender for Endpoint.
- Defender for Cloud detects any previous Defender for Endpoint installations on Linux machines and reconfigures them to integrate with Defender for Cloud.
- In case you are configuring Defender for Endpoint on the first subscription in your tenant, onboarding might take up to 12 hours. For new machines created after the integration has been enabled, onboarding takes up to an hour.
To verify Defender for Endpoint sensor installation on a Linux machine, run the following shell command on each machine.
mdatp healthIf Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is installed, you see its health status:
healthy : truelicensed: trueIn the Azure portal, you can check that Linux machines have a new Azure extension called
MDE.Linux.
Note
Enabling Defender for Endpoint integration on Linux machines is a one-time action. If you disable the plan and re-enable it, integration remains enabled.
Enable integration with PowerShell in multiple subscriptions
To enable Defender for Servers integration for Linux machines or Windows Server 2012 R2 and 2016 with MDE Unified solution on multiple subscriptions, you can use one of the PowerShell scripts in the Defender for Cloud GitHub repository.
- Use this script to enable integration with the Defender for Endpoint modern unified solution on Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016
- Use this script to enable Defender for Endpoint integration on Linux machines
Manage automatic updates for Linux
In Windows, Defender for Endpoint version updates are provided via continuous knowledge base updates. In Linux, you need to update the Defender for Endpoint package.
When you use Defender for Servers with the
MDE.Linuxextension, automatic updates for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint are enabled by default.If you want to manage version updates manually, you can disable automatic updates on your machines. To do this, add the following tag for machines onboarded with the
MDE.Linuxextension.- Tag name:
ExcludeMdeAutoUpdate - Tag value:
true
- Tag name:
This configuration is supported for Azure VMs and Azure Arc machines, where the MDE.Linux extension initiates autoupdate.
Enable integration at scale
You can enable the Defender for Endpoint integration at scale through the supplied REST API version 2022-05-01. For full details, see the API documentation.
Here's an example request body for the PUT request to enable the Defender for Endpoint integration:
URI: https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<subscriptionId>/providers/Microsoft.Security/settings/WDATP?api-version=2022-05-01
{
"name": "WDATP",
"type": "Microsoft.Security/settings",
"kind": "DataExportSettings",
"properties": {
"enabled": true
}
}
Note
Both the Defender for Endpoint Unified Solution and Defender for Endpoint for Linux are automatically included on new subscriptions when you enable the Defender for Endpoint integration using microsoft.security/settings/WDATP.
The settings WDATP_UNIFIED_SOLUTION and WDATP_EXCLUDE_LINUX_PUBLIC_PREVIEW are relevant for legacy subscriptions. These settings apply to subscriptions that already have the Defender for Endpoint integration enabled when these features were introduced in August 2021 and Spring 2022.
Track Defender for Endpoint deployment status
You can use the Defender for Endpoint deployment status workbook to track the Defender for Endpoint deployment status on your Azure VMs and Azure Arc-enabled VMs. The interactive workbook provides an overview of machines in your environment showing their Microsoft Defender for Endpoint extension deployment status.
Access the Microsoft Defender portal
Make sure you have the right permissions for portal access.
Check whether you have a proxy or firewall that is blocking anonymous traffic.
- The Defender for Endpoint sensor connects from the system context, so anonymous traffic must be permitted.
- To ensure unhindered access to the Microsoft Defender portal, enable access to service URLs in the proxy server.
Open the Microsoft Defender portal. Learn about Incidents and alerts in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Run a detection test
Follow the instructions in EDR detection test for verifying device's onboarding and reporting services.
Remove Defender for Endpoint from a machine
To remove the Defender for Endpoint solution from your machines:
- To disable the integration, in Defender for Cloud > Environment settings, select the subscription with the relevant machines.
- In the Defender plans page, select Settings & Monitoring.
- In the status of the Endpoint protection component, select Off to disable the integration with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for the subscription.
- Select Continue and Save to save your settings.
- Remove the
MDE.WindowsorMDE.Linuxextension from the machine. - Offboard the device from the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint service.