Use MirrorMaker 2 to migrate Kafka clusters between different Azure HDInsight versions
Learn how to use Apache Kafka's mirroring feature to replicate topics to a secondary cluster. You can run mirroring as a continuous process, or intermittently, to migrate data from one cluster to another.
In this article, you use mirroring to replicate topics between two HDInsight clusters. These clusters are in different virtual networks in different datacenters.
Note
- We can use mirroring cluster as a fault tolerance.
- This is valid only is primary cluster HDI Kafka 2.4.1, 3.2.0 and secondary cluster is HDI Kafka 3.2.0 versions.
- Secondary cluster would work seamlessly if your primary cluster went down.
- Consumer group offsets will be automatically translated to secondary cluster.
- Just point your primary cluster consumers to secondary cluster with same consumer group and your consumer group will start consuming from the offset where it left in primary cluster.
- The only difference would be that the topic name in backup cluster will change from TOPIC_NAME to primary-cluster-name.TOPIC_NAME.
How Apache Kafka mirroring works
Mirroring works by using the MirrorMaker2 tool, which is part of Apache Kafka. MirrorMaker consumes records from topics on the primary cluster, and then creates a local copy on the secondary cluster. MirrorMaker2 uses one (or more) consumers that read from the primary cluster, and a producer that writes to the local (secondary) cluster.
The most useful mirroring setup for disaster recovery uses Kafka clusters in different Azure regions. To achieve this result, the virtual networks where the clusters reside peered together.
The primary and secondary clusters can be different in the number of nodes and partitions, and offsets within the topics are different also. Mirroring maintains the key value that used for partitioning, so record order preserved on a per-key basis.
Mirroring across network boundaries
If you need to mirror between Kafka clusters in different networks, there are the following more considerations:
Gateways: The networks must be able to communicate at the TCP/IP level.
Server addressing: You can choose to address your cluster nodes by using their IP addresses or fully qualified domain names.
IP addresses: If you configure your Kafka clusters to use IP address advertising, you can proceed with the mirroring setup by using the IP addresses of the broker nodes and ZooKeeper nodes.
Domain names: If you don't configure your Kafka clusters for IP address advertising, the clusters must be able to connect to each other by using fully qualified domain names (FQDNs). This requires a domain name system (DNS) server in each network that configured to forward requests to the other networks. When you're creating an Azure virtual network, instead of using the automatic DNS provided with the network, you must specify a custom DNS server and the IP address for the server. After you create the virtual network, you must then create an Azure virtual machine that uses that IP address. Then you install and configure DNS software on it.
Important
Create and configure the custom DNS server before installing HDInsight into the virtual network. There is no additional configuration required for HDInsight to use the DNS server configured for the virtual network.
For more information on connecting two Azure virtual networks, see Configure a connection.
Mirroring architecture
This architecture features two clusters in different resource groups and virtual networks: a primary and a secondary.
Creation steps
Create two new resource groups:
Resource group Location kafka-primary-rg Central US kafka-secondary-rg North Central US Create a new virtual network kafka-primary-vnet in kafka-primary-rg. Leave the default settings.
Create a new virtual network kafka-secondary-vnet in kafka-secondary-rg, also with default settings.
Note
Keep the address of both vnet nonoverlapping otherwise vnet peering won't work. Example:
- kafka-primary-vnet can have address space 10.0.0.0
- kafka-secondary-vnet can have address space 10.1.0.0
Create virtual network peerings. This step creates two peerings: one from kafka-primary-vnet to kafka-secondary-vnet, and one back from kafka-secondary-vnet to kafka-primary-vnet.
Select the kafka-primary-vnet virtual network.
Under Settings, select Peerings.
Select Add.
On the Add peering screen, enter the details as shown in the following screenshot.
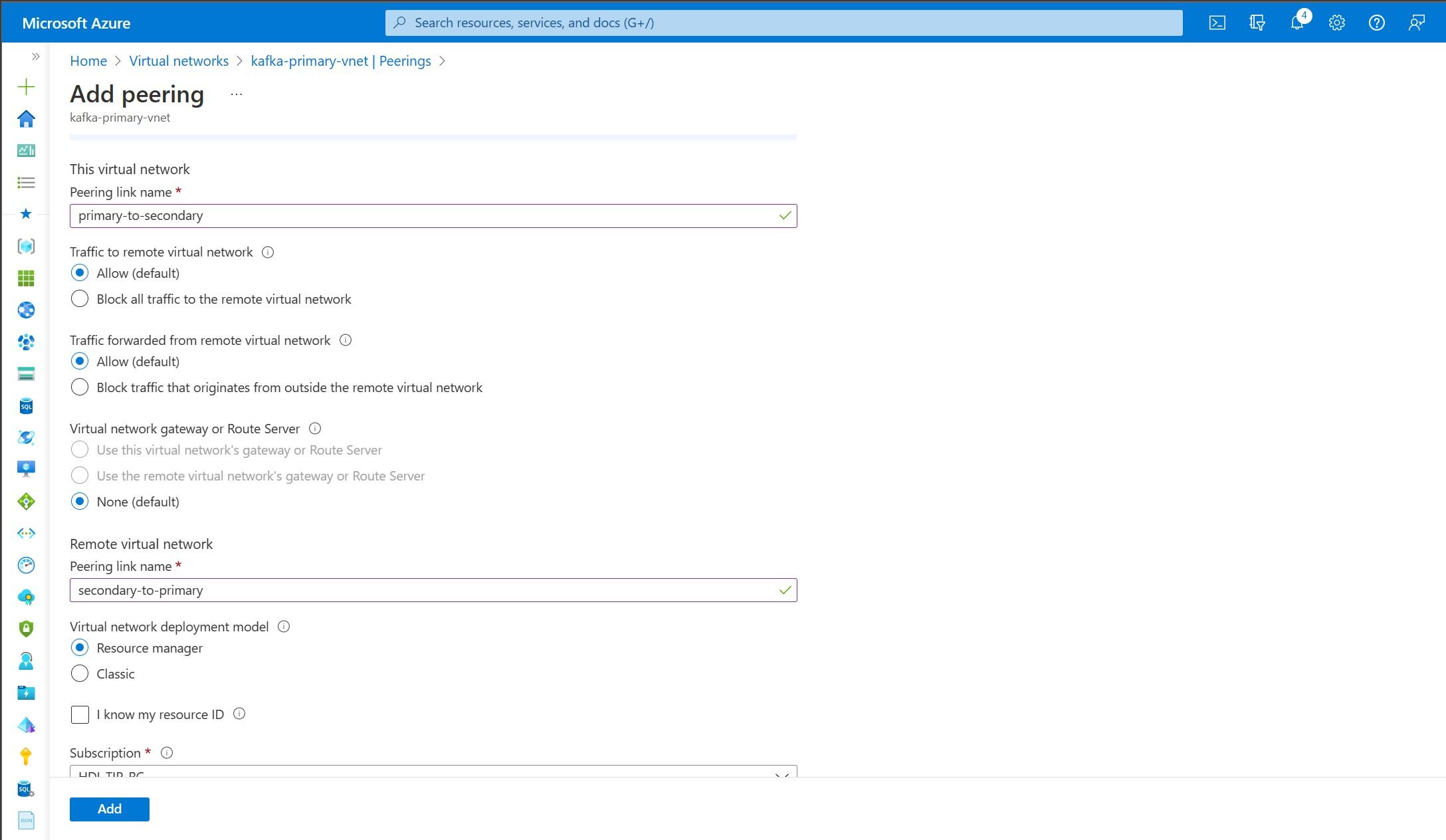
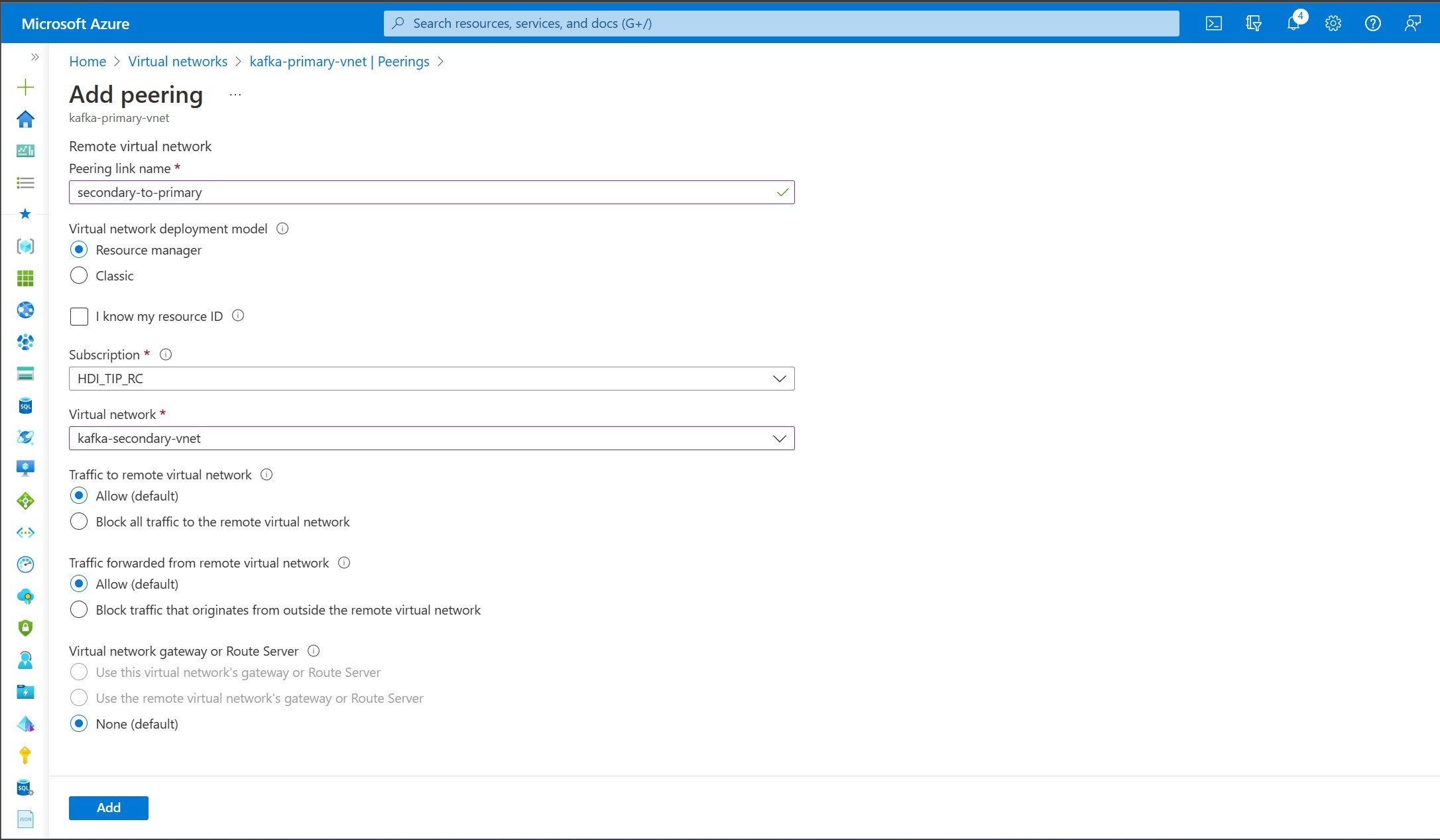
Create two new Kafka clusters:
Cluster name HDInsight version Resource group Virtual network Storage account primary-kafka-cluster 5.0 kafka-primary-rg kafka-primary-vnet kafkaprimarystorage secondary-kafka-cluster 5.1 kafka-secondary-rg kafka-secondary-vnet kafkasecondarystorage Note
From now onwards we will use
primary-kafka-clusterasPRIMARYCLUSTERandsecondary-kafka-clusterasSECONDARYCLUSTER.
Configure IP address of PRIMARYCLUSTER worker nodes into client machine for DNS resolution
Use head node of
SECONDARYCLUSTERto run mirror maker script. Then we need IP address of worker nodes of PRIMARYCLUSTER in/etc/hostsfile ofSECONDARYCLUSTER.Connect to
PRIMARYCLUSTERssh sshuser@PRIMARYCLUSTER-ssh.azurehdinsight.netExecute the following command and get the entries of worker nodes IPs and FQDNs
cat /etc/hostsCopy those entries and connect to
SECONDARYCLUSTERand runssh sshuser@SECONDARYCLUSTER-ssh.azurehdinsight.net`Edit the
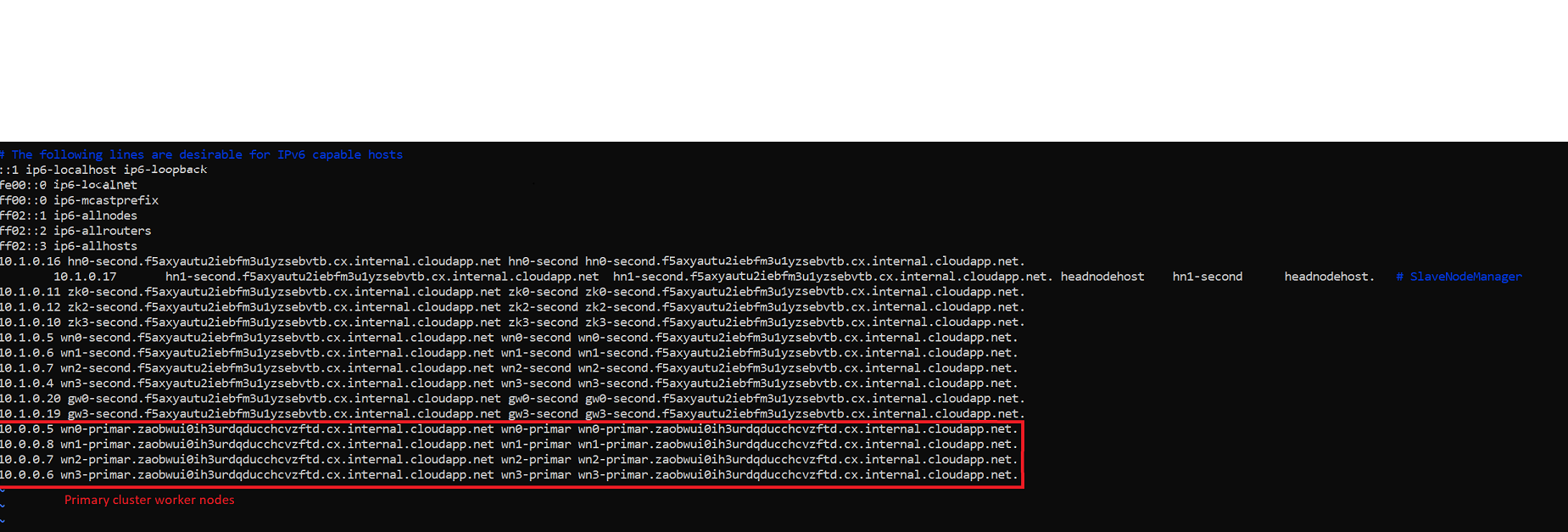
/etc/hostsfile of secondary cluster and add those entries here.After you making the changes, the
/etc/hostsfile forSECONDARYCLUSTERlooks like the given image.Save and close the file.
Create multiple topics in PRIMARYCLUSTER
Use this command to create topics and replace variables.
bash /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper $KAFKAZKHOSTS --create --topic $TOPICNAME --partitions $NUM_PARTITIONS --replication-factor $REPLICATION_FACTOR
Configure MirrorMaker2 in SECONDARYCLUSTER
Now change the configuration in MirrorMaker2 properties file.
Execute following command with admin privilege
sudo su vi /etc/kafka/conf/connect-mirror-maker.propertiesNote
This article contains references to a term that Microsoft no longer uses. When the term is removed from the software, we’ll remove it from this article.
Property file looks like this.
# specify any number of cluster aliases clusters = source, destination # connection information for each cluster # This is a comma separated host:port pairs for each cluster # for example. "A_host1:9092, A_host2:9092, A_host3:9092" and you can see the exact host name on Ambari > Hosts source.bootstrap.servers = wn0-src kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn1-src-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn2-src-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092 destination.bootstrap.servers = wn0-dest-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn1-dest-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn2-dest-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092 # enable and configure individual replication flows source->destination.enabled = true # regex which defines which topics gets replicated. For eg "foo-.*" source->destination.topics = .* groups=.* topics.blacklist="*.internal,__.*" # Setting replication factor of newly created remote topics Replication.factor=3 checkpoints.topic.replication.factor=1 heartbeats.topic.replication.factor=1 offset-syncs.topic.replication.factor=1 offset.storage.replication.factor=1 status.storage.replication.factor=1 config.storage.replication.factor=1Here source is your
PRIMARYCLUSTERand destination is yourSECONDARYCLUSTR. Replace it everywhere with correct name and replacesource.bootstrap.serversanddestination.bootstrap.serverswith correct FQDN or IP of their respective worker nodes.You can use regular expressions to specify the topics and their configurations that you want to replicate. By setting the
replication.factorparameter to 3, you can ensure that all topics created by the MirrorMaker script hsd a replication factor of 3.Increase the replication factor from 1 to 3 for these topics
checkpoints.topic.replication.factor=1 heartbeats.topic.replication.factor=1 offset-syncs.topic.replication.factor=1 offset.storage.replication.factor=1 status.storage.replication.factor=1 config.storage.replication.factor=1Note
The reason being default insync replica for all the topics at the broker level is 2. Keeping replication factor=1, will throw exception while running mirrormaker2
You need to Enable Auto Topic Creation functionality and then mirror maker script replicates topics with the name as
PRIMARYCLUSTER.TOPICNAMEand same configs in secondary cluster. Save the file and we're good with configs.If you want to mirror topics on both sides, like
Primary to SecondaryandSecondary to Primary(active-active) then you can add extra configsdestination->source.enabled=true destination->source.topics = .*For automated consumer offset sync, we need to enable replication and control the sync duration too. Following property syncs offset every 30 second. For active-active scenario, we need to do it both ways.
groups=.* emit.checkpoints.enabled = true source->destination.sync.group.offsets.enabled = true source->destination.sync.group.offsets.interval.ms=30000 destination->source.sync.group.offsets.enabled = true destination->source.sync.group.offsets.interval.ms=30000If we don’t want to replicate internal topics across clusters, then use following property
topics.blacklist="*.internal,__.*"Final Configuration file after changes should look like this
# specify any number of cluster aliases clusters = primary-kafka-cluster, secondary-kafka-cluster # connection information for each cluster # This is a comma separated host:port pairs for each cluster # for example. "A_host1:9092, A_host2:9092, A_host3:9092" and you can see the exact host name on Ambari -> Hosts primary-kafka-cluster.bootstrap.servers = wn0-src-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn1-src-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn2-src-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092 secondary-kafka-cluster.bootstrap.servers = wn0-dest-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn1-dest-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092,wn2-dest-kafka.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9092 # enable and configure individual replication flows primary-kafka-cluster->secondary-kafka-cluster.enabled = true # enable this for both side replication secondary-kafka-cluster->primary-kafka-cluster.enabled = true # regex which defines which topics gets replicated. For eg "foo-.*" primary-kafka-cluster->secondary-kafka-cluster.topics = .* secondary-kafka-cluster->primary-kafka-cluster.topics = .* groups=.* emit.checkpoints.enabled = true primary-kafka-cluster->secondary-kafka-cluster.sync.group.offsets.enabled=true primary-kafka-cluster->secondary-kafka-cluster.sync.group.offsets.interval.ms=30000 secondary-kafka-cluster->primary-kafka-cluster.sync.group.offsets.enabled = true secondary-kafka-cluster->primary-kafka-cluster.sync.group.offsets.interval.ms=30000 topics.blacklist="*.internal,__.*" # Setting replication factor of newly created remote topics Replication.factor=3 checkpoints.topic.replication.factor=3 heartbeats.topic.replication.factor=3 offset-syncs.topic.replication.factor=3 offset.storage.replication.factor=3 status.storage.replication.factor=3 config.storage.replication.factor=3Start Mirror Maker2 in
SECONDARYCLUSTERand it should run fine/usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker ./bin/connect-mirror-maker.sh ./config/connect-mirror-maker.propertiesNow start producer in
PRIMARYCLUSTERexport clusterName='primary-kafka-cluster' export TOPICNAME='TestMirrorMakerTopic' export KAFKABROKERS='wn0-primar:9092' export KAFKAZKHOSTS='zk0-primar:2181' //Start Producer # For Kafka 2.4 bash /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --zookeeper $KAFKAZKHOSTS --topic $TOPICNAME # For Kafka 3.2 bash /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --boostrap-server $KAFKABROKERS --topic $TOPICNAMENow start the consumer in PRIMARYCLUSTER with a consumer group
//Start Consumer # For Kafka 2.4 bash /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper $KAFKAZKHOSTS --topic $TOPICNAME -–group my-group –-from- beginning # For Kafka 3.2 bash /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --boostrap-server $KAFKABROKERS --topic $TOPICNAME -–group my-group –-from-beginningNow stop the consumer in PRIMARYCONSUMER and start consumer in SECONDARYCLUSTER with same consumer group
export clusterName='secondary-kafka-cluster' export TOPICNAME='primary-kafka-cluster.TestMirrorMakerTopic' export KAFKABROKERS='wn0-second:9092' export KAFKAZKHOSTS='zk0-second:2181' # List all the topics whether they're replicated or not bash /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper $KAFKAZKHOSTS --list # Start Consumer bash /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server $KAFKABROKERS --topic $TOPICNAME --from-beginningYou can notice that in secondary cluster consumer group my-group cant't consume any messages because, already consumed by primary cluster consumer group. Now produce more messages in primary-cluster and try to consumer then in secondary-cluster. You are able to consume from
SECONDARYCLUSTER.
Delete cluster
Warning
Billing for HDInsight clusters is prorated per minute, whether you use them or not. Be sure to delete your cluster after you finish using it. See how to delete an HDInsight cluster.
The steps in this article created clusters in different Azure resource groups. To delete all the resources created, you can delete the two resource groups created: kafka-primary-rg and kafka-secondary-rg. Deleting the resource groups removes all of the resources created by following this article, including clusters, virtual networks, and storage accounts.
Next steps
In this article, you learned how to use MirrorMaker2 to create a replica of an Apache Kafka cluster.
Use the following links to discover other ways to work with Kafka: