Get started with IoT Hub module identity and module twin (C)
Module identities and module twins are similar to Azure IoT Hub device identity and device twin, but provide finer granularity. While Azure IoT Hub device identity and device twin enable the back-end application to configure a device and provides visibility on the device's conditions, a module identity and module twin provide these capabilities for individual components of a device. On capable devices with multiple components, such as operating system devices or firmware devices, it allows for isolated configuration and conditions for each component.
Note
The features described in this article are available only in the standard tier of IoT Hub. For more information about the basic and standard/free IoT Hub tiers, see Choose the right IoT Hub tier for your solution.
At the end of this article, you have two C apps:
CreateIdentities: creates a device identity, a module identity and associated security key to connect your device and module clients.
UpdateModuleTwinReportedProperties: sends updated module twin, reported properties to your IoT Hub.
Note
See Azure IoT SDKs for more information about the SDK tools available to build both device and back-end apps.
Prerequisites
An IoT hub. Create one with the CLI or the Azure portal.
The latest Azure IoT C SDK.
Get the IoT hub connection string
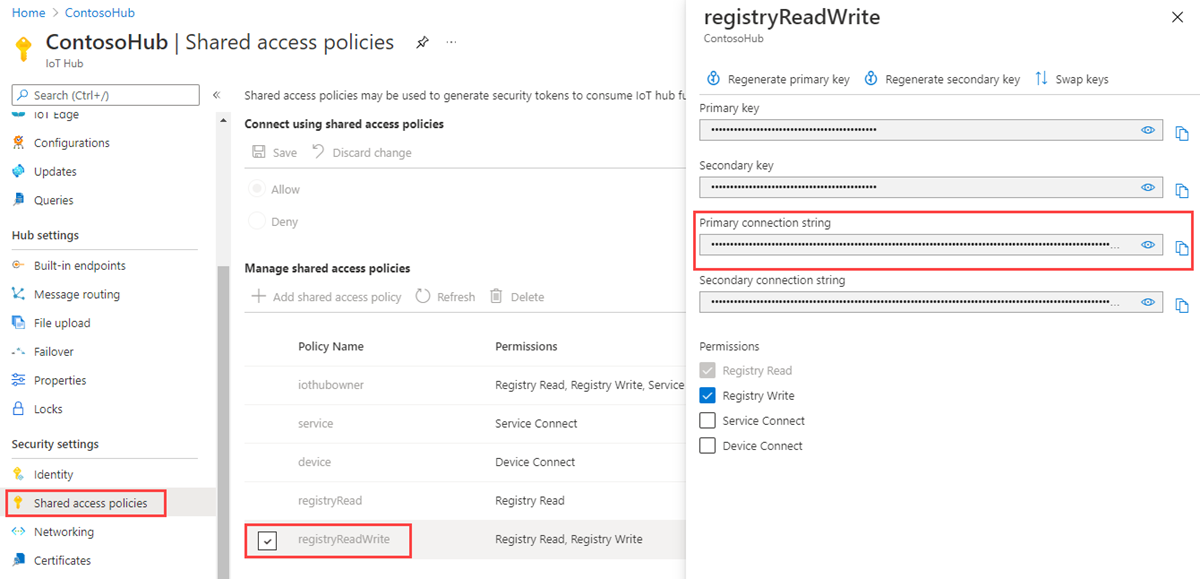
In this article, you create a back-end service that adds a device in the identity registry and then adds a module to that device. Your service requires the registry write permission. By default, every IoT hub is created with a shared access policy named registryReadWrite that grants this permission.
To get the IoT Hub connection string for the registryReadWrite policy, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, select Resource groups. Select the resource group where your hub is located, and then select your hub from the list of resources.
On the left-side pane of your hub, select Shared access policies.
From the list of policies, select the registryReadWrite policy.
Copy the Primary connection string and save the value.
For more information about IoT Hub shared access policies and permissions, see Access control and permissions.
Create a device identity and a module identity in IoT Hub
In this section, you create a C app that creates a device identity and a module identity in the identity registry in your IoT hub. A device or module can't connect to IoT hub unless it has an entry in the identity registry. For more information, see Understand the identity registry in your IoT hub. When you run this console app, it generates a unique ID and key for both device and module. Your device and module use these values to identify itself when it sends device-to-cloud messages to IoT Hub. The IDs are case-sensitive.
Add the following code to your C file:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "azure_c_shared_utility/crt_abstractions.h"
#include "azure_c_shared_utility/threadapi.h"
#include "azure_c_shared_utility/platform.h"
#include "iothub_service_client_auth.h"
#include "iothub_registrymanager.h"
static const char* hubConnectionString ="[your hub's connection string]"; // modify
static void createDevice(IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_HANDLE
iotHubRegistryManagerHandle, const char* deviceId)
{
IOTHUB_REGISTRY_DEVICE_CREATE_EX deviceCreateInfo;
IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_RESULT result;
(void)memset(&deviceCreateInfo, 0, sizeof(deviceCreateInfo));
deviceCreateInfo.version = 1;
deviceCreateInfo.deviceId = deviceId;
deviceCreateInfo.primaryKey = "";
deviceCreateInfo.secondaryKey = "";
deviceCreateInfo.authMethod = IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_AUTH_SPK;
IOTHUB_DEVICE_EX deviceInfoEx;
memset(&deviceInfoEx, 0, sizeof(deviceInfoEx));
deviceInfoEx.version = 1;
// Create device
result = IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateDevice_Ex(iotHubRegistryManagerHandle,
&deviceCreateInfo, &deviceInfoEx);
if (result == IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_OK)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateDevice: Device has been created successfully: deviceId=%s, primaryKey=%s\n", deviceInfoEx.deviceId, deviceInfoEx.primaryKey);
}
else if (result == IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_DEVICE_EXIST)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateDevice: Device already exists\n");
}
else if (result == IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_ERROR)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateDevice failed\n");
}
// You will need to Free the returned device information after it was created
IoTHubRegistryManager_FreeDeviceExMembers(&deviceInfoEx);
}
static void createModule(IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_HANDLE iotHubRegistryManagerHandle, const char* deviceId, const char* moduleId)
{
IOTHUB_REGISTRY_MODULE_CREATE moduleCreateInfo;
IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_RESULT result;
(void)memset(&moduleCreateInfo, 0, sizeof(moduleCreateInfo));
moduleCreateInfo.version = 1;
moduleCreateInfo.deviceId = deviceId;
moduleCreateInfo.moduleId = moduleId;
moduleCreateInfo.primaryKey = "";
moduleCreateInfo.secondaryKey = "";
moduleCreateInfo.authMethod = IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_AUTH_SPK;
IOTHUB_MODULE moduleInfo;
memset(&moduleInfo, 0, sizeof(moduleInfo));
moduleInfo.version = 1;
// Create module
result = IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateModule(iotHubRegistryManagerHandle, &moduleCreateInfo, &moduleInfo);
if (result == IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_OK)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateModule: Module has been created successfully: deviceId=%s, moduleId=%s, primaryKey=%s\n", moduleInfo.deviceId, moduleInfo.moduleId, moduleInfo.primaryKey);
}
else if (result == IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_DEVICE_EXIST)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateModule: Module already exists\n");
}
else if (result == IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_ERROR)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubRegistryManager_CreateModule failed\n");
}
// You will need to Free the returned module information after it was created
IoTHubRegistryManager_FreeModuleMembers(&moduleInfo);
}
int main(void)
{
(void)platform_init();
const char* deviceId = "myFirstDevice";
const char* moduleId = "myFirstModule";
IOTHUB_SERVICE_CLIENT_AUTH_HANDLE iotHubServiceClientHandle = NULL;
IOTHUB_REGISTRYMANAGER_HANDLE iotHubRegistryManagerHandle = NULL;
if ((iotHubServiceClientHandle = IoTHubServiceClientAuth_CreateFromConnectionString(hubConnectionString)) == NULL)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubServiceClientAuth_CreateFromConnectionString failed\n");
}
else if ((iotHubRegistryManagerHandle = IoTHubRegistryManager_Create(iotHubServiceClientHandle)) == NULL)
{
(void)printf("IoTHubServiceClientAuth_CreateFromConnectionString failed\n");
}
else
{
createDevice(iotHubRegistryManagerHandle, deviceId);
createModule(iotHubRegistryManagerHandle, deviceId, moduleId);
}
if (iotHubRegistryManagerHandle != NULL)
{
(void)printf("Calling IoTHubRegistryManager_Destroy...\n");
IoTHubRegistryManager_Destroy(iotHubRegistryManagerHandle);
}
if (iotHubServiceClientHandle != NULL)
{
(void)printf("Calling IoTHubServiceClientAuth_Destroy...\n");
IoTHubServiceClientAuth_Destroy(iotHubServiceClientHandle);
}
platform_deinit();
return 0;
}
This app creates a device identity with ID myFirstDevice and a module identity with ID myFirstModule under device myFirstDevice. (If that module ID already exists in the identity registry, the code simply retrieves the existing module information.) The app then displays the primary key for that identity. You use this key in the simulated module app to connect to your IoT hub.
Note
The IoT Hub identity registry only stores device and module identities to enable secure access to the IoT hub. The identity registry stores device IDs and keys to use as security credentials. The identity registry also stores an enabled/disabled flag for each device that you can use to disable access for that device. If your application needs to store other device-specific metadata, it should use an application-specific store. There is no enabled/disabled flag for module identities. For more information, see IoT Hub developer guide.
Update the module twin using C device SDK
In this section, you create a C app on your simulated device that updates the module twin reported properties.
Get your module connection string. In the Azure portal, navigate to your IoT hub and select IoT devices. Find myFirstDevice, open it and you see myFirstModule was successfully created. Copy the module connection string. It is needed in the next step.
Create UpdateModuleTwinReportedProperties app
Add the following to your C file:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "azure_c_shared_utility/crt_abstractions.h" #include "azure_c_shared_utility/threadapi.h" #include "azure_c_shared_utility/platform.h" #include "iothub_service_client_auth.h" #include "iothub_devicetwin.h" const char* deviceId = "bugbash-test-2"; const char* moduleId = "module-id-1"; static const char* hubConnectionString ="[your hub's connection string]"; // modify const char* testJson = "{\"properties\":{\"desired\":{\"integer_property\": b-1234, \"string_property\": \"abcd\"}}}"; int main(void) { (void)platform_init(); IOTHUB_SERVICE_CLIENT_AUTH_HANDLE iotHubServiceClientHandle = NULL; IOTHUB_SERVICE_CLIENT_DEVICE_TWIN_HANDLE iothubDeviceTwinHandle = NULL; if ((iotHubServiceClientHandle = IoTHubServiceClientAuth_CreateFromConnectionString(moduleConnectionString)) == NULL) { (void)printf("IoTHubServiceClientAuth_CreateFromConnectionString failed\n"); } else if ((iothubDeviceTwinHandle = IoTHubDeviceTwin_Create(iotHubServiceClientHandle)) == NULL) { (void)printf("IoTHubServiceClientAuth_CreateFromConnectionString failed\n"); } else { char *result = IoTHubDeviceTwin_UpdateModuleTwin(iothubDeviceTwinHandle, deviceId, moduleId, testJson); printf("IoTHubDeviceTwin_UpdateModuleTwin returned %s\n", result); } if (iothubDeviceTwinHandle != NULL) { (void)printf("Calling IoTHubDeviceTwin_Destroy...\n"); IoTHubDeviceTwin_Destroy(iothubDeviceTwinHandle); } if (iotHubServiceClientHandle != NULL) { (void)printf("Calling IoTHubServiceClientAuth_Destroy...\n"); IoTHubServiceClientAuth_Destroy(iotHubServiceClientHandle); } platform_deinit(); return 0; }
This code sample shows you how to retrieve the module twin and update reported properties.
Get updates on the device side
In addition to the previous code, you can add the following code block to get the twin update message on your device:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "azure_c_shared_utility/crt_abstractions.h"
#include "azure_c_shared_utility/macro_utils.h"
#include "azure_c_shared_utility/threadapi.h"
#include "azure_c_shared_utility/platform.h"
#include "iothub_module_client_ll.h"
#include "iothub_client_options.h"
#include "iothub_message.h"
// The protocol you wish to use should be uncommented
//
//#define SAMPLE_MQTT
//#define SAMPLE_MQTT_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
#define SAMPLE_AMQP
//#define SAMPLE_AMQP_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
//#define SAMPLE_HTTP
#ifdef SAMPLE_MQTT
#include "iothubtransportmqtt.h"
#endif // SAMPLE_MQTT
#ifdef SAMPLE_MQTT_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
#include "iothubtransportmqtt_websockets.h"
#endif // SAMPLE_MQTT_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
#ifdef SAMPLE_AMQP
#include "iothubtransportamqp.h"
#endif // SAMPLE_AMQP
#ifdef SAMPLE_AMQP_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
#include "iothubtransportamqp_websockets.h"
#endif // SAMPLE_AMQP_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
#ifdef SAMPLE_HTTP
#include "iothubtransporthttp.h"
#endif // SAMPLE_HTTP
/* Paste in the your iothub connection string */
static const char* connectionString = "[Fill in connection string]";
static bool g_continueRunning;
#define DOWORK_LOOP_NUM 3
static void deviceTwinCallback(DEVICE_TWIN_UPDATE_STATE update_state, const unsigned char* payLoad, size_t size, void* userContextCallback)
{
(void)userContextCallback;
printf("Device Twin update received (state=%s, size=%zu): %s\r\n",
MU_ENUM_TO_STRING(DEVICE_TWIN_UPDATE_STATE, update_state), size, payLoad);
}
static void reportedStateCallback(int status_code, void* userContextCallback)
{
(void)userContextCallback;
printf("Device Twin reported properties update completed with result: %d\r\n", status_code);
g_continueRunning = false;
}
void iothub_module_client_sample_device_twin_run(void)
{
IOTHUB_CLIENT_TRANSPORT_PROVIDER protocol;
IOTHUB_MODULE_CLIENT_LL_HANDLE iotHubModuleClientHandle;
g_continueRunning = true;
// Select the Protocol to use with the connection
#ifdef SAMPLE_MQTT
protocol = MQTT_Protocol;
#endif // SAMPLE_MQTT
#ifdef SAMPLE_MQTT_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
protocol = MQTT_WebSocket_Protocol;
#endif // SAMPLE_MQTT_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
#ifdef SAMPLE_AMQP
protocol = AMQP_Protocol;
#endif // SAMPLE_AMQP
#ifdef SAMPLE_AMQP_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
protocol = AMQP_Protocol_over_WebSocketsTls;
#endif // SAMPLE_AMQP_OVER_WEBSOCKETS
#ifdef SAMPLE_HTTP
protocol = HTTP_Protocol;
#endif // SAMPLE_HTTP
if (platform_init() != 0)
{
(void)printf("Failed to initialize the platform.\r\n");
}
else
{
if ((iotHubModuleClientHandle = IoTHubModuleClient_LL_CreateFromConnectionString(connectionString, protocol)) == NULL)
{
(void)printf("ERROR: iotHubModuleClientHandle is NULL!\r\n");
}
else
{
bool traceOn = true;
const char* reportedState = "{ 'device_property': 'new_value'}";
size_t reportedStateSize = strlen(reportedState);
(void)IoTHubModuleClient_LL_SetOption(iotHubModuleClientHandle, OPTION_LOG_TRACE, &traceOn);
// Check the return of all API calls when developing your solution. Return checks omitted for sample simplification.
(void)IoTHubModuleClient_LL_SetModuleTwinCallback(iotHubModuleClientHandle, deviceTwinCallback, iotHubModuleClientHandle);
(void)IoTHubModuleClient_LL_SendReportedState(iotHubModuleClientHandle, (const unsigned char*)reportedState, reportedStateSize, reportedStateCallback, iotHubModuleClientHandle);
do
{
IoTHubModuleClient_LL_DoWork(iotHubModuleClientHandle);
ThreadAPI_Sleep(1);
} while (g_continueRunning);
for (size_t index = 0; index < DOWORK_LOOP_NUM; index++)
{
IoTHubModuleClient_LL_DoWork(iotHubModuleClientHandle);
ThreadAPI_Sleep(1);
}
IoTHubModuleClient_LL_Destroy(iotHubModuleClientHandle);
}
platform_deinit();
}
}
int main(void)
{
iothub_module_client_sample_device_twin_run();
return 0;
}
Next steps
To continue getting started with IoT Hub and to explore other IoT scenarios, see:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for