Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Schema Registry in Azure Event Hubs has many benefits. Schema Registry helps maintain data consistency, simplify schema evolution, enhance interoperability, and reduce development effort in loosely coupled and event-streaming workflows. Large distributed organizations that employ a centralized repository for schemas can use Schema Registry to achieve highly reliable data processing and governance with little operational overhead.
Schema registries in Azure Event Hubs fulfill many roles in schema-driven event-streaming scenarios:
- Provide a repository where multiple schemas can be registered, managed, and evolved
- Manage schema evolution with multiple compatibility rules
- Perform data validation for all schematized data
- Provide client-side libraries (serializers and deserializers) for producers and consumers
- Improve network throughput efficiency by passing the schema ID instead of the schema definition for every payload
Schema registries in Azure Event Hubs are supported on Standard, Premium, and Dedicated tiers.
Schema registry components
The schema registry is part of the Event Hubs namespace but can also be used with other message or event brokers, including Azure messaging services. It comprises multiple schema groups, which act as a logical grouping of schemas and can be managed independently of other schema groups.
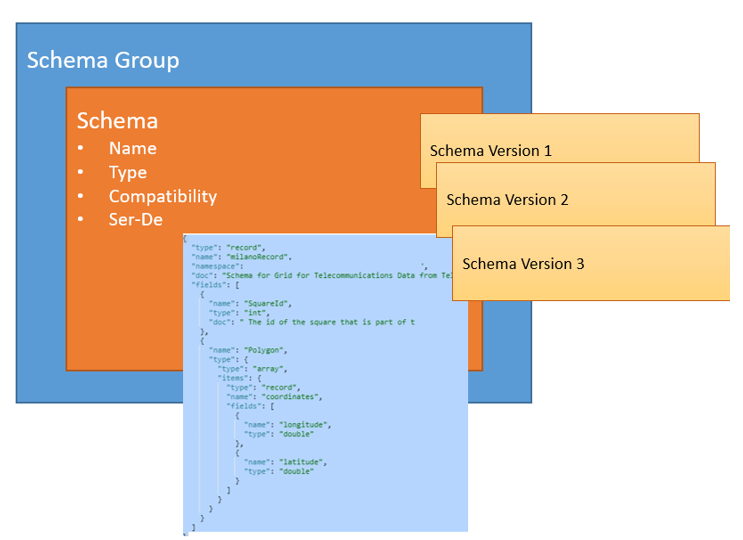
Schemas
In any loosely coupled system, multiple applications communicate, primarily through data. Schemas define the structure of the data in a declarative way. As a result, the contract between producer and consumer applications is well defined, ensuring reliable processing at scale.
A schema definition includes:
- Fields: Individual data elements like name, book title, or address.
- Data types: The type of data that can be stored, like string, date-time, or array.
- Structure: How the fields are organized, like nested structures or arrays.
Schemas define the contract between producers and consumers. A schema defined in an Event Hubs schema registry helps manage the contract outside event data, which removes the payload overhead.
Schema formats
Schema formats are used to determine the manner in which a schema is structured and defined. Each format outlines specific guidelines and syntax for defining the structure of the events that are used for event streaming.
Avro schema
Apache Avro is a popular data serialization system that uses a compact binary format and provides schema evolution capabilities.
To learn more about using Avro schema format with an Event Hubs schema registry, see:
- How to use Schema Registry with Kafka and Avro
- How to use Schema Registry with Event Hubs, .NET, an SDK (AMQP), and Avro
JSON schema
A JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) schema is a standardized way of defining the structure and data types of the events. A JSON schema enables the confident and reliable use of the JSON data format in event streaming.
To learn more about using the JSON schema format with an Event Hubs schema registry, see How to use a schema registry with Kafka and JSON schema.
Protocol Buffers
Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) is a language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data. It's used for efficiently defining data structures and serializing them into a compact binary format.
Schema groups
Schema groups are logical groups of similar schemas that are organized according to your business criteria. A schema group holds:
- Multiple schema definitions.
- Multiple versions of a specific schema.
- Metadata regarding the schema type and compatibility for all schemas in the group.
You can think of a schema group as a subset of the schema registry that aligns with a particular application or organizational unit, with a separate authorization model. This extra security boundary helps ensure that metadata and trade secrets aren't leaked in the shared services model. It also allows application owners to manage schemas independently of other applications that share the same namespace.
Schema evolution
Schemas need to evolve with the business requirement of producers and consumers. Schema Registry supports schema evolution by introducing compatibility modes at the schema group level. When you create a schema group, you can specify the compatibility mode of the schemas that you include in that schema group. When you update a schema, the change needs to comply with the assigned compatibility mode so that it can create a new version of the schema.
Schema evolution is supported for Avro schema format only.
Schema Registry is supported in the following compatibility modes.
Backward compatibility
Backward compatibility mode allows the consumer code to use a new version of a schema and process messages with an old version of the schema. Backward compatibility mode allows the following changes to be made on a schema:
- Delete fields
- Add optional fields
Forward compatibility
Forward compatibility allows the consumer code to use an old schema version and read messages with the new schema. Forward compatibility mode allows the following changes to be made on a schema:
- Add fields
- Delete optional fields
No compatibility
When the None compatibility mode is used, Schema Registry doesn't do any compatibility checks when you update schemas.
Client SDKs
You can use one of the following libraries to include an Avro serializer. You can use Avro serializers to serialize and deserialize payloads that contain schema identifiers for the schema registry and Avro-encoded data:
| Programming language | SDK | Samples |
|---|---|---|
| .NET | Microsoft.Azure.Data.SchemaRegistry.ApacheAvro | .NET Samples |
| Java | azure-data-schemaregistry-avro | Java samples |
| Python | azure-schemaregistry-avroserializer | Python samples |
| JavaScript | @azure/schema-registry-avro | Node.js samples |
Additionally, the below libraries are also available based on your workloads.
- Apache Kafka: Run Kafka-integrated Avro serializers and deserializers backed by Schema Registry. The Java client's Apache Kafka client serializer for Schema Registry can be used in any Apache Kafka scenario and with any Apache Kafka-based deployment or cloud service.
- Azure CLI: For an example of adding a schema to a schema group by using the Azure CLI, see Adding a schema to a schema group by using the Azure CLI.
- PowerShell: For an example of adding a schema to a schema group by using PowerShell, see Adding a schema to a schema group by using PowerShell.
Limits
For limits (like the number of schemas you can use in a namespace) of Event Hubs, see Event Hubs quotas and limits.
Azure role-based access control
To access a schema registry programmatically, follow these steps:
- Register your application in Microsoft Entra ID.
- Add the security principal of the application to one of the following Azure role-based access control (RBAC) roles at the namespace level.
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Owner | Read, write, and delete schema registry groups and schemas |
| Contributor | Read, write, and delete schema registry groups and schemas |
| Schema Registry Reader | Read and list schema registry groups and schemas |
| Schema Registry Contributor | Read, write, and delete schema registry groups and schemas |
To learn how to create and register an application by using the Azure portal, see Register an application with Microsoft Entra ID. You need the client ID (application ID), the tenant ID, and the secret to use in the code.
Related content
- To learn how to create a schema registry by using the Azure portal, see Create an Event Hubs schema registry by using the Azure portal.
- See the following samples from the Schema Registry Avro client library: