Azure Pipelines - Sprint 240 Update
Features
- Access Azure Service Bus from Pipelines using Microsoft Entra ID authentication
- Pipelines and tasks populate variables to customize Workload identity federation authentication
- Retries for server tasks
- Tasks that use an end-of-life Node runner version to execute emit warnings
- DockerCompose0 uses Docker Compose v2 in v1 compatibility mode
Access Azure Service Bus from Pipelines using Microsoft Entra ID authentication
You can now use Microsoft Entra ID authentication to access Azure Service Bus from Azure Pipelines. This allows you to take advantage of Workload identity federation to remove secrets management and Azure RBAC for fine grained access control.
Identities accessing Azure Service Bus need to be granted one of the Azure built-in roles for Azure Service Bus on the Service Bus accessed.
PublishToAzureServiceBus@2 task
The new PublishToAzureServiceBus@2 tasks can be configured using an Azure service connection. Create an Azure service connection and populate the serviceBusQueueName and serviceBusNamespace properties of the new task:
- task: PublishToAzureServiceBus@2
inputs:
azureSubscription: my-azure-service-connection
serviceBusQueueName: my-service-bus-queue
serviceBusNamespace: my-service-bus-namespace
useDataContractSerializer: false
messageBody: |
{
"foo": "bar"
}
Server tasks
Custom server (agent-less) tasks that use ServiceBus execution can specify an Azure Service Connection as EndpointId and omit ConnectionString. See Server task authoring.
Pipelines and tasks populate variables to customize Workload identity federation authentication
The REST API endpoint for requesting OIDC tokens is now available in the System.OidcRequestUri pipeline variable. Task developers can leverage this variable to generate an idToken for authentication with Entra ID.
If you are using Marketplace tasks or custom tasks to deploy to Azure, please be aware that these tasks may not support workload identity federation yet. We recommend task developers to enable workload identity federation to improve security measures.
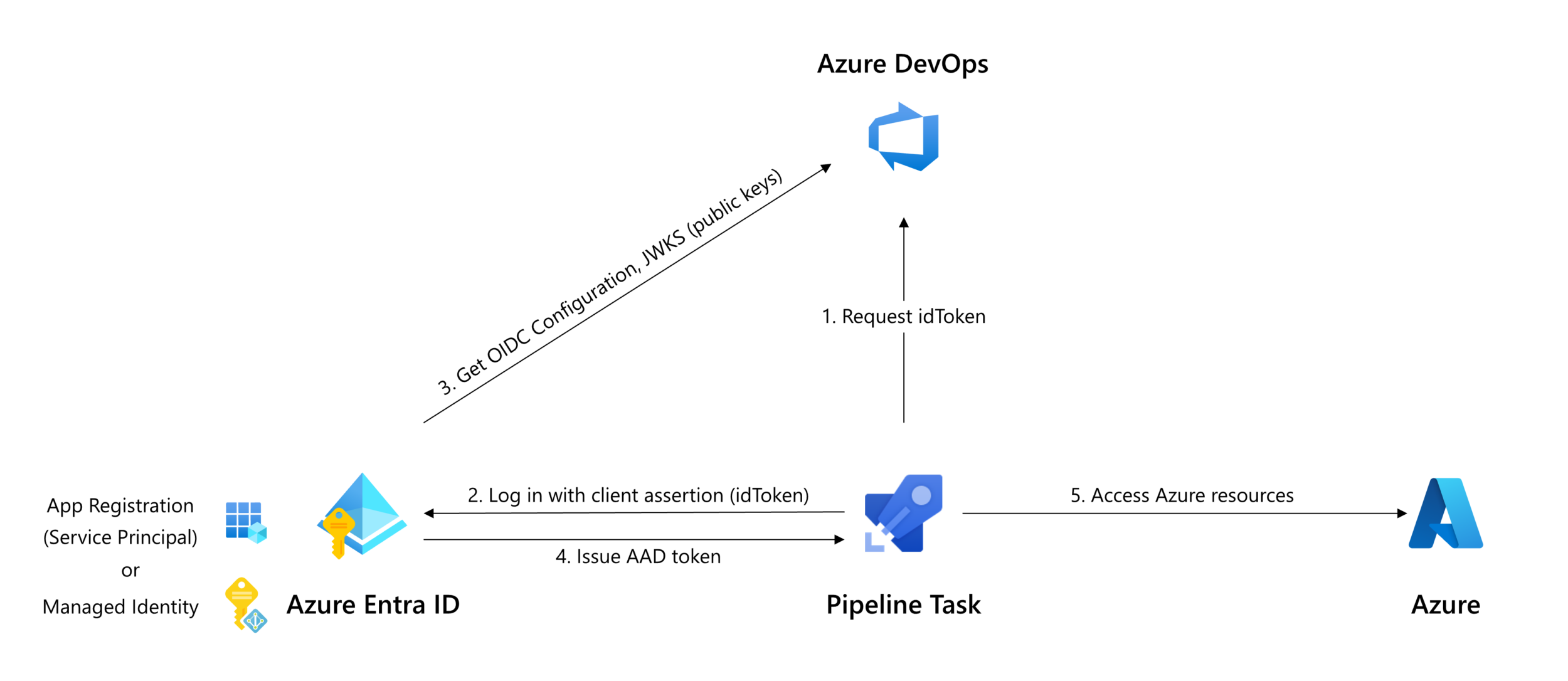
Tasks that take a connectedService:AzureRM input in task.json can be updated to support workload identity federation by following these steps:
- Utilize the Oidctoken REST API to request an idToken (arrow 1 in above diagram).
- Exchange the idToken for an access token using the federated credential flow of the OAuth API, specifying the idToken as
client_assertion(arrows 2 & 4 in above diagram);
or: - For tasks that act as a wrapper around a tool that performs authentication itself, use the tools' authentication method to specify the federated token.
Node tasks can use the azure-pipelines-tasks-artifacts-common npm package to obtain the idToken. Refer to the code example for implementation details.
Requesting a fresh idToken
The System.OidcRequestUri pipeline variable and AZURESUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE_CONNECTION_ID environment variable exposed in the AzureCLI@2 and AzurePowerShell@5 tasks allow pipeline authors to authenticate from their own script:
PowerShell Az
- task: AzurePowerShell@5
inputs:
azureSubscription: 'my-azure-subscription'
scriptType: inlineScript
inline: |
# Request fresh idToken
Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{
Authorization = "Bearer $(System.AccessToken)"
'Content-Type' = 'application/json'
} `
-Uri "${env:SYSTEM_OIDCREQUESTURI}?api-version=7.1&serviceConnectionId=${env:AZURESUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE_CONNECTION_ID}" `
-Method Post `
| Select-Object -ExpandProperty oidcToken
| Set-Variable idToken
# Fetch current context
$azContext = Get-AzContext
# Start new Az session
Connect-AzAccount -ApplicationId $azContext.Account.Id `
-TenantId $azContext.Tenant.Id `
-SubscriptionId $azContext.Subscription.Id `
-FederatedToken $idToken
Azure CLI
- task: AzureCLI@2
inputs:
addSpnToEnvironment: true
azureSubscription: 'my-azure-subscription'
scriptType: bash
scriptLocation: inlineScript
inlineScript: |
# Request fresh idToken
OIDC_REQUEST_URL="${SYSTEM_OIDCREQUESTURI}?api-version=7.1&serviceConnectionId=${AZURESUBSCRIPTION_SERVICE_CONNECTION_ID}"
ARM_OIDC_TOKEN=$(curl -s -H "Content-Length: 0" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer $(System.AccessToken)" -X POST $OIDC_REQUEST_URL | jq -r '.oidcToken')
# Save subscription context
ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(az account show --query id -o tsv)
# New az-cli session
az login --service-principal -u $servicePrincipalId --tenant $tenantId --allow-no-subscriptions --federated-token $ARM_OIDC_TOKEN
az account set --subscription $ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID
Retries for server tasks
Server tasks that call external systems, such as AzureFunction or InvokeRESTAPI, can occasionally fail due to transient errors like compute resource exhaustion. Previously, such failures would cause the entire job, and potentially the pipeline, to fail.
To improve resilience against transient errors, we have introduced support for the retryCountOnTaskFailure property in server tasks. Assume you have the following YAML code in your pipeline:
- stage: deploy
jobs:
- job:
pool: server
steps:
- task: AzureFunction@1
retryCountOnTaskFailure: 2
inputs:
function: 'https://api.fabrikamfiber.com'
key: $(functionKey)
method: 'POST'
waitForCompletion: 'false'
If https://api.fabrikamfiber.com experiences a transient error, Azure Pipelines will retry the request up to three times (the initial attempt plus two retries specified by retryCountOnTaskFailure). Each retry includes an increasing wait period. The maximum number of retries allowed is 10.
The retryCountOnTaskFailure isn't available for the ManualValidation task and other tasks that don't involve external system calls.
Tasks that use an end-of-life Node runner version to execute emit warnings
Pipeline tasks that rely on a Node version no longer maintained will start receiving warnings:
Task
TaskNameversion<version>is dependent on a Node version (10) that is end-of-life. Contact the extension owner for an updated version of the task. Task maintainers should review Node upgrade guidance: https://aka.ms/node-runner-guidance
To suppress these warnings, you can set an environment or pipeline variable at either the pipeline (job) or task level. For example:
variables:
AZP_AGENT_CHECK_IF_TASK_NODE_RUNNER_IS_DEPRECATED: false
DockerCompose@0 uses Docker Compose v2 in v1 compatibility mode
Docker Compose v1 will reach its end-of-life and will be removed from Hosted Agents July 24 2024. We have updated the DockerCompose@0 task to use Docker Compose v2 in v1 compatibility mode if Docker Compose v1 is not available on the agent.
However, compatibility mode does not address all compatibility issues. See Migrate to Compose V2. Some users will need more time to update their Docker Compose projects for Docker Compose v2 compatibility. In those cases, follow these instructions to use the DockerComposeV0 task with docker-compose v1.
NOTE: This guide is based on Install Compose standalone documentation
Use docker-compose v1 on Windows
Add the powershell step to your pipeline to download the docker-Compose v1.29.2 and use it with the DockerComposeV0 task on Windows:
variables:
dockerComposePath: C:\docker-compose
steps:
- powershell: |
mkdir -f $(dockerComposePath)
# GitHub now requires TLS1.2. In PowerShell, run the following
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
Start-BitsTransfer -Source "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.1/docker-compose-windows-x86_64.exe" -Destination $(dockerComposePath)\docker-compose.exe
displayName: Download docker-compose
- task: DockerCompose@0
inputs:
containerregistrytype: 'Azure Container Registry'
dockerComposeFile: '**/docker-compose.yml'
action: 'Run a Docker Compose command'
dockerComposeCommand: 'run'
dockerComposePath: $(dockerComposePath)\docker-compose.exe
Use docker-compose v1 on Linux
Add the bash step to your pipeline to download Docker-Compose v1.29.2 and use it with the DockerComposeV0 task on Linux:
variables:
dockerComposePath: /tmp/docker-compose
steps:
- bash: |
sudo mkdir $(dockerComposePath)
sudo curl -SL https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-linux-x86_64 -o $(dockerComposePath)/docker-compose
sudo chmod 755 $(dockerComposePath)/docker-compose
displayName: Download docker-compose
- task: DockerCompose@0
inputs:
containerregistrytype: 'Azure Container Registry'
dockerComposeFile: $(Build.SourcesDirectory)/DockerComposeV0/docker-compose.yml
action: 'Run a Docker Compose command'
dockerComposeCommand: 'run'
dockerComposePath: $(dockerComposePath)/docker-compose
Next steps
Note
These features will roll out over the next two to three weeks.
Head over to Azure DevOps and take a look.
How to provide feedback
We would love to hear what you think about these features. Use the help menu to report a problem or provide a suggestion.
You can also get advice and your questions answered by the community on Stack Overflow.