Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server | Azure DevOps Server 2022 | Azure DevOps Server 2020
Work item fields track information within Azure DevOps. The system defines these fields at the organization level and shares them across all projects in the organization. To review the fields defined for your organization, you can use one of the following two tools, available for both Inherited and Hosted XML process models:
Work item fields track information within Azure DevOps. The system defines these fields at the collection level and shares them across all projects within that collection. To review the fields defined for your collection, use one of the following tools:
- Process > Fields web page: Available for the Inherited process model.
- Work Item Field Explorer: Available for both Inherited and On-premises XML process models.
For a description of each field defined with a system process, see Work item field index.
Why work item fields matter
Work item fields serve several critical functions in Azure DevOps:
- Data tracking: Capture and store essential information about work items
- Query functionality: Enable powerful searching and filtering capabilities
- Reporting: Support analytics and dashboard creation
- Workflow management: Drive state transitions and business rules
- Integration: Connect with external tools and systems
Understanding field attributes helps you:
- Optimize queries: Choose the right fields for efficient searches
- Plan customizations: Understand limitations and possibilities
- Troubleshoot issues: Diagnose problems with field behavior
- Design processes: Create effective work item types and workflows
Prerequisites
| Category | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Permissions | To view the fields defined for an organization or collection: Member of the Project Collection Valid Users application group or View instance-level information permission set to Allow for the organization or collection. |
List or review fields
To list or review fields, use one of the following tools based on your process model—Inherited, Hosted XML, or On-premises XML. For an index of fields defined within the default processes, see Work item field index.
| Tool | Inheritance | Hosted XML | On-premises XML |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web portal: List inherited and custom-defined fields | ✔️ | ✔️1 | |
| Work item field explorer | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| witadmin listfields command line tool | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Note
- Only supported for default processes (Agile, CMMI, Scrum).
Field data types and names
Each work item type specifies the fields included in work items of that type. Each field has multiple attributes, many of which are system-defined and immutable.
Three key attributes define fields:
- Data type: Indicates the kind of data that you can enter into the field, such as Boolean, Double, Integer, HTML, or String. For detailed descriptions of each data type, see Query fields, operators, and macros.
- Friendly name: The user-friendly name assigned to the field, used when selecting a Field in a query clause. This name might differ from the name displayed on the work item form.
- Reference name: The identifier used when creating WIQL queries, work item templates, executing REST API commands, or defining XML work item type definitions. The reference name is permanent and can't be changed once set.
For a detailed description of each field attribute and instructions on how to list them, see Field attributes and List field attributes later in this article. For an overview of work item types (WITs) and work items, refer to Track work with user stories, issues, bugs, features, and epics.
What is a field? How do field names work?
Each work item type includes 31 system fields and several type-specific fields. Work items help you plan and track your project.
Each field captures specific information about the work to be performed. The values you assign to these fields are stored in the work tracking data store, enabling you to create queries that determine status and trends.
For descriptions and usage of each field defined for the core system processes—Agile, Basic, Scrum, and CMMI—refer to the Work item field index.
Field naming requirements
A work item field name uniquely identifies each work item field. Ensure your field names adhere to the following guidelines:
- Uniqueness: Field names must be unique within the account or project collection.
- Length: Field names must contain 128 Unicode characters or fewer.
- Spacing: Field names can't have leading or trailing spaces or contain two or more consecutive spaces.
- Composition: Field names must include at least one alphabetic character.
- Prohibited Characters: Field names can't include the following characters:
.,;':~/*|?"&%$!+=()[]{}<>`.
Since the system defines custom fields at the organization or collection level, you can't add a custom field with the same name to multiple processes.
For more information, see Naming restrictions and conventions.
System and predefined fields
The system defines work item fields with specific naming and structural requirements to ensure consistency and functionality:
- Uniqueness: Field names must be unique within an account or project collection.
- Length: Field names must be 128 Unicode characters or fewer.
- Spacing: Field names can't have leading or trailing spaces or contain multiple consecutive spaces.
- Composition: Field names must include at least one alphabetic character.
- Prohibited Characters: Field names can't include the following characters:
.,;':~/*|?"&%$!+=()[]{}<>`.
Since the system defines custom fields at the organization or collection level, you can't add a custom field with the same name to multiple processes.
For more information, see Naming restrictions and conventions.
Custom fields
Because the system defines custom fields at the organization or project collection level, you can't add a custom field with the same name to multiple processes.
When adding custom fields, note the following limits:
- Maximum fields per work item type (WIT): 64
- Maximum fields per process: 512
The field data type determines the kind and size of data that you can store in the field. Each field can have only one type defined within a project collection, encouraging the use of common fields across different projects and work item types.
When you add a custom field to an inherited process, Azure DevOps assigns a reference name prefixed with Custom followed by the field name without spaces. For example, adding a field named DevOps Triage results in the reference name Custom.DevOpsTriage. Spaces aren't allowed in reference names.
For more information, see Naming restrictions and conventions.
How can I determine the field data type?
You can view the data type of fields defined for your organization by opening the Process > Fields page.
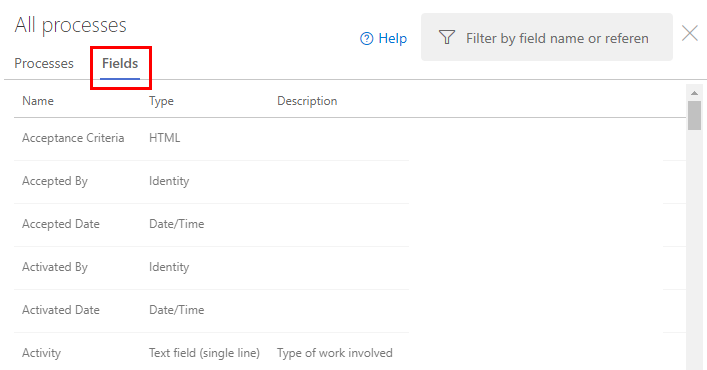
When your project collection uses the Inheritance process model to customize work tracking, you can view the data type of fields by opening the Process > Fields page.

If your project collection uses the On-premises XML process model, you can determine the data type through the Work item field index. Alternatively, you can:
- Open the Work Item Field Explorer to review defined fields and their attributes.
- Use the witadmin listfields command to list field attributes.
For more information, see Work Item Field Explorer and List field attributes later in this article.
Review fields list
To review the list of fields defined for an organization or collection, follow these steps:
Select the
 Azure DevOps logo to open Projects. Then select Organization settings.
Azure DevOps logo to open Projects. Then select Organization settings.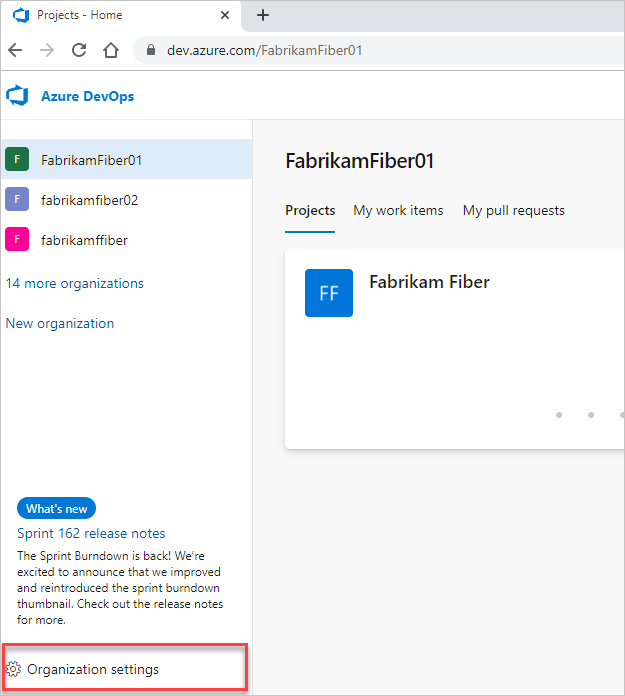
Select Process.
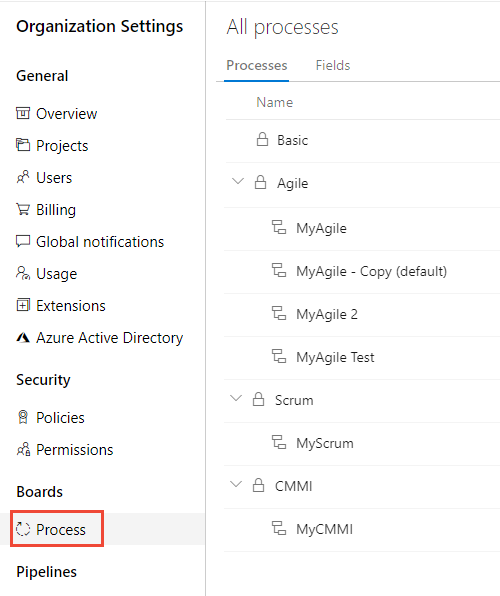
Select Fields.
Fields listed correspond to all fields defined for the organization or collection, which includes all custom fields and the fields defined for system processes.

Note
If you don't see Fields, then your collection uses the On-premises XML process. The Fields page isn't supported for that process.
For descriptions, usage, and reference names of each field, refer to the Work item field index. Additionally, you can retrieve field reference names using the Work Item Types Field - List REST API.
Work Item Field Explorer
You can look up the assignments of field attributes using the Work Item Field Explorer tool.
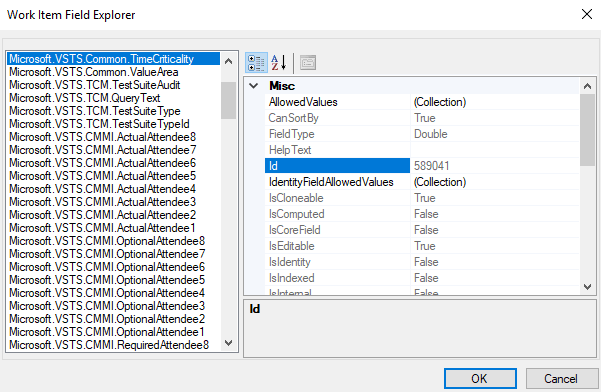
To access the Work Item Field Explorer, install the Process Editor Tool. Based on your installed version of Visual Studio, get the Process Editor Tool from one of the following extensions.
- Visual Studio 2019 & 2022: As of now, there's no specific Process Template Editor extension available. But, you can still customize process templates using other tools such as any text editor or XML editor. You can also use the Azure DevOps web portal for certain customizations, especially for inherited processes.
- Visual Studio 2017: TFS Process Template Editor. You can also use this version of the Process Editor to modify the old-style work item forms. You can't use it to edit forms associated with the new web forms.
- Visual Studio 2015: TFS Power Tools.
Field attributes
Many nonchangeable and hidden attributes exist for each work item field. The following table describes each attribute. Attributes have different names depending on whether you retrieve them through the Fields - Get REST API or view them through the Work Item Field Explorer (WIFE) tool.
Attributes assigned to a field depend on the platform and version you use. For example, some attributes aren't supported with the Inheritance process. To look up the reference name for a field, see the Work item field index.
Attribute
Attribute type
Description
REST:
WIFE: AllowedValues
collection
Gets the collection of valid values for a field that contains picklist values. You can change this by specifying a picklist or global list (on-premises).
Can change?=Yes
REST: canSortBy
WIFE: CanSortBy
boolean
Indicates whether you can sort query results with this field.
Can change?=No
REST: description
WIFE: HelpText
string
Specifies a description for the field, which also defines the help text that appears when you hover over the field within the work item form.
Can change?=Yes
REST:
WIFE: ID
Integer
Specifies the internal ID of the field.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsCloneable
boolean
Indicates whether the system copies the value defined for the field when a user chooses to copy a work item. For example, the system copies Title, Tags, and Description fields, but doesn't copy the ID and History fields.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsComputed
boolean
Indicates if the system computes the value the field sets (True) or not (False). Examples of computed fields are ones that the system sets, such as the ID, Revised Date, Changed Date, and External Link Count.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsCoreField
boolean
Indicates whether this field is specified for all work item types.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsEditable
boolean
Indicates if users can modify this field (True) or not (False). Examples of noneditable fields are ones that the system sets, such as the ID, Revision, Created By, and Changed By fields
Can change?=No
REST: isIdentity
WIFE: IsIdentity
boolean
Indicates whether this field is an Identity field. Identity fields are string fields used to store user identities.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsIndexed1
boolean
Indicates whether this field is indexed to support search.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsLongText
boolean
Indicates that the field can contain more than 255 characters, such as fields assigned a data type of PlainText, HTML, or History.
Can change?=No
REST: isPicklist2 WIFE:
Boolean
Indicates whether the field associates with a picklist. The system sets the value to True when you define a custom field for Azure DevOps and select Picklist (String) or Picklist (Integer) type. The system sets the value to False for inherited fields that define picklists.
Can change?=No
REST: isPicklistSuggested2 WIFE:
Boolean
Indicates whether the field allows users to enter their own values for a picklist. The system sets the value to True when you define a custom field for Azure DevOps, select Picklist (String) or Picklist (Integer) type, and check the checkbox for Allow users to set their own values.
Can change?=Yes
REST: isQueryable
WIFE: IsQueryable
boolean
Indicates if the field shows up within the fields you can add to filter a work item query (True), or not (False). Most fields are queryable.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsReportable 3
boolean
Indicates if the reportable attribute is defined or set to anything other than None. You can change this attribute for on-premises environments.
Can change?=Yes
REST:
WIFE: IsUsedInGlobalWorkflow
boolean
Indicates if the field is defined within a global workflow.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: IsUserNameField
boolean
Indicates if the field is used to display an Identity field.
Can change?=No
REST: name
WIFE: Name
string
Friendly name assigned to the field. You can't change the friendly name for Azure DevOps, but you can change it for on-premises using the witadmin changefield command.
Can change?=On-premises only
REST: picklistId
WIFE: HelpText
GUID
If the field is a picklist, the identifier of the associated picklist, otherwise null. The system assigns a unique GUID value when you define a custom field for Azure DevOps and select Picklist (String) or Picklist (Integer) type.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: ProhibitedValues
collection
Gets the collection of prohibited values for a field that specifies such values. You can only define prohibited values for on-premises deployments.
Can change?=On-premises only
REST: readOnly
WIFE:
Boolean
Indicates whether the field is set to read only. For Azure DevOps Services, only custom fields can be changed to be read-only. System fields can't be modified.
Can change?=Yes
REST: referenceName
WIFE: ReferenceName
string
Specifies the reference name of a field.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: ReportingAttributes3
Specifies Detail, Dimension, or Measure, depending on whether and how you want the field to be included in reports. The system exports data from fields that have a value other than None for this attribute to the data warehouse and can include them in SQL reports.
Can change?=On-premises only
REST:
WIFE: ReportingName3
string
Specifies the label for a field when data appears in SQL reports. If you don't specify a value, the system uses the field's friendly name.
Can change?=On-premises only
REST:
WIFE: ReportingReferenceName3
string
Specifies a different reference name to a field that the system uses when it exports data to the relational data warehouse. If you don't specify a value, the system uses the fields reference name.
Can change?=On-premises only
REST: supportedOperations
WIFE:
set
The collection of query operators that are valid for use when referencing this field. For a quick reference of supported operations based on data type, see Query quick reference, Operators, and macros supported for each data type.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: SupportsTextQuery
boolean
Indicates whether the field supports text queries such as Contains Words, Does Not Contains Words.
Can change?=No
REST:
WIFE: SystemType
string
Specifies the data type of the field, referencing the system name such as System.DateTime or System.String.
Can change?=No
REST: type
WIFE: FieldType
string
Specifies the data type of the field, such as Boolean, DateTime, Integer, String, and so on. For a complete list and descriptions, see Query fields, operators, and macros.
Can change?=No
REST: usage
WIFE: Usage
string
Specifies whether the field is intended for use with work items (WorkItem) or work item link (WorkItemLink) objects. The usage for most fields is WorkItem. For a complete list of usage values, see Get Fields, FieldUsage.
Can change?=No
Note
- For on-premises deployments, you can enable indexing for a field to improve query response times when filtering on the field. For more information, see Indexed fields later in this article.
- The system assigns the isPicklist and isPicklistSuggested attributes only to custom fields defined for an inherited process. The Inherited process model supports Azure DevOps Server 2020 and later versions. For more information, see Inherited process model.
- All reporting attributes are valid only for on-premises deployments whose projects have been configured to support SQL Server Reporting and SQL Server Analysis Services.
Reportable attributes
All reporting attributes are valid only for on-premises deployments where you configure projects to support SQL Server Reporting and SQL Server Analysis Services. For more information, see Add reports to a project.
For descriptions of each reportable attribute, refer to Add or modify work item fields to support reporting.
To see a list of fields with reportable attributes defined by default, see Reportable fields reference.
Indexed fields
Use the witadmin indexfield command to enable or disable indexing for a work item field. Enabling indexing for a field can improve the performance of queries that specify that field. By default, the system indexes the following fields:
- Assigned To
- Created Date
- Changed By
- State
- Reason
- Area ID
- Iteration ID
- Work Item Type
If you add a custom field used frequently in your work item queries, consider enabling indexing for that field. For more information, see Manage work item fields (witadmin).
List field attributes
You can list the attributes assigned to a field by using the Fields - Get REST API. Replace OrganizationName with your actual organization name.
https://dev.azure.com/OrganizationName/_apis/wit/fields/FieldReferenceName
For example, to list the attributes for the Iteration Path, use the reference name System.IterationPath for the fabrikam organization:
https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam/_apis/wit/fields/System.IterationPath
Returned data:
{
"name": "Iteration Path",
"referenceName": "System.IterationPath",
"description": "The iteration within which this bug will be fixed",
"type": "treePath",
"usage": "workItem",
"readOnly": false,
"canSortBy": true,
"isQueryable": true,
"supportedOperations": [
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.Under",
"name": "Under"
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.NotUnder",
"name": "Not Under"
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.Equals",
"name": "="
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.NotEquals",
"name": "<>"
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.In",
"name": "In"
},
{
"name": "Not In"
}
],
"isIdentity": false,
"isPicklist": false,
"isPicklistSuggested": false,
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/mseng/_apis/wit/fields/System.IterationPath"
}
You can list the attributes assigned to a field by using the Fields - Get REST API. Enter your organization name for OrganizationName. To get started using REST, see Azure DevOps Services REST API Reference
https://{ServerName:Port}/tfs/{Collection}/_apis/wit/fields/FieldReferenceName?api-version={version}
For example, here we list the attributes for the Iteration Path, specifying the reference name, System.IterationPath, for the fabrikam server.
https://fabrikam:8080/tfs/DefaultCollection/_apis/wit/fields/System.IterationPath?api-version=4.1
Returned data:
{
"name": "Iteration Path",
"referenceName": "System.IterationPath",
"description": "The iteration within which this bug will be fixed",
"type": "treePath",
"usage": "workItem",
"readOnly": false,
"canSortBy": true,
"isQueryable": true,
"supportedOperations": [
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.Under",
"name": "Under"
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.NotUnder",
"name": "Not Under"
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.Equals",
"name": "="
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.NotEquals",
"name": "<>"
},
{
"referenceName": "SupportedOperations.In",
"name": "In"
},
{
"name": "Not In"
}
],
"isIdentity": false,
"isPicklist": false,
"isPicklistSuggested": false,
"url": "https://fabrikam:8080/tfs/DefaultCollection/_apis/wit/fields/System.IterationPath?api-version=4.1"
}
List attributes using witadmin command-line tool
You can list select field attributes—such as the data type, reportable attributes, and indexing—using the witadmin listfields command.
For example, you can enter the following command to list the attributes defined for a specified field, such as Microsoft.VSTS.Common.Issue.
witadmin listfields /collection:http://fabrikam:8080/tfs/DefaultCollection /n:Microsoft.VSTS.Common.Issue
Field and attribute information appears for the named field, as shown in this example.
Field: Microsoft.VSTS.Common.Issue
Name: Issue
Type: String
Reportable As: dimension
Use: Adventure Works (Shared Steps), AW Future (Shared Steps), AW Current (Shared Steps)
Indexed: False
The Use parameter indicates the name of each project and the work item type where the field is used.
Best practices for working with fields
Consider these recommendations when working with work item fields:
Field selection and design
- Choose meaningful names: Use descriptive field names that clearly indicate their purpose
- Standardize naming: Establish consistent naming conventions across your organization
- Limit custom fields: Add custom fields judiciously to avoid overwhelming users
- Consider data types: Select appropriate data types for the information you're storing
Performance optimization
- Use indexed fields: For on-premises deployments, consider indexing frequently queried custom fields
- Avoid heavy queries: Be mindful of query performance when using many field filters
- Optimize picklists: Keep picklist values manageable in size and well-organized
Maintenance and governance
- Document field usage: Maintain documentation explaining the purpose and usage of custom fields
- Review regularly: Periodically review custom fields to identify unused or redundant fields
- Plan for changes: Consider the impact of field changes on existing work items and queries
- Test modifications: Always test field changes in a development environment first
Add and modify fields
To add fields to a process, you add them to one or more work item types. For more information, see Customize an inheritance process.
You can add or modify the fields contained within a WIT or add a custom WIT. For more information, see:
- For project collections that use the Inheritance process model: Customize an inheritance process.
- For project collections that use the On-premises XML process model: Customize the On-premises XML process model.
You can change the field name, the index, and the report attributes for any field except system fields by using the witadmin command-line tool. For more information, see Manage work item fields-witadmin.
Troubleshooting field issues
Common issues and solutions when working with work item fields:
Field visibility problems
- Field not appearing: Check if the field is added to the work item type layout
- Permission issues: Verify you have appropriate permissions to view or edit fields
- Process differences: Ensure the field exists in the current process
Query and search issues
- Field not queryable: Check the
IsQueryableattribute for the field - Performance problems: Consider indexing frequently queried custom fields (on-premises)
- Operator limitations: Verify which operators are supported for the field data type
Data entry and validation
- Invalid values: Check if the field has restricted allowed values or validation rules
- Read-only fields: Verify the field's
IsEditableattribute - Format requirements: Ensure data matches the expected field data type
Related content
- Query quick reference to quickly understand query syntax and usage.
- Work item field index to view all available work item fields.
- Add and manage fields for an inherited process to customize fields according to your inherited process requirements.
- Metadata reference for Azure Boards Analytics to understand analytics metadata and reporting capabilities.
- Query quick reference to quickly understand query syntax and usage.
- Work item field index to view all available work item fields.
- Choose the process model for your project collection to select the appropriate process model for your needs.
- Modify a work item field according to your project's requirements.
- Manage work item fields using witadmin to perform advanced field management tasks.
- Metadata reference for Azure Boards Analytics to understand analytics metadata and reporting capabilities.