Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to add IPv6 support to connect via ExpressRoute to your resources in Azure using the Azure portal.
Note
Some aspects of the portal experience are still being implemented. Therefore, follow the exact order of steps provided in this document to successfully add IPv6 support via the portal. Specifically, make sure to create your virtual network and subnet, or add IPv6 address space to your existing virtual network and GatewaySubnet, prior to creating a new virtual network gateway in the portal.
Sign in to the Azure portal
From a web browser, sign in to the Azure portal.
Add IPv6 Private Peering to your ExpressRoute circuit
Create an ExpressRoute circuit or navigate to the existing circuit you want to change.
Select the Azure private peering configuration.
Add an IPv6 Private Peering to your existing IPv4 Private Peering configuration by selecting "Both" for Subnets, or only enable IPv6 Private Peering on your new circuit by selecting "IPv6". Provide a pair of /126 IPv6 subnets that you own for your primary link and secondary links. From each of these subnets, you assign the first usable IP address to your router as Microsoft uses the second usable IP for its router. Save your peering configuration once you defined all parameters.
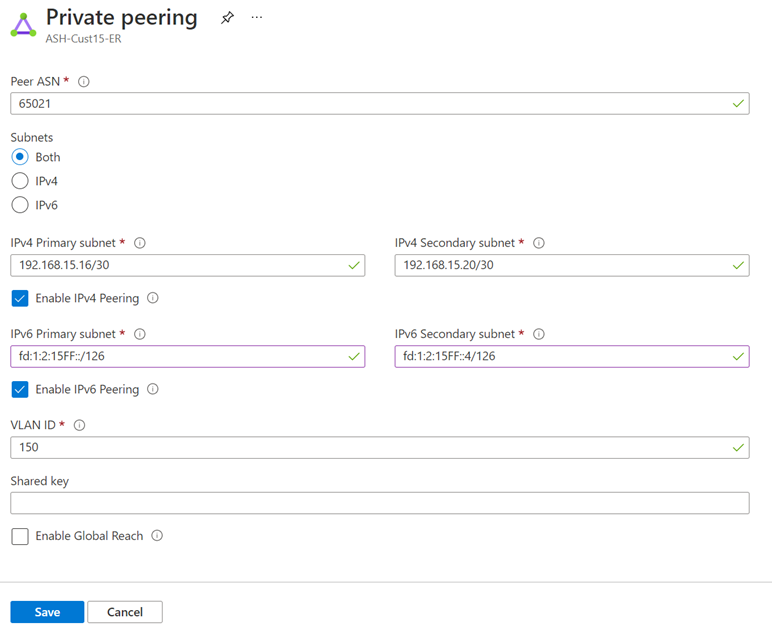
After the configuration is accepted successfully, you should see something similar to the following example.
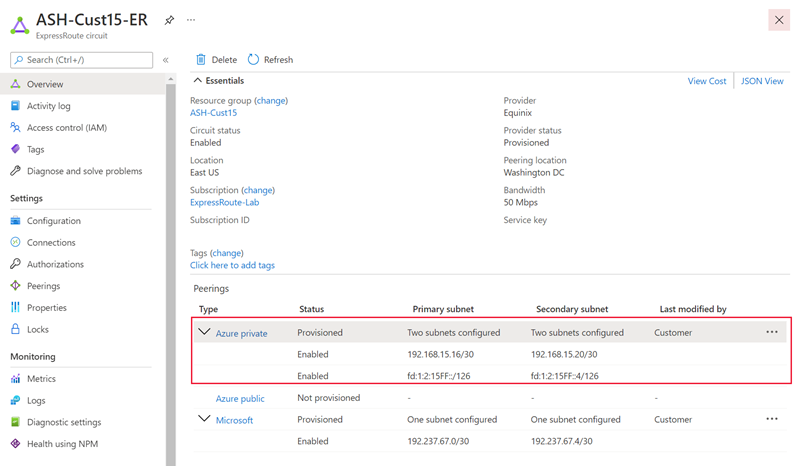
Update your connection to an existing virtual network
Follow these steps if you have an existing environment of Azure resources that you would like to use your IPv6 Private Peering with.
Navigate to the virtual network that your ExpressRoute circuit is connected to.
Navigate to the Address space tab and add an IPv6 address space to your virtual network. Save your address space.

Navigate to the Subnets tab and select the GatewaySubnet. Check Add IPv6 address space and provide an IPv6 address space for your subnet. The gateway IPv6 subnet should be /64 or larger. Save your configuration once you defined all parameters.
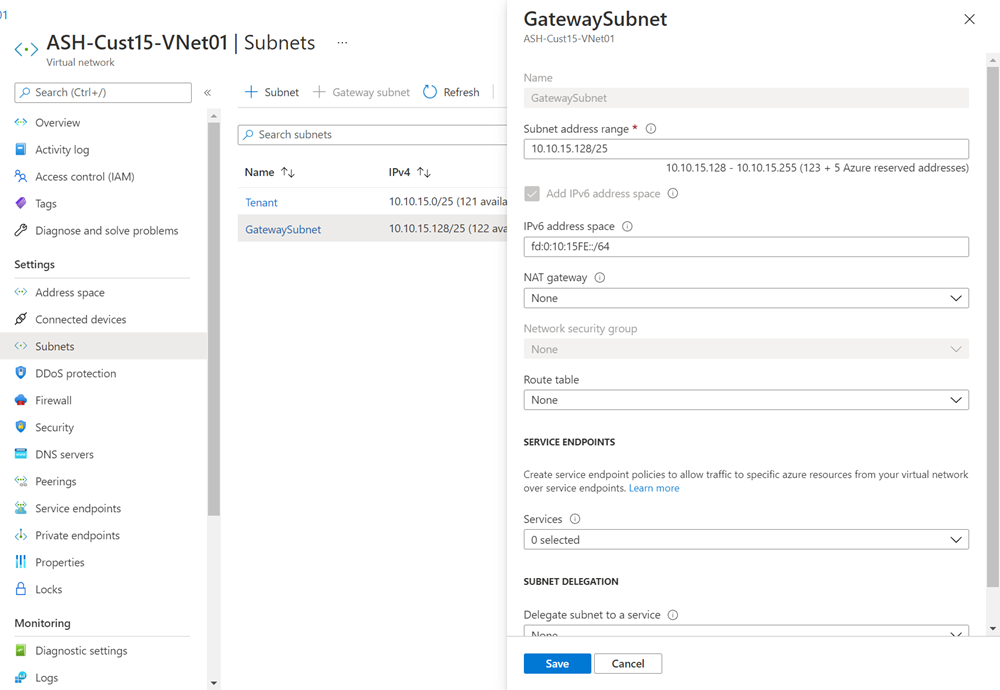
If you have an existing zone-redundant gateway, run the following command in PowerShell to enable IPv6 connectivity (note that it can take up to 1 hour for changes to reflect). Otherwise, create the virtual network gateway using any SKU and a Standard, Static public IP address. If you plan to use FastPath, use UltraPerformance or ErGw3AZ (note that this option is only available for circuits using ExpressRoute Direct).
$gw = Get-AzVirtualNetworkGateway -Name "GatewayName" -ResourceGroupName "ExpressRouteResourceGroup" Set-AzVirtualNetworkGateway -VirtualNetworkGateway $gw
Note
If you have an existing gateway that is not zone-redundant (meaning it is Standard, High Performance, or Ultra Performance SKU) and uses a Basic public IP address, you will need to delete and recreate the gateway using any SKU and a Standard, Static public IP address.
Create a connection to a new virtual network
Follow these steps if you plan to connect to a new set of Azure resources using your IPv6 Private Peering.
Create a dual-stack virtual network with both IPv4 and IPv6 address space. For more information, see Create a virtual network.
Create the virtual network gateway using any SKU and a Standard, Static public IP address. If you plan to use FastPath, use UltraPerformance or ErGw3AZ (note that this option is only available for circuits using ExpressRoute Direct). NOTE: Use the PowerShell instructions for this step as the Azure portal experience is still under development.
Limitations
While IPv6 support is available for connections to deployments in global Azure regions, it doesn't support the following use cases:
- Connections to existing ExpressRoute gateways that aren't zone-redundant. Newly created ExpressRoute gateways of any SKU (both zone-redundant and not) using a Standard, Static IP address can be used for dual-stack ExpressRoute connections
- Use of ExpressRoute with Virtual WAN
- Use of ExpressRoute with Route Server
- FastPath with non-ExpressRoute Direct circuits
- FastPath with circuits in the following peering locations: Dubai
- Coexistence with VPN Gateway for IPv6 traffic. You can still configure coexistence with VPN Gateway in a dual-stack virtual network, but VPN Gateway only supports IPv4 traffic.
- It isn't possible to connect a dual-stack ExpressRoute Virtual Network Gateway to an ExpressRoute Circuit that only has IPv4 enabled on the Private Peering. IPv6 must also be enabled on the ExpressRoute Circuit. You must also configure IPv6 on your on-premises CPE device.
Next steps
To troubleshoot ExpressRoute problems, see the following articles: