Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to create a load test for an Azure App Service web app with Azure Load Testing. Directly create a URL-based load test from your app service in the Azure portal, and then use the load testing dashboard to analyze performance issues and identify bottlenecks.
With the integrated load testing experience in Azure App Service, you can:
- Create a URL-based load test for the app service endpoint or a deployment slot
- View the test runs associated with the app service
- Create a load testing resource
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
- An Azure App Service web app. If you need to create a web app, see the App Service Getting started documentation.
Create a load test for a web app
You can create load test directly from your Azure App Service web app in the Azure portal. You can either create by entering your HTTP requests directly in portal or by uploading a JMeter or Locust test script.
To create a load test for a web app:
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure App Service web app.
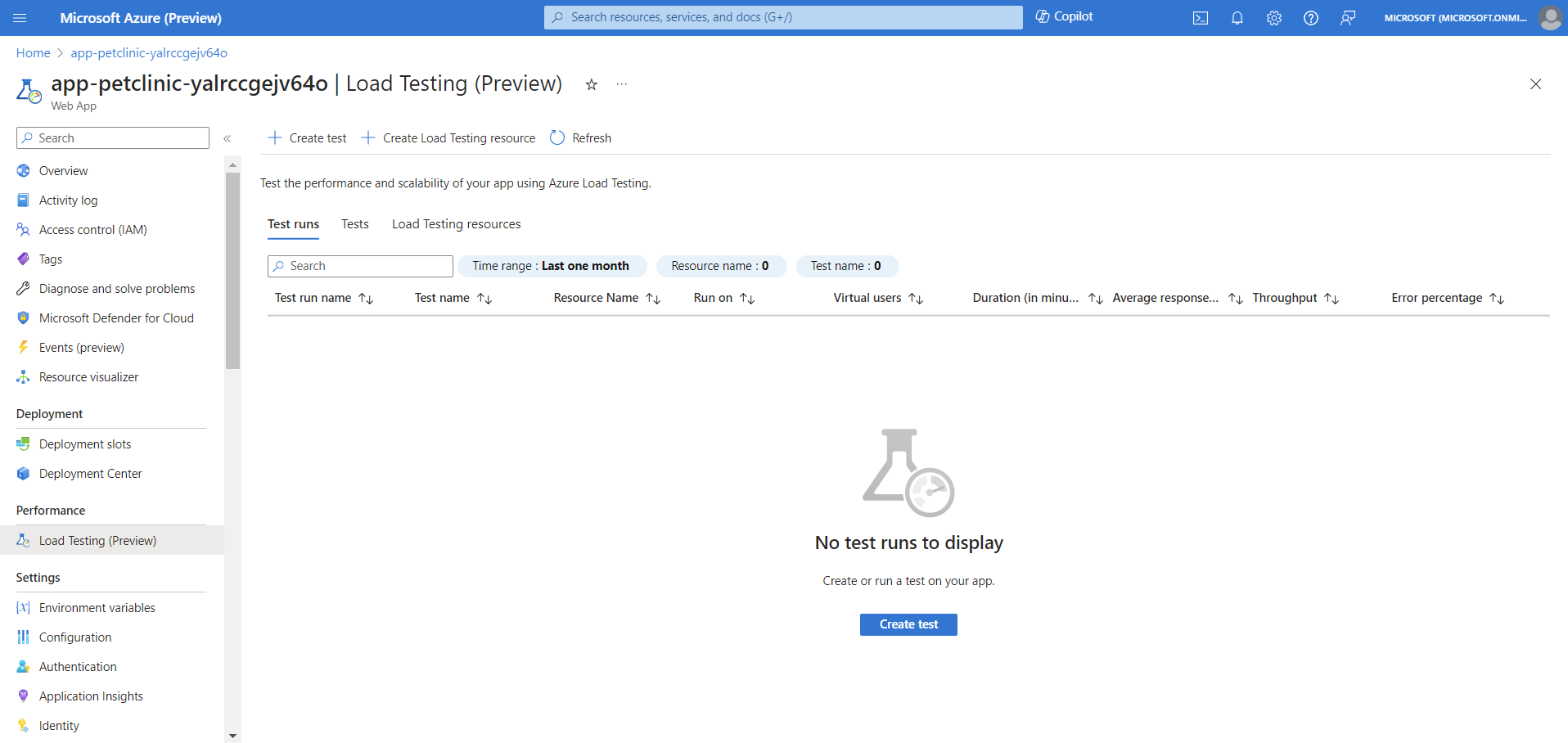
On the left pane, select Load Testing under the Performance section.
On this page, you can see the list of tests and the load test runs for this web app.
Select Create test to start load test for the web app. Select Create a URL-based test if you don't have a test script. Select Upload a script if you have a JMeter or Locust test script.
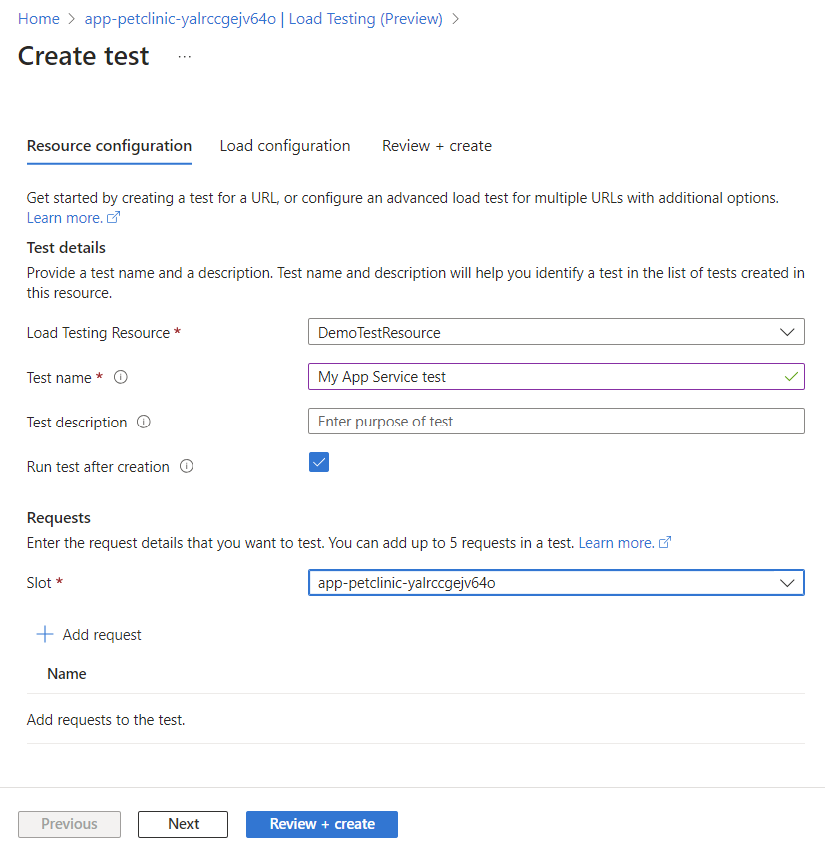
On the Create test page, first enter the test details:
Field Description Load Testing Resource Select your load testing resource. Create new if you don't have one in the Azure subscription. Test name Enter a unique test name. Test description (Optional) Enter a load test description. Run test after creation When selected, the load test starts automatically after creating the test. If you have multiple deployment slots for the web app, select the Slot against which to run the load test.
For a URL-based test, select Add request to add HTTP requests to the load test:
On the Add request page, enter the details for the request:
Field Description Request name Unique name within the load test to identify the request. You can use this request name when defining test criteria. URL Select the base URL for the web endpoint Path (Optional) Enter a URL path name within the web endpoint. The path is appended to the URL to form the endpoint that is load tested. HTTP method Select an HTTP method from the list. Azure Load Testing supports GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, HEAD, and OPTIONS. Query parameters (Optional) Enter query string parameters to append to the URL. Headers (Optional) Enter HTTP headers to include in the HTTP request. Body (Optional) Depending on the HTTP method, you can specify the HTTP body content. Azure Load Testing supports the following formats: raw data, JSON view, JavaScript, HTML, and XML. Learn more about adding HTTP requests to a load test.
For a script-based test, upload your test script in the Test plan tab. Learn more about creating a test by uploading a test script.
After entering all the required details, select Review + create to review the test configuration, and then select Create to create the load test.
Azure Load Testing now creates the load test. If you selected Run test after creation previously, the load test starts automatically.
Note
If the test was converted from a URL test to a JMX test directly from the Load Testing resource, the test cannot be modified from the App Service.
View test runs
You can view the list of test runs and a summary overview of the test results directly from within the web app configuration in the Azure portal.
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure App Service web app.
On the left pane, select Load testing.
In the Test runs tab, you can view the list of test runs for your web app.
For each test run, you can view the test details and a summary of the test outcome, such as average response time, throughput, and error state.
Select a test run to go to the Azure Load Testing dashboard and analyze the test run details.
Next steps
- Learn more about load testing Azure App Service applications.