Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Event Grid's MQTT broker supports authentication of clients using X.509 certificates. X.509 certificate provides the credentials to associate a particular client with the tenant. In this model, authentication generally happens once during session establishment. Then, all future operations using the same session are assumed to come from that identity.
Supported authentication modes are:
- Certificates issued by a Certificate Authority (CA)
- Self-signed client certificate - thumbprint
- Microsoft Entra ID token
This article focuses on certificates. To learn about authentication using Microsoft Entra ID tokens, see authenticate client using Microsoft Entra ID token.
Certificate Authority (CA) signed certificates
In this method, a root or intermediate X.509 certificate is registered with the service. Essentially, the root or intermediary certificate that is used to sign the client certificate, must be registered with the service first.
Important
- Ensure to upload the root or intermediate certificate that is used to sign the client certificate. It is not needed to upload the entire certificate chain.
- For example, if you have a chain of root, intermediate, and leaf certificates, ensure to upload the intermediate certificate that signed the leaf/client certificates.
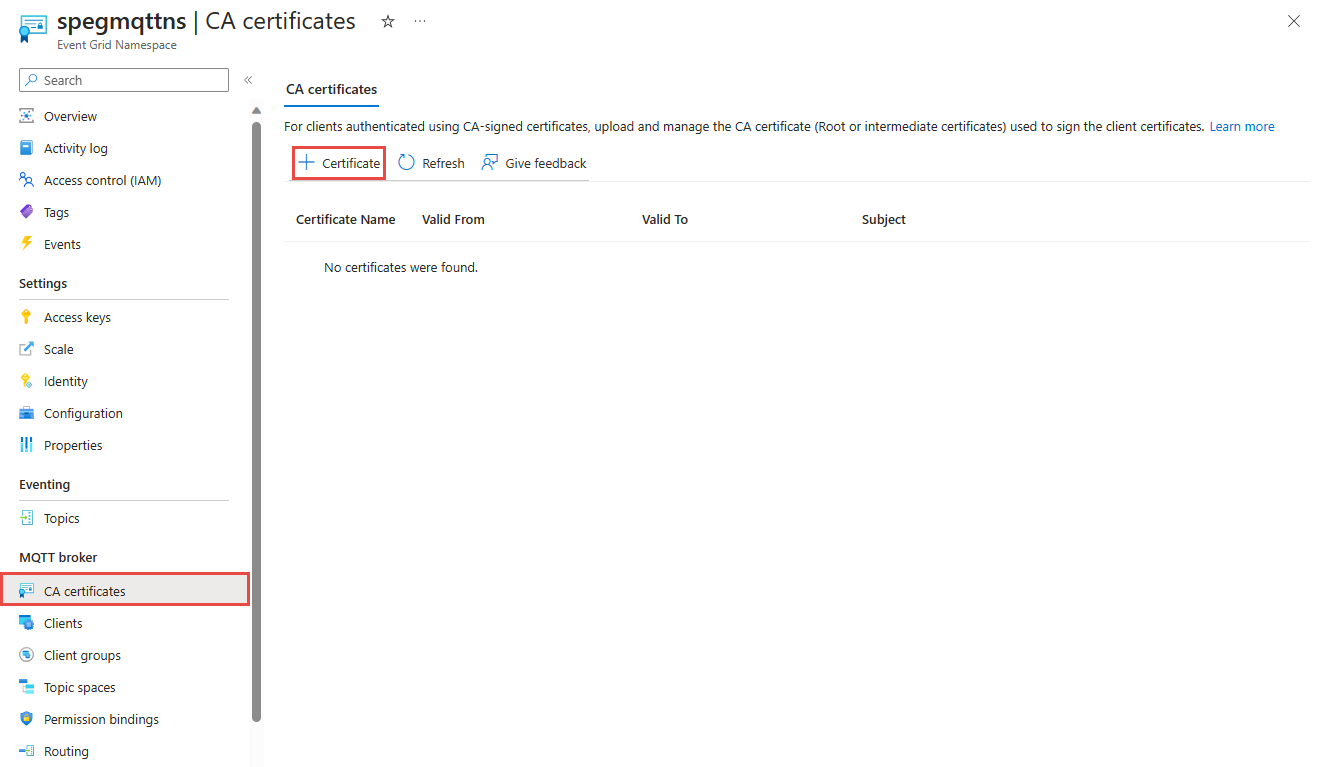
While registering clients, you need to identify the certificate field used to hold the client's authentication name. The service matches the authentication name from the certificate with the client's authentication name in the client metadata to validate the client. The service also validates the client certificate by verifying whether it's signed by the previously registered root or intermediary certificate.
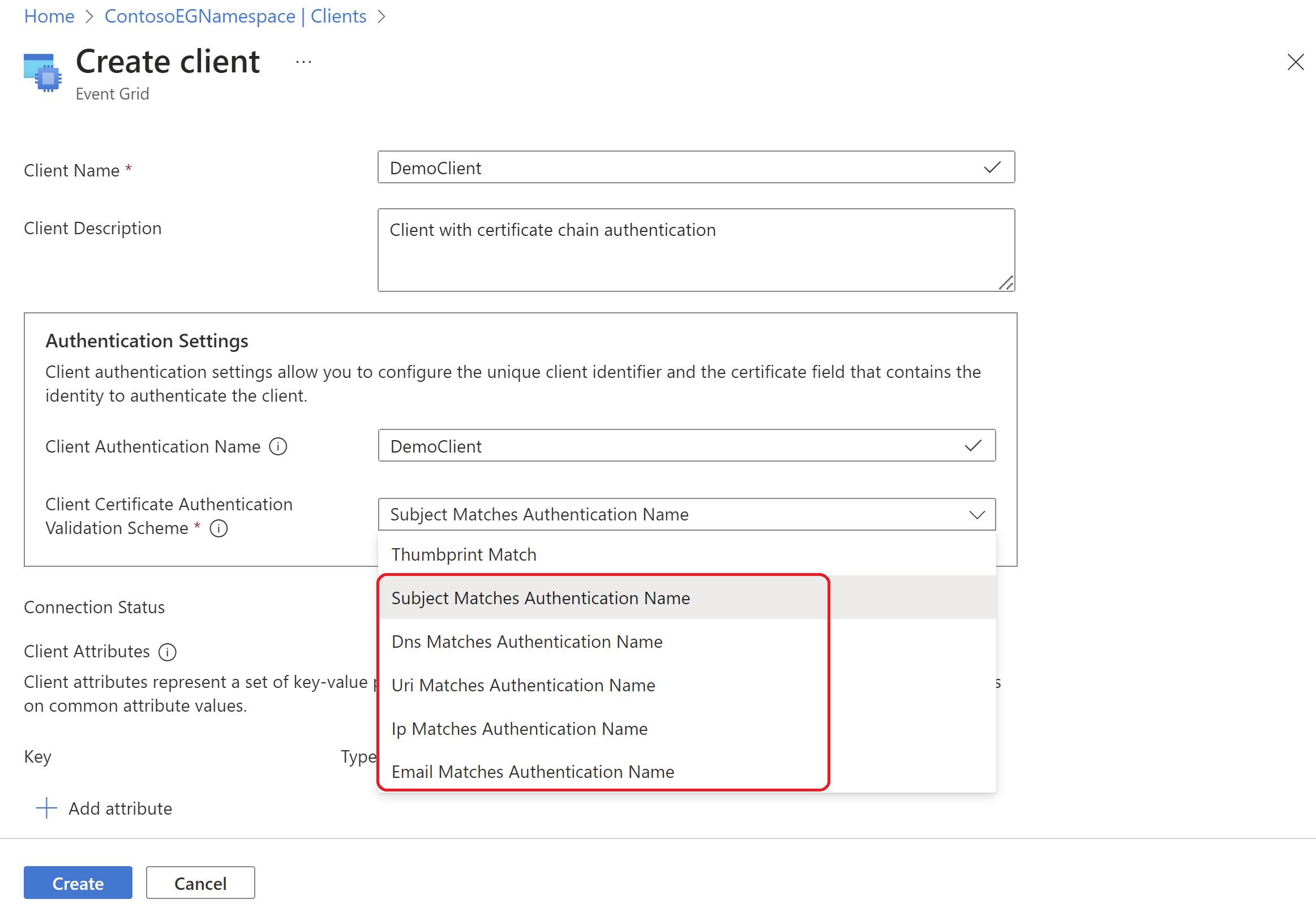
Self-signed client certificate - thumbprint
In this method of authentication, the client registry stores the exact thumbprint of the certificate that the client is going to use to authenticate. When client tries to connect to the service, service validates the client by comparing the thumbprint presented in the client certificate with the thumbprint stored in client metadata.
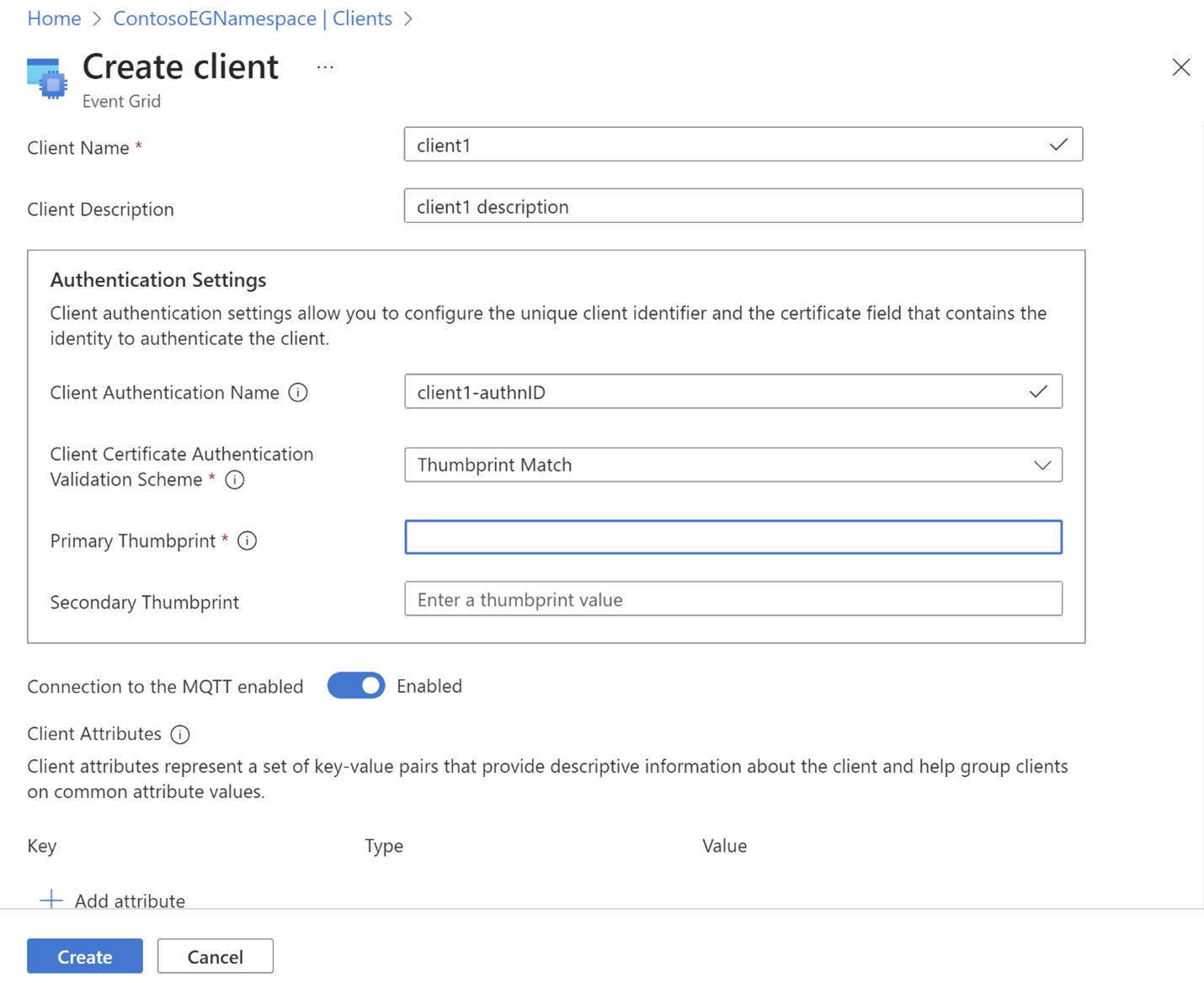
Note
- We recommend that you include the client authentication name in the username field of the client's connect packet. Using this authentication name along with the client certificate, service will be able to authenticate the client.
- If you do not provide the authentication name in the username field, you need to configure the alternative source fields for the client authentication name at the namespace scope. Service looks for the client authentication name in corresponding field of the client certificate to authenticate the client connection.
In the configuration page at namespace scope, you can enable alternative client authentication name sources and then select the client certificate fields that have the client authentication name.
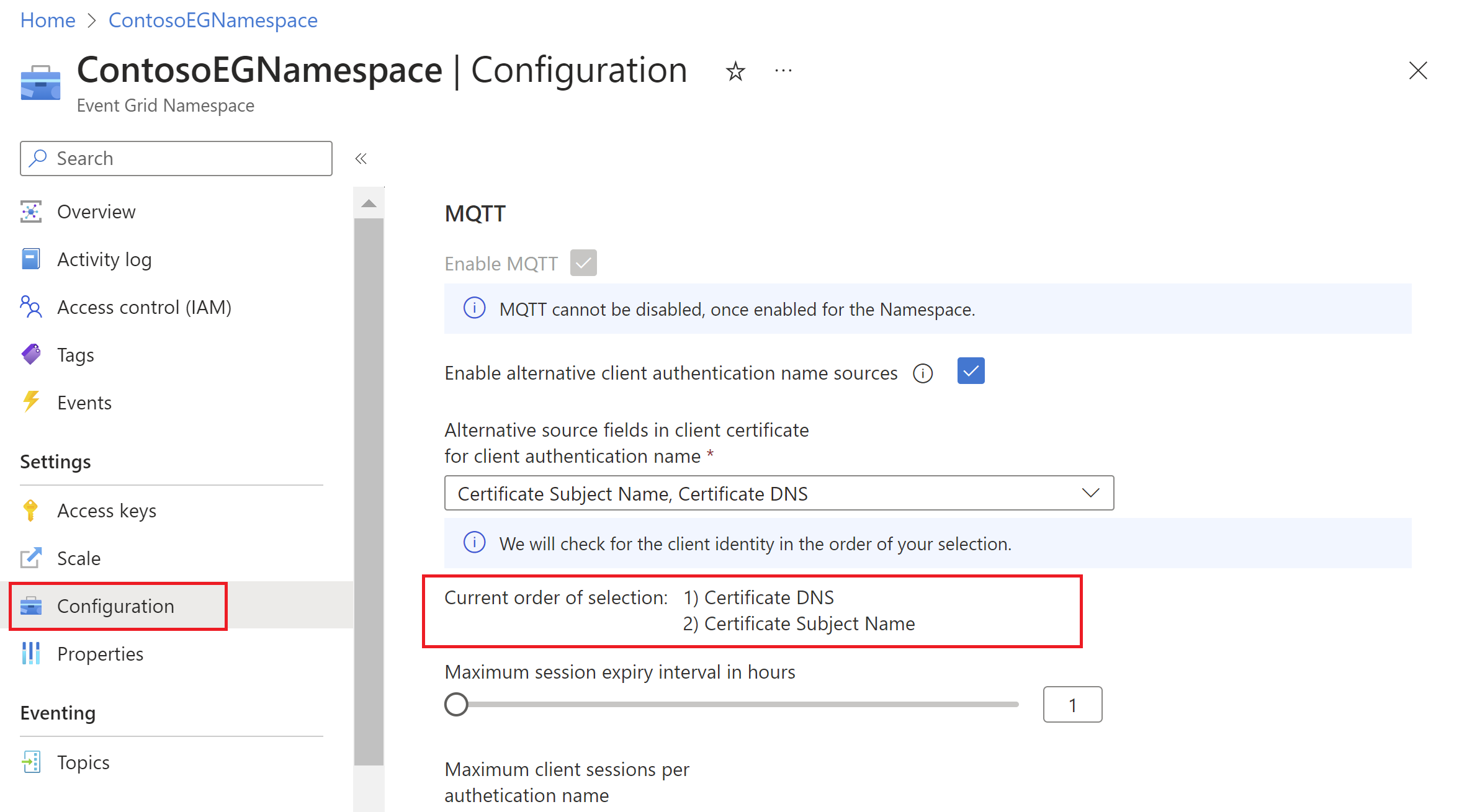
The order of selection of the client certificate fields on the namespace configuration page is important. Service looks for the client authentication name in the client certificate fields in the same order.
For example, if you select the Certificate DNS option first and then the Subject Name option - while authenticating the client connection,
- service checks the subject alternative name DNS field of the client certificate first for the client authentication name
- if the DNS field is empty, then service checks the Subject Name field of the client certificate
- if client authentication name isn't present in either of these two fields, client connection is denied
In both modes of client authentication, we expect the client authentication name to be provided either in the username field of the connect packet or in one of the client certificate fields.
Supported client certificate fields for alternative source of client authentication name
You can use one of the following fields to provide client authentication name in the client certificate.
| Authentication name source option | Certificate field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Certificate Subject Name | tls_client_auth_subject_dn | The subject distinguished name of the certificate. |
| Certificate Dns | tls_client_auth_san_dns | The dNSName SAN entry in the certificate. |
| Certificate Uri | tls_client_auth_san_uri | The uniformResourceIdentifier SAN entry in the certificate. |
| Certificate Ip | tls_client_auth_san_ip | The IPv4 or IPv6 address present in the iPAddress SAN entry in the certificate. |
| Certificate Email | tls_client_auth_san_email | The rfc822Name SAN entry in the certificate. |
Next steps
- Learn how to authenticate clients using certificate chain
- Learn how to authenticate client using Microsoft Entra ID token