Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article explains how to add and configure a catalog for your Azure Deployment Environments dev center or project.
Catalogs help you provide a set of curated infrastructure-as-code(IaC) templates, known as environment definitions for your development teams to create environments. You can attach your own source control repository from GitHub or Azure Repos as a catalog and specify the folder with your environment definitions. Deployment Environments scans the folder for environment definitions and makes them available for dev teams to create environments.
To further secure your templates, the catalog is encrypted; Azure Deployment Environments supports encryption at rest with platform-managed encryption keys, which Microsoft for Azure Services manages.
- To learn how to host a repository in GitHub, see Get started with GitHub.
- To learn how to host a Git repository in an Azure Repos project, see Azure Repos.
Microsoft offers a quick start catalog that you can add to the dev center or project, and a sample catalog that you can use as your repository. You also can use your own private repository, or you can fork and customize the environment definitions in the sample catalog.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Configure project-level catalogs
- Configure a managed identity
- Add a catalog from Azure Repos or GitHub
- Update a catalog
- Delete a catalog
- Troubleshoot catalog sync errors
Configure project-level catalogs
Attaching catalogs at the project level enables platform engineers to provide curated environment definitions that are specific to the development teams. Additionally, it empowers dev team leads assigned as Project Admins to manage the environment definitions made available to their teams.
Platform engineers have full control over the use of catalogs at the project level. The use of project-level catalogs must be enabled at the dev center level before a catalog can be added to a project. Platform engineers can also configure which types of catalogs items, such as environment definitions, can be consumed at the project level.
By default, use of catalogs at the project level is disabled and none of the catalog item types are enabled. Environment definitions from a project-level catalog are synced and usable under two conditions. First, you must enable project-based catalogs at the corresponding dev center level. Second, you must enable the use of environment definitions for the project.
Add a catalog to a project
You must enable project-level catalogs at the dev center level before you can add a catalog to a project. You should also enable the use of environment definitions at the project level.
To enable the use of project-level catalogs at the dev center level:
In the Azure portal, navigate to your dev center.
In the left menu, under Settings, select Dev center settings.
Under Project level catalogs, select Enable catalogs per project, and then select Apply.
To enable the use of environment definitions in the project:
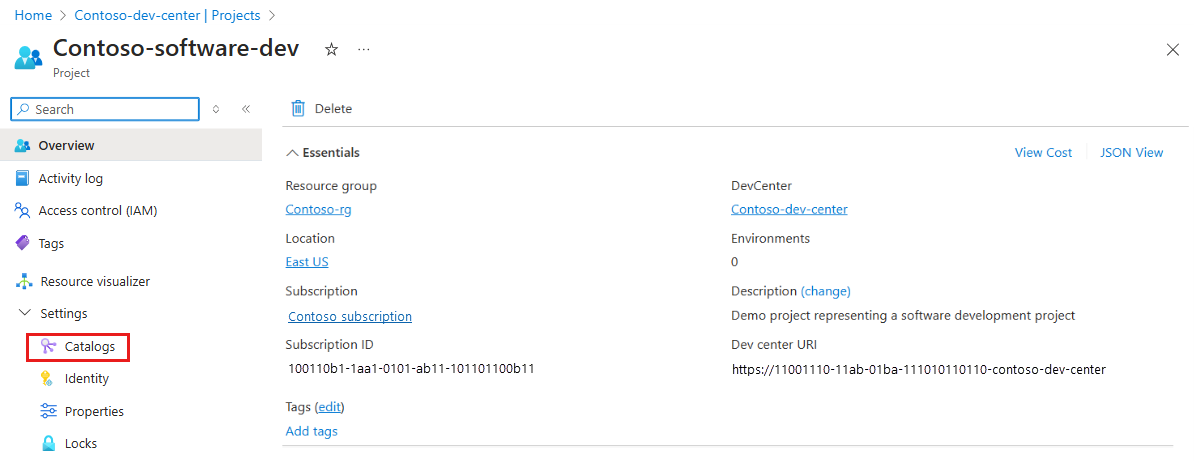
In the Azure portal, navigate to your project.
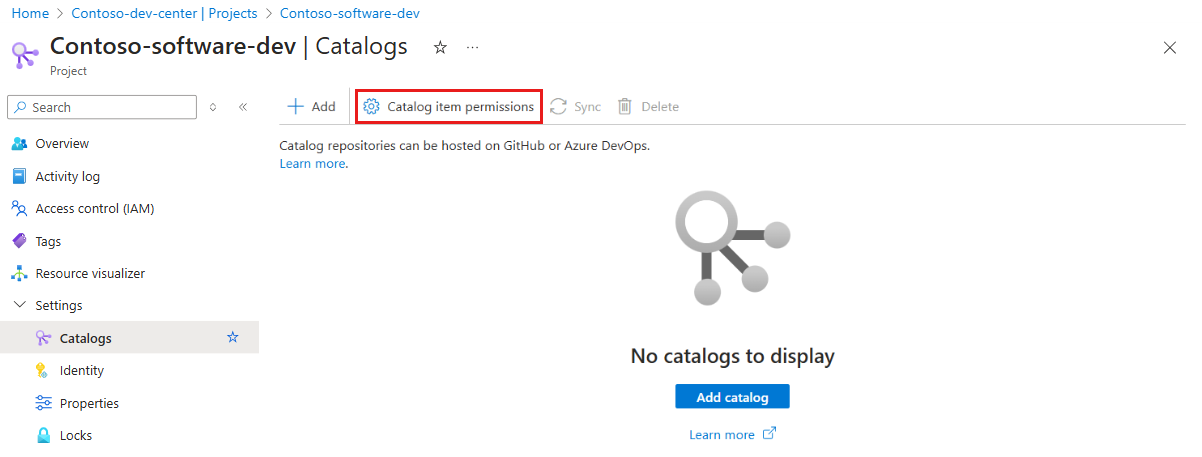
In the left menu, under Settings, select Catalogs.
On the Catalogs page, select Catalog item permissions.
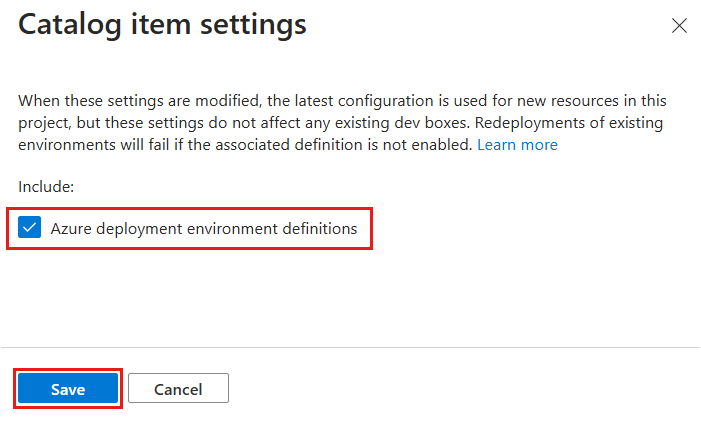
In the Catalog item settings pane, select Azure deployment environment definitions to enable the use of environment definitions at the project level.
Now, you can add a catalog to the project.
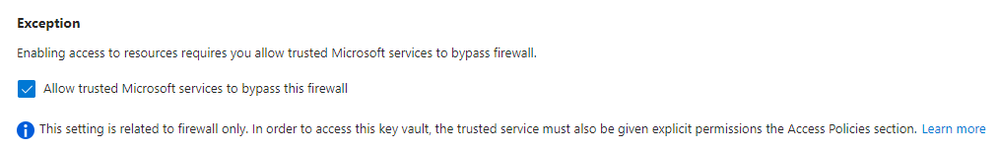
For catalogs that use a managed identity or Personal Access Token (PAT) for authentication, you must assign a managed identity for the project. For catalogs that use a PAT, you must store the PAT in a key vault and grant the managed identity access to the key vault secret.
Configure a managed identity
Before you can attach a catalog to a dev center or project, you must configure a managed identity, also called a Managed Service Identity (MSI). You can attach either a system-assigned managed identity (system-assigned MSI) or a user-assigned managed identity (user-assigned MSI). You then assign roles to the managed identity to allow the dev center or project to create environment types in your subscription and read the Azure Repos project that contains the catalog repo.
If your dev center or project doesn't have an MSI attached, follow the steps in Configure a managed identity to create one and to assign roles for the managed identity.
To learn more about managed identities, see What are managed identities for Azure resources?
Add a catalog
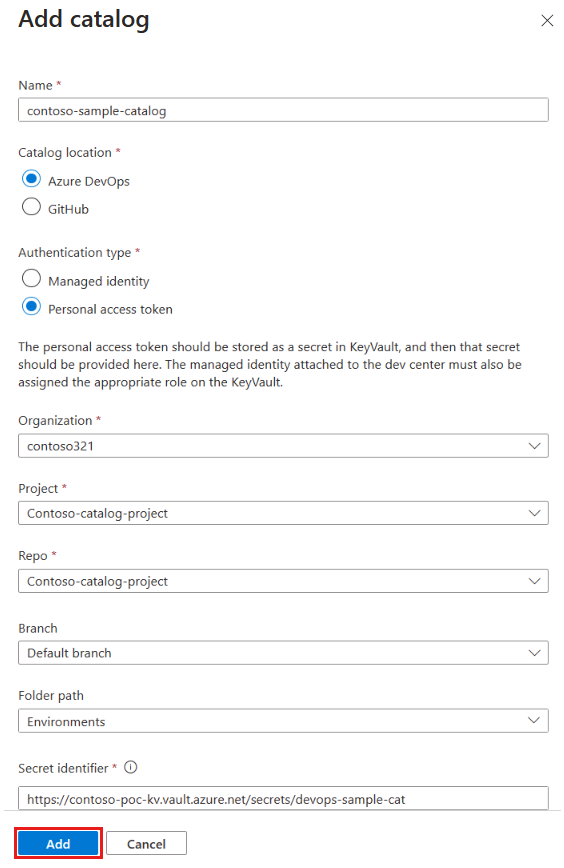
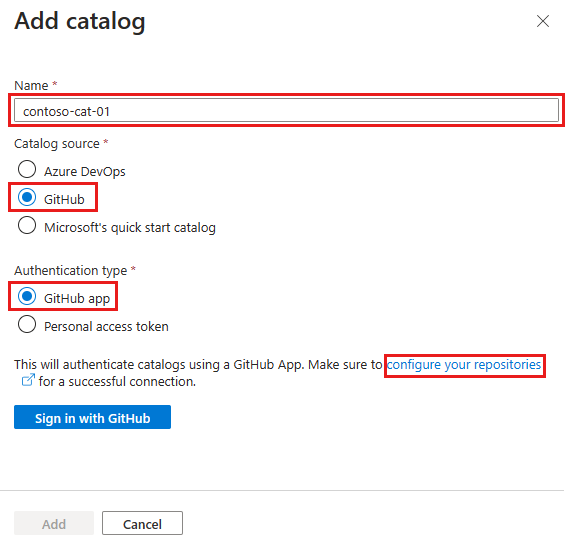
You can add a catalog from an Azure Repos repository or a GitHub repository. You can choose to authenticate by assigning permissions to an MSI or by using a PAT, which you store in a key vault.
Select the tab for the type of repository and authentication you want to use.
To add a catalog, complete the following tasks:
- Assign permissions in Azure Repos for the managed identity.
- Add your repository as a catalog.
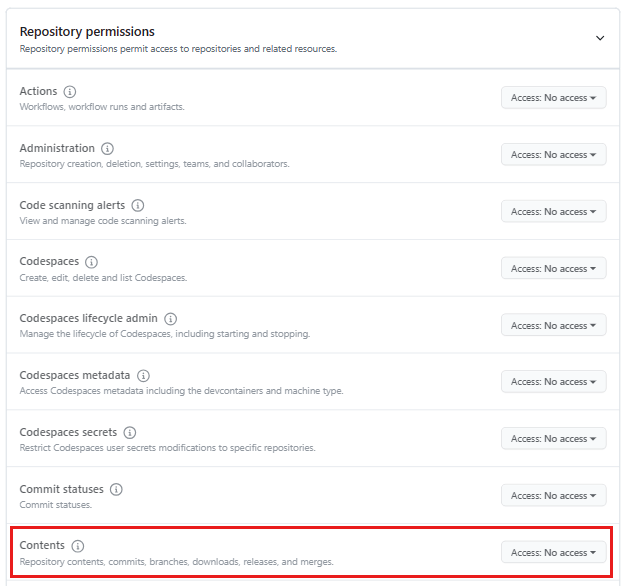
Assign permissions in Azure Repos for the managed identity
You must give the managed identity permissions to the repository in Azure Repos.
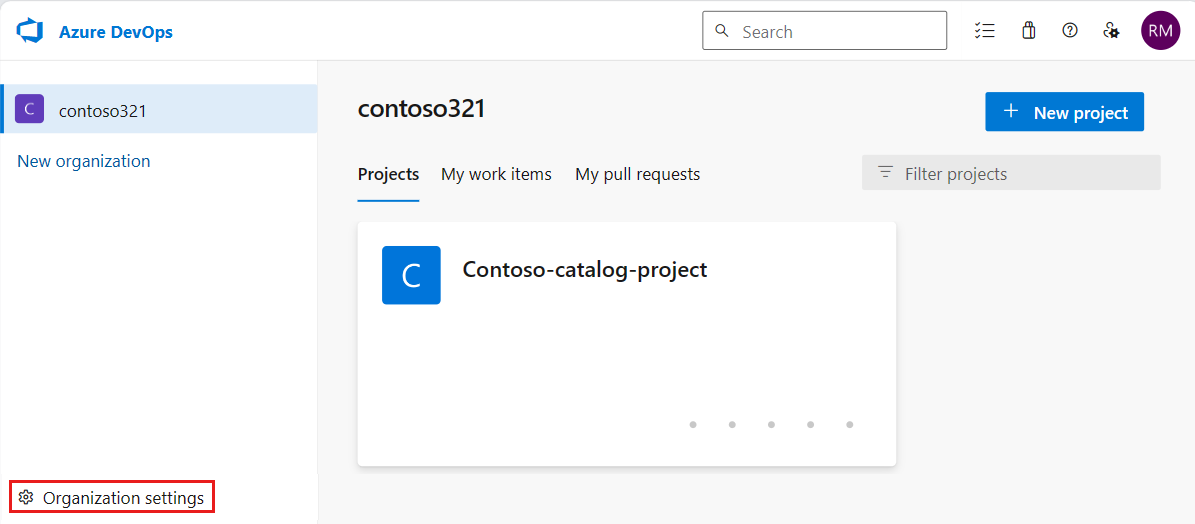
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization.
Note
Your Azure DevOps organization must be in the same directory as the Azure subscription that contains your dev center or project.
Select Organization settings.
On the Overview page, select Users.
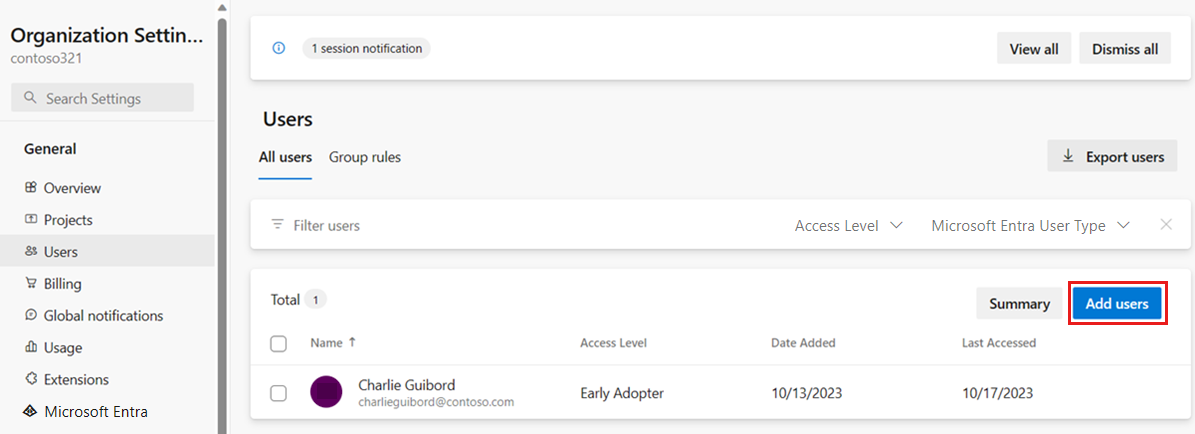
On the Users page, select Add users.
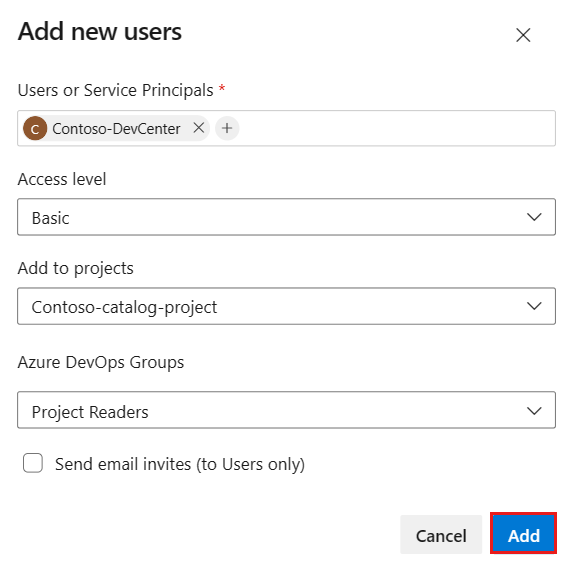
Complete Add new users by entering or selecting the following information, and then select Add:
Name Value Users or Service Principals Enter the name of your dev center or project.
When you use a system-assigned MSI, specify the name of the dev center or project, not the object ID of the managed account. When you use a user-assigned MSI, use the name of the managed account.Access level Select Basic. Add to projects Select the project that contains your repository. Azure DevOps Groups Select Project Readers. Send email invites (to Users only) Clear the checkbox.
Add your repository as a catalog
Azure Deployment Environments supports attaching Azure Repos repositories and GitHub repositories. You can store a set of curated IaC templates in a repository. Attaching the repository to a dev center or project as a catalog gives your development teams access to the templates and enables them to quickly create consistent environments.
The following steps let you attach an Azure Repos repository.
In the Azure portal, navigate to your dev center or project.
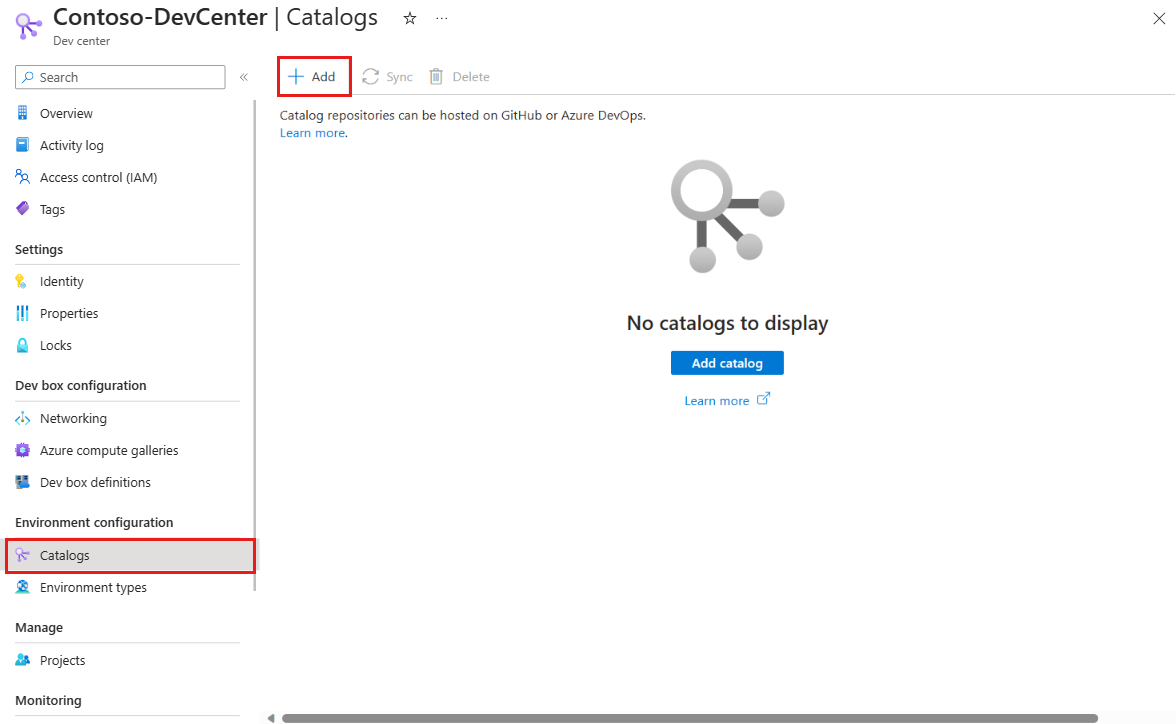
In the left menu under Environment configuration, select Catalogs, and then select Add.
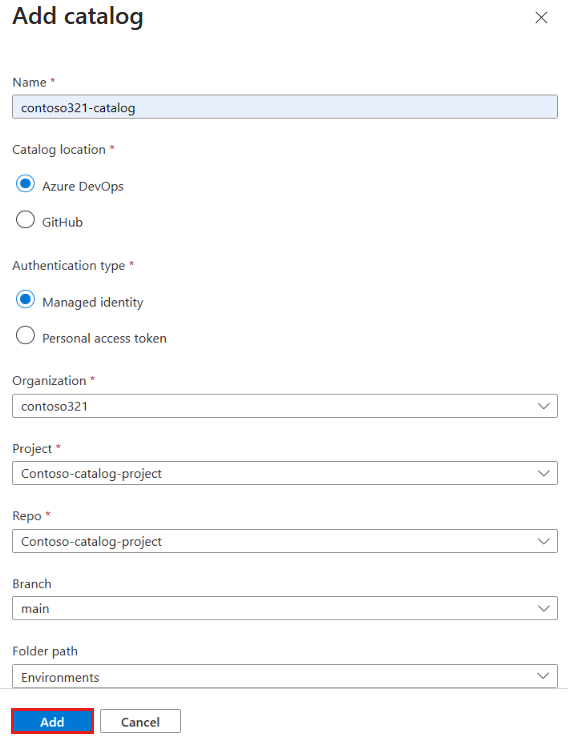
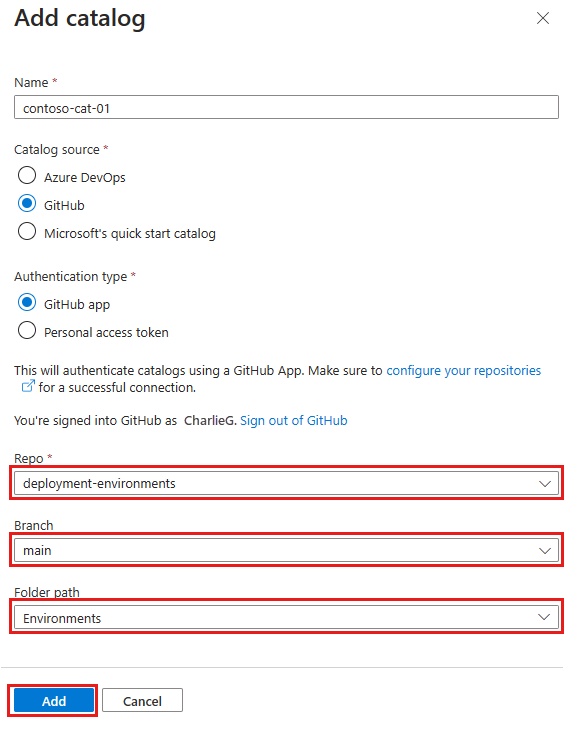
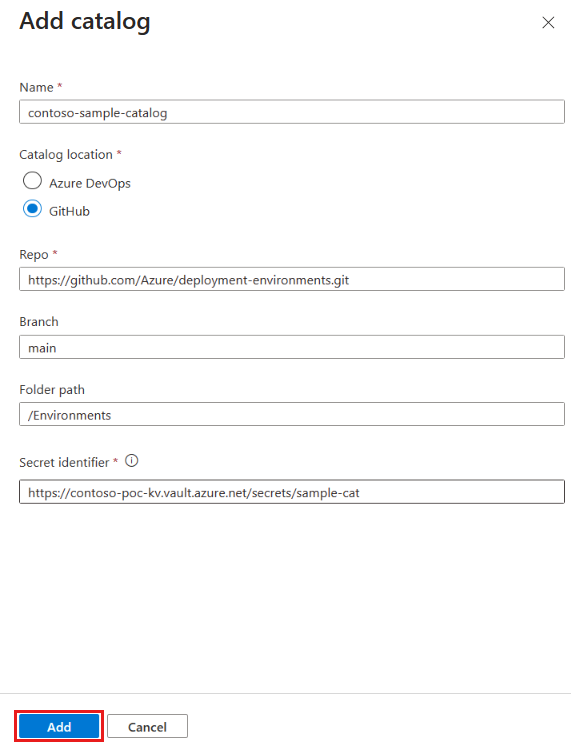
In Add catalog, enter the following information, and then select Add:
Field Value Name Enter a name for the catalog. Catalog location Select Azure DevOps. Authentication type Select Managed Identity. Organization Select your Azure DevOps organization. Project From the list of projects, select the project that stores the repo. Repo From the list of repos, select the repo you want to add. Branch Select the branch. Folder path Dev Box retrieves a list of folders in your branch. Select the folder that stores your IaC templates. In Catalogs for the dev center or project, verify that your catalog appears. When the connection is successful, the Status reads Sync successful. Connecting to a catalog can take a few minutes the first time.
View synced catalog items
Regardless of the type of repository you use, you can view the catalog items that are synced from the catalog.
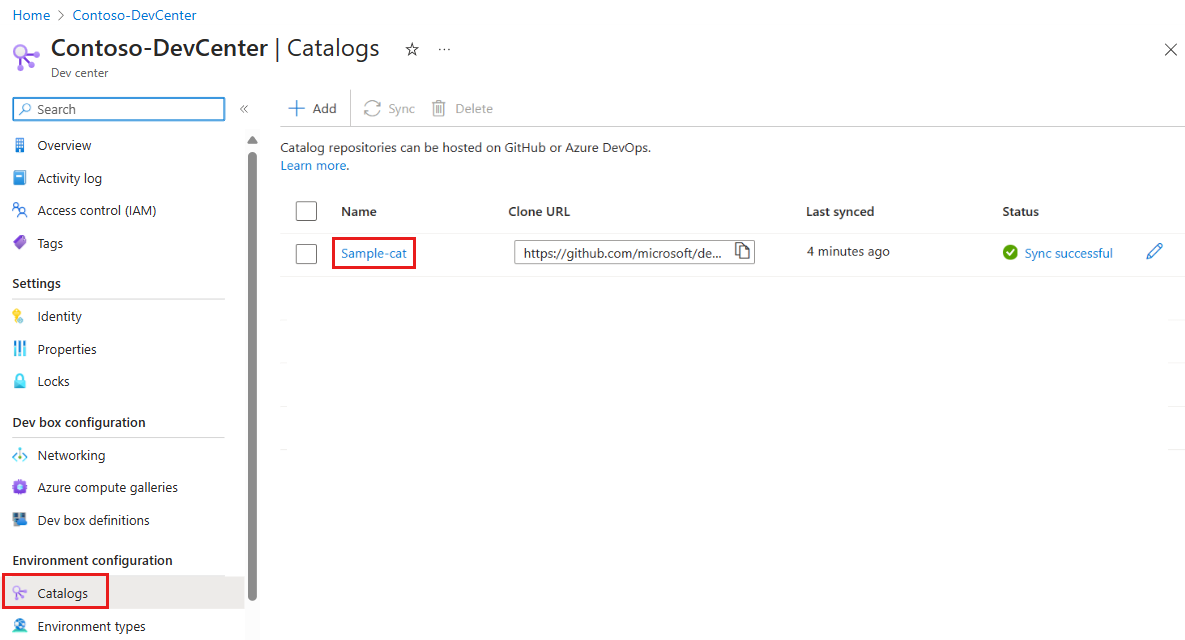
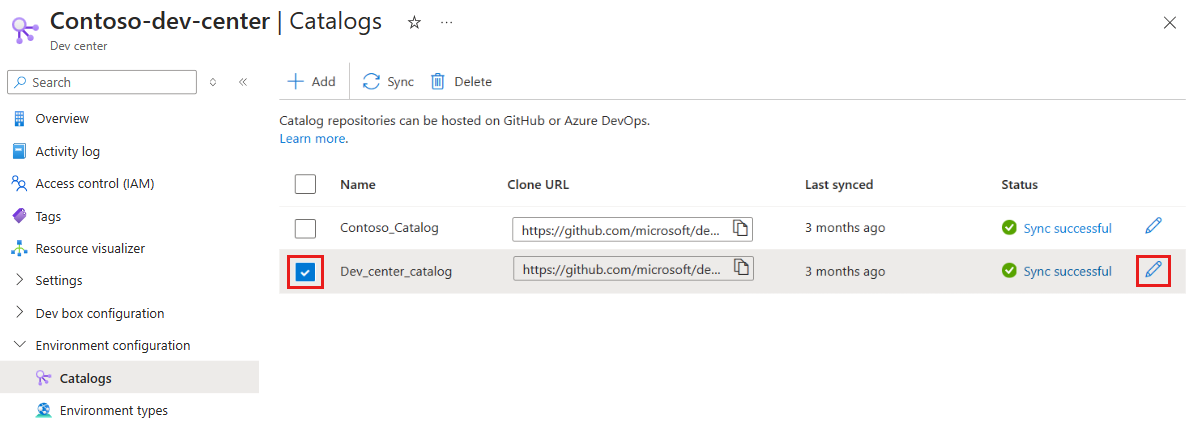
On the left menu for your dev center or project, under Environment configuration, select Catalogs.
In the Catalogs pane, select the catalog name.
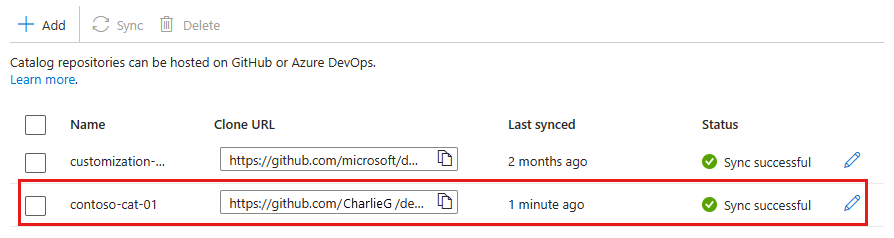
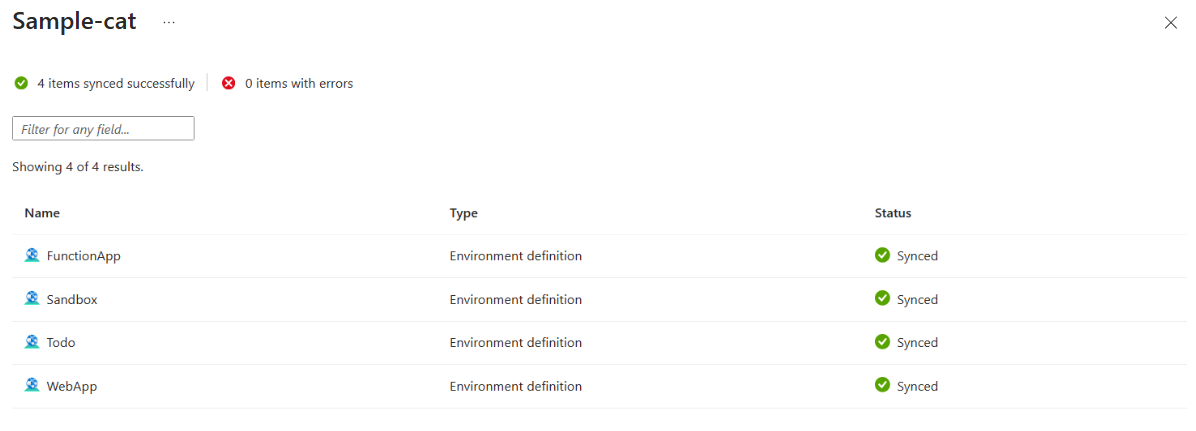
You see a list of successfully synced catalog items.
Update a catalog
If you update the definition or template contents in the attached repository, you can provide the latest set of environment definitions to your development teams by syncing the catalog. You can sync a catalog manually or automatically.
Manually sync a catalog
When you manually sync a catalog, Deployment Environments scans through the repository and makes the latest list of environment definitions available to all of the associated projects in the dev center.
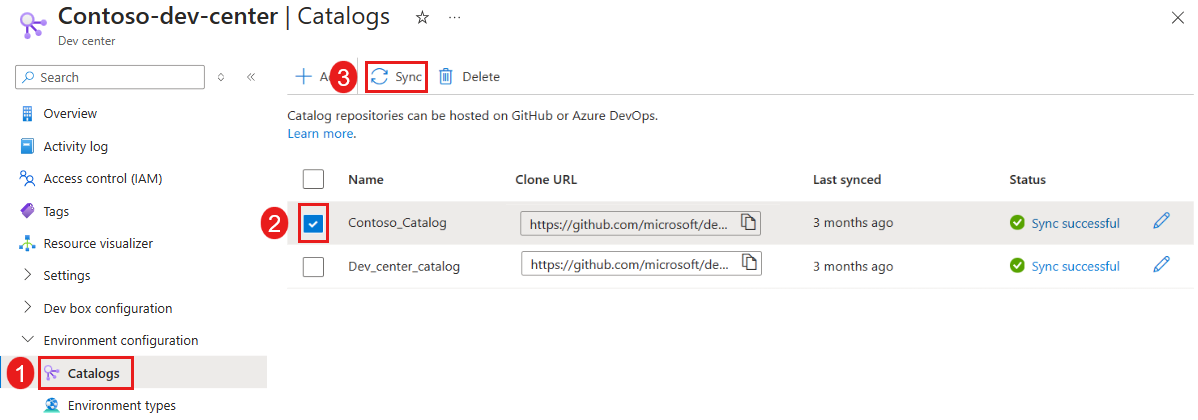
On the left menu for your dev center, under Environment configuration, select Catalogs.
Select the specific catalog, and then from the command bar, select Sync.
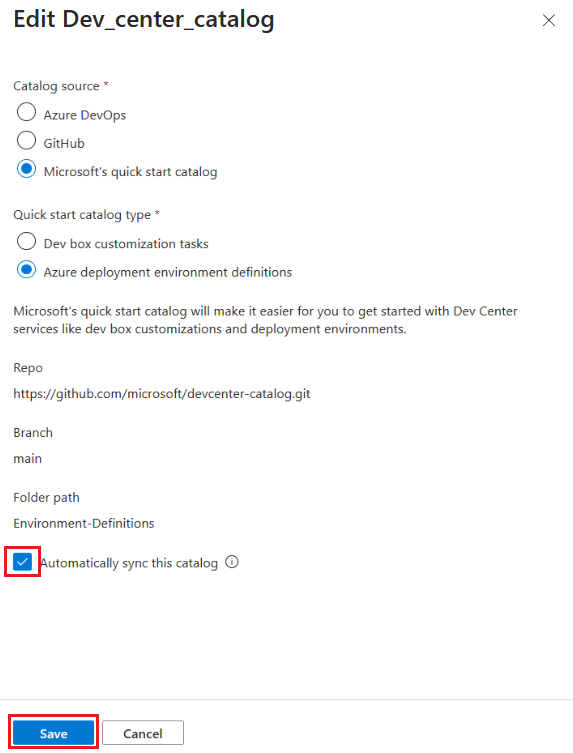
Automatically sync a catalog
When you configure a catalog to sync automatically, Deployment Environments scans through the repository every 30 minutes and makes the latest list of environment definitions available to all of the associated projects in the dev center.
On the left menu for your dev center or project, under Environment configuration, select Catalogs.
Select the specific catalog, and then select edit.
In the Edit catalog pane, select Automatically sync this catalog, and then select Save.
If an autosync fails, you should perform a manual sync. Deployment Environments doesn't make any further autosync attempts until a manual sync succeeds.
Delete a catalog
You can delete a catalog to remove it from the Azure Deployment Environments dev center or project. Templates in a deleted catalog aren't available to development teams when they deploy new environments. Update the environment definition reference for any existing environments that were created by using the environment definitions in the deleted catalog. If the reference isn't updated and the environment is redeployed, the deployment fails.
To delete a catalog:
On the left menu for your dev center or project, under Environment configuration, select Catalogs.
Select the specific catalog, and then select Delete.
In the Delete catalog dialog, select Continue to delete the catalog.
Troubleshoot catalog sync errors
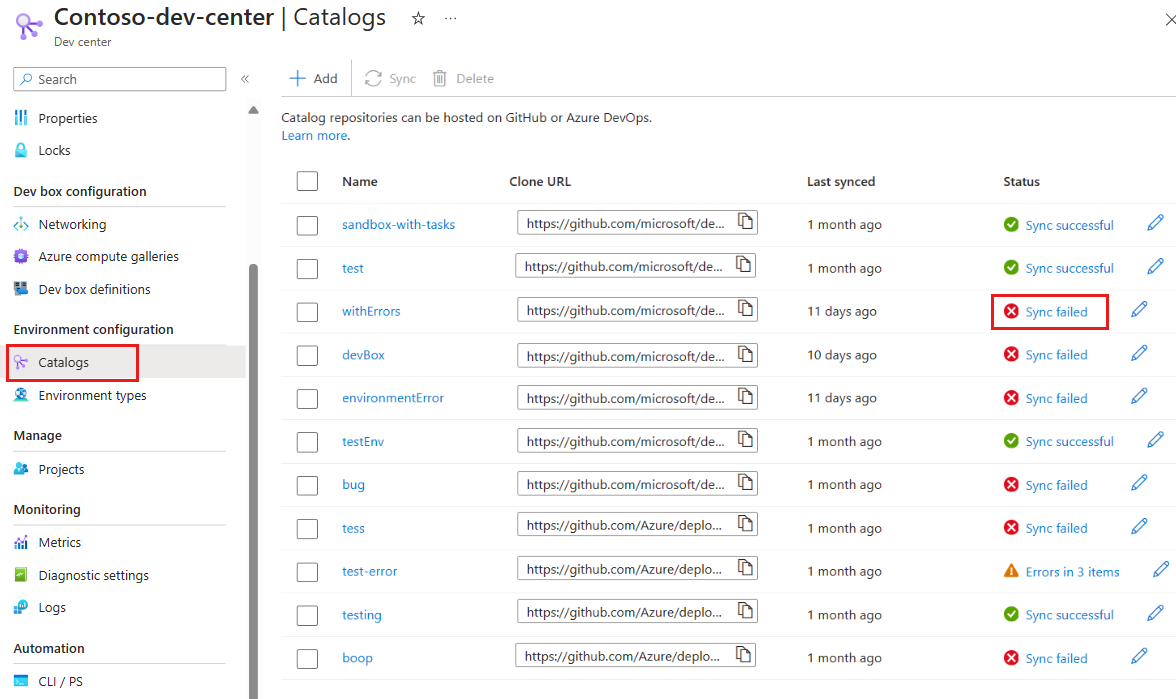
When you add or sync a catalog, you might encounter a sync error or warning. A sync error indicates that a catalog failed to sync successfully, A sync warning indicates that some or all of the catalog items have errors. You can view the sync status and errors in the Azure portal, or use the Azure CLI and REST API to troubleshoot and resolve the errors.
View catalog sync status
In the Azure portal, you can get more information about the catalog sync status and any warnings or errors by selecting the status link. The status link opens a pane that shows the sync status, the number of environment definitions that were added, and the number of environment definitions that were ignored or failed.
View catalog sync failures
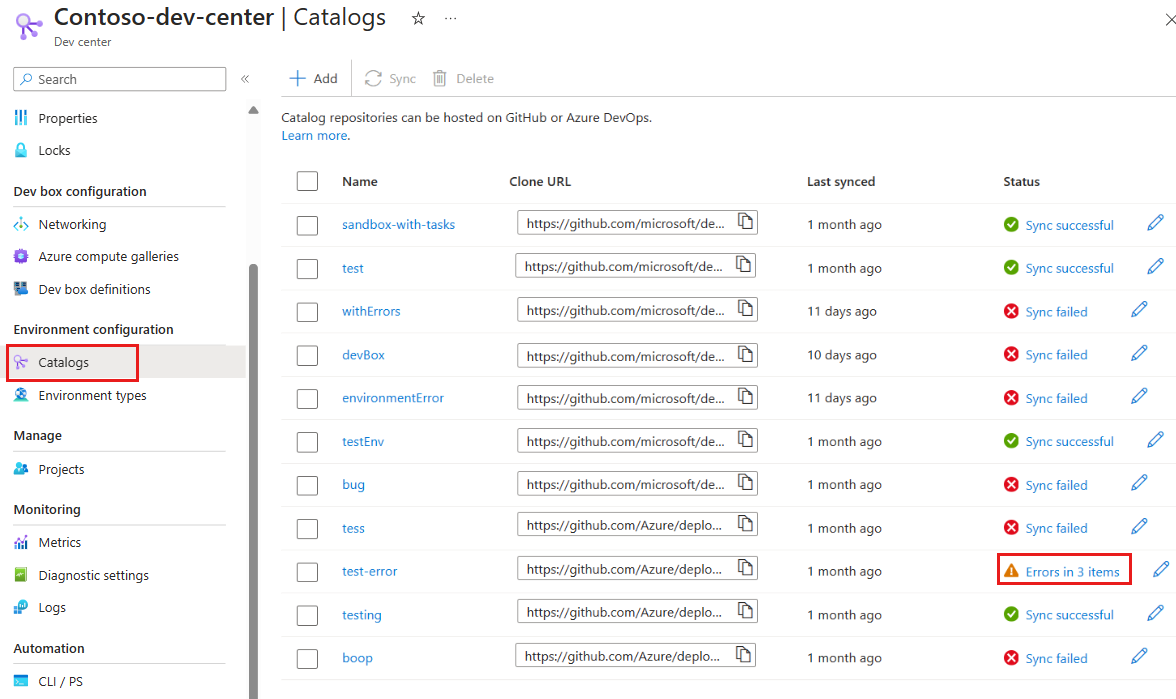
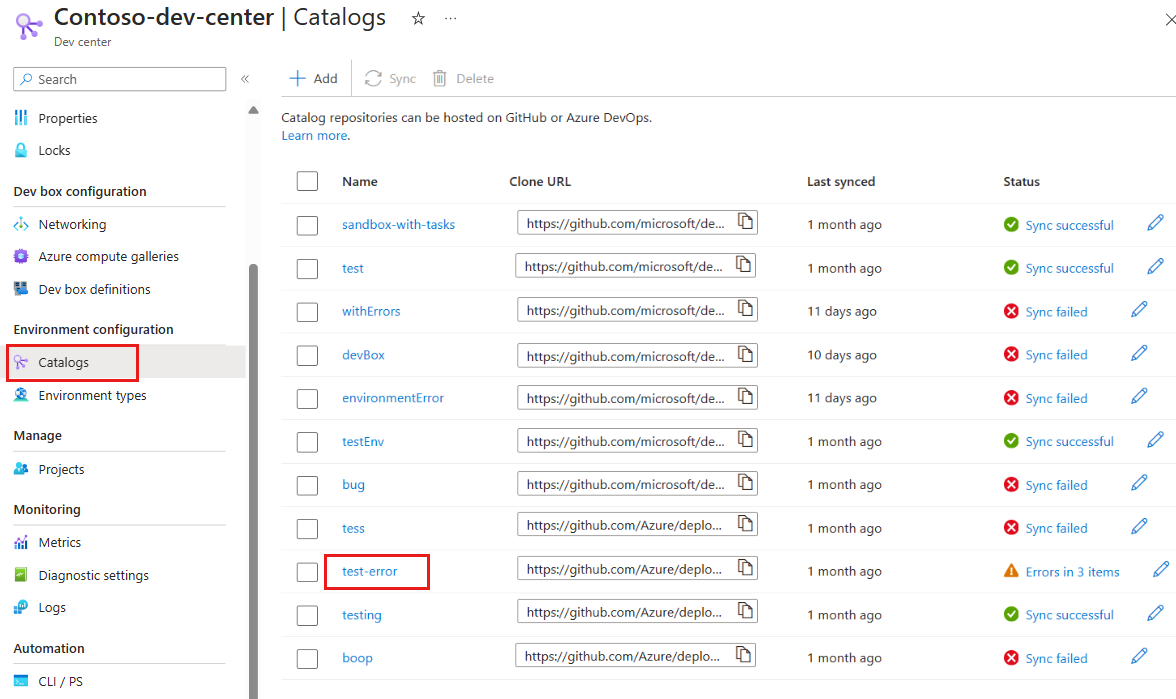
On the left menu for your dev center or project, under Environment configuration, select Catalogs.
In the Status column, select the status link for the catalog that failed to sync.
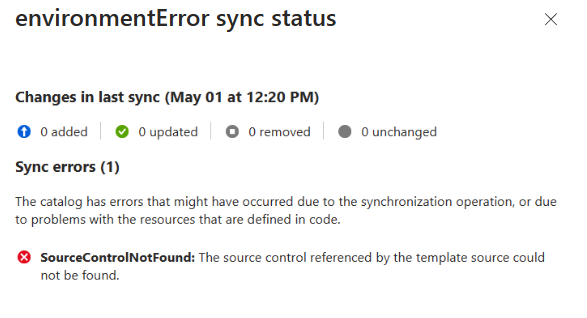
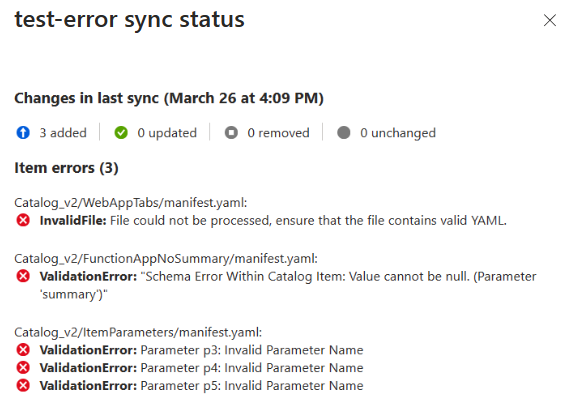
You see a details pane that shows the changes in the last sync, the number of sync errors, and the type of errors.
View catalog sync warnings
On the left menu for your dev center or project, under Environment configuration, select Catalogs.
In the Status column, select the status link for the catalog that synced but reports a warning.
You see a details pane that shows the changes in the last sync, the number of item errors, and the type and source of each error.
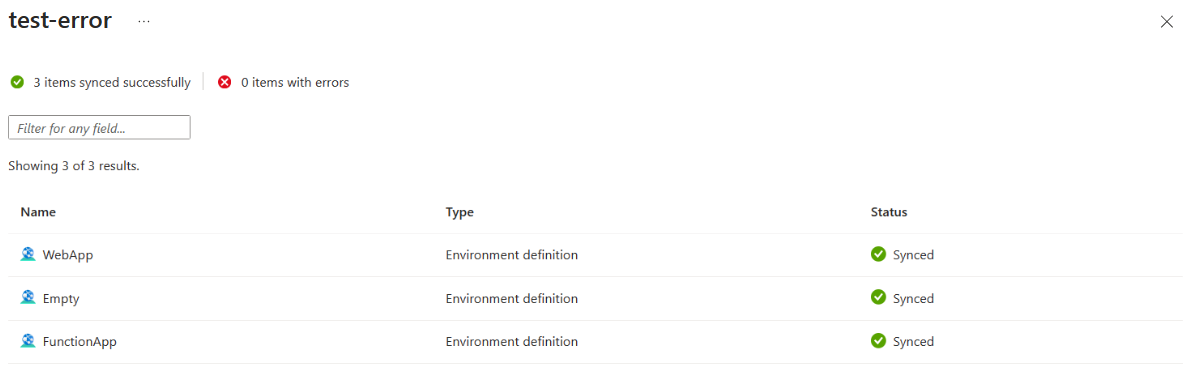
You can view items that synced successfully from a catalog that also reports sync errors. From the Catalogs pane, select the catalog name.
You see a list of successfully synced catalog items.
Troubleshoot catalog sync errors by using the Azure CLI
Use the Azure CLI or the REST API to GET the catalog. The GET response shows you the type of error:
- Ignored environment definitions that were detected to be duplicates.
- Invalid environment definitions that failed due to schema, reference, or validation errors.
Resolve ignored environment definition errors
An ignored environment definition error occurs if you add two or more environment definitions that have the same name. You can resolve this issue by renaming environment definitions so that each environment definition has a unique name within the catalog.
Resolve invalid environment definition errors
An invalid environment definition error might occur for various reasons:
Manifest schema errors. Ensure that your environment definition environment file matches the required schema.
Validation errors. Check the following items to resolve validation errors:
- Ensure that the environment file's engine type is correctly configured.
- Ensure that the environment definition name is between 3 and 63 characters.
- Ensure that the environment definition name includes only characters that are valid for a URL, which are alphanumeric characters and these symbols:
~!,.';:=-_+()*&$@
Reference errors. Ensure that the template path that the environment file references is a valid relative path to a file in the repository.