Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
To handle interactive Azure Machine Learning notebook data wrangling, Azure Machine Learning integration with Azure Synapse Analytics provides easy access to the Apache Spark framework. This access allows for Azure Machine Learning Notebook interactive data wrangling.
In this quickstart guide, you learn how to perform interactive data wrangling with Azure Machine Learning serverless Spark compute, Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 storage account, and user identity passthrough.
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription; if you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you start.
- An Azure Machine Learning workspace. Visit Create workspace resources.
- An Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 storage account. Visit Create an Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 storage account.
Store Azure storage account credentials as secrets in Azure Key Vault
To store Azure storage account credentials as secrets in the Azure Key Vault, with the Azure portal user interface:
Navigate to your Azure Key Vault in the Azure portal
Select Secrets from the left panel
Select + Generate/Import
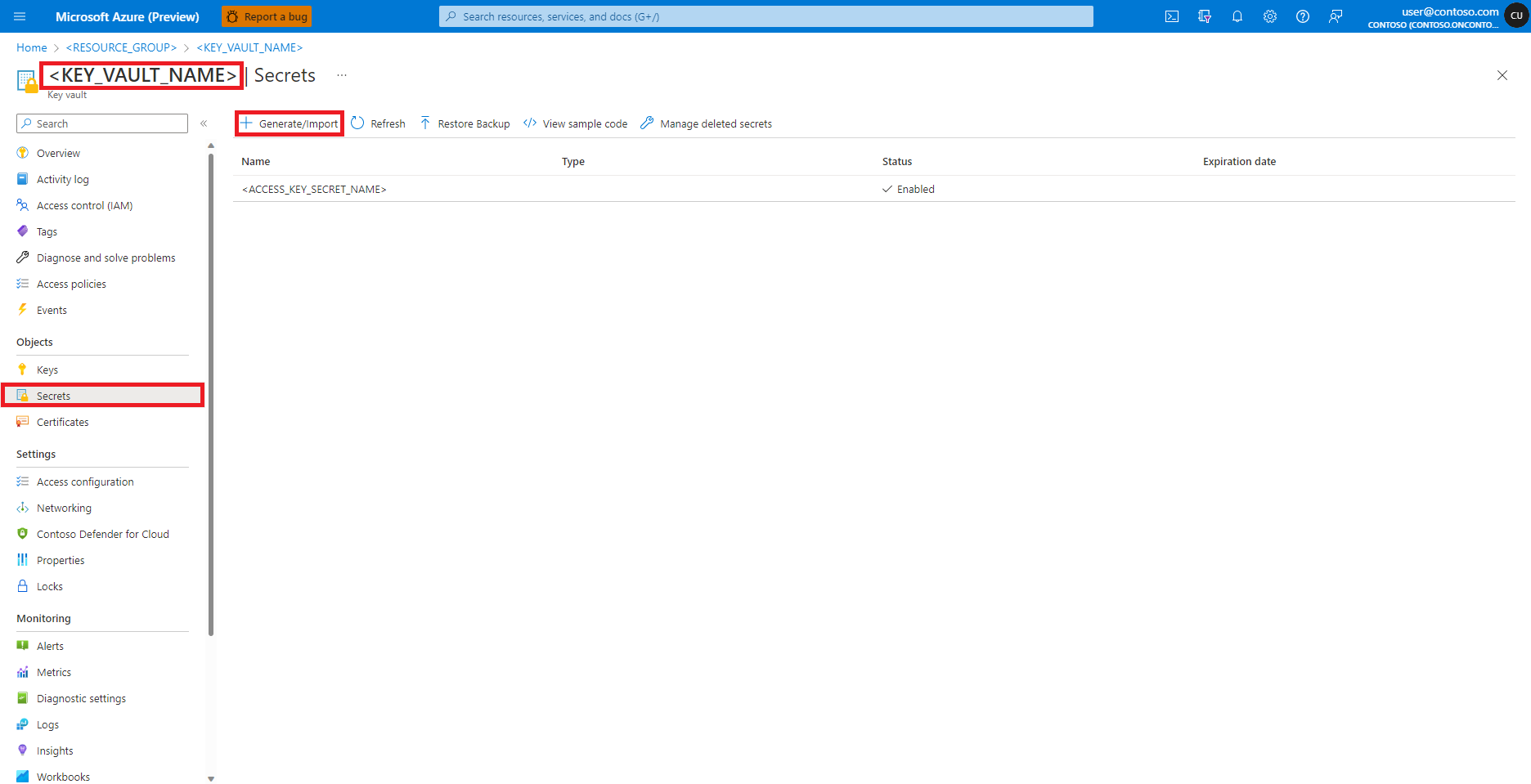
At the Create a secret screen, enter a Name for the secret you want to create
Navigate to Azure Blob Storage Account, in the Azure portal, as shown in this image:
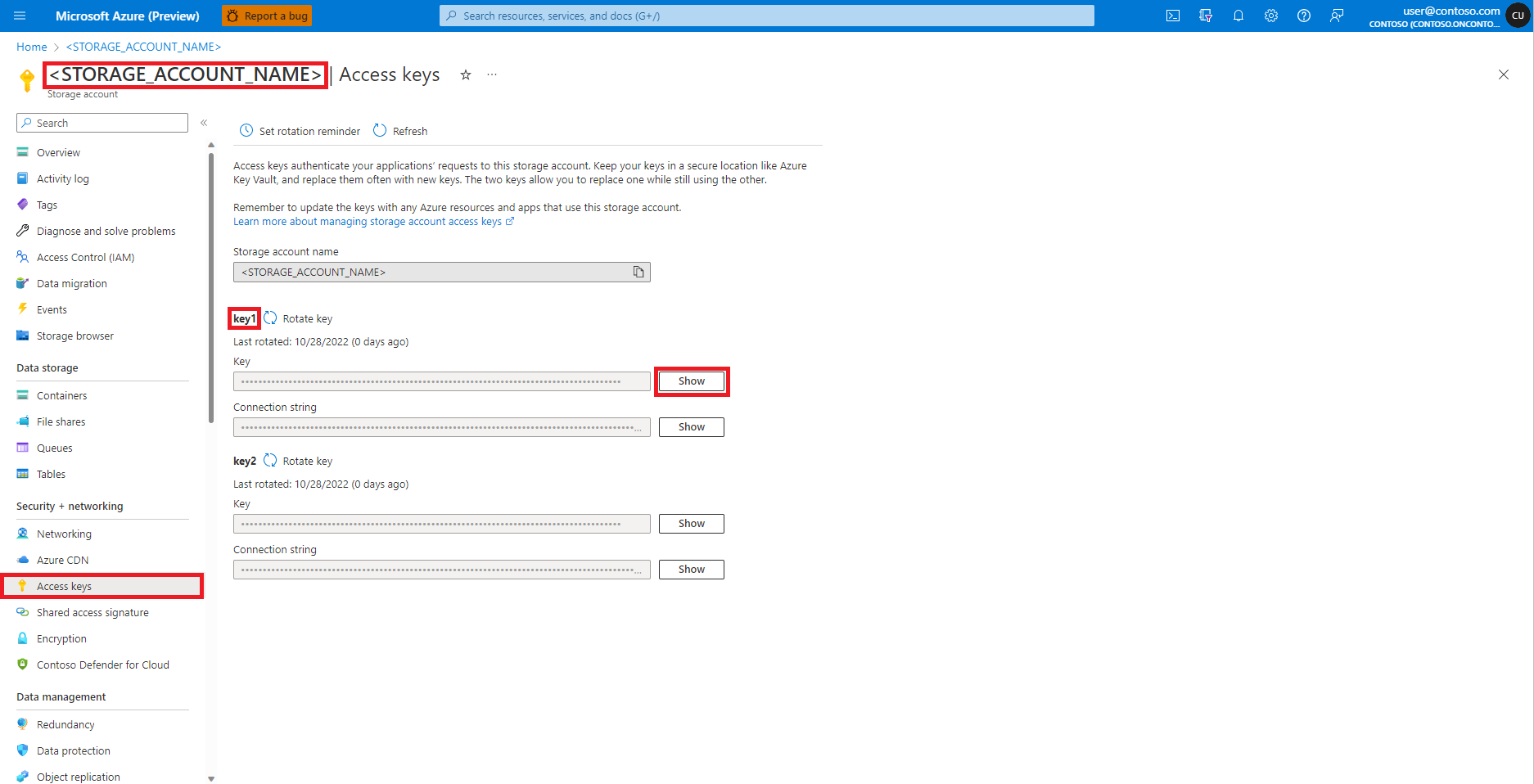
Select Access keys from the Azure Blob Storage Account page left panel
Select Show next to Key 1, and then Copy to clipboard to get the storage account access key
Note
Select the appropriate options to copy
- Azure Blob storage container shared access signature (SAS) tokens
- Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 storage account service principal credentials
- tenant ID
- client ID and
- secret
on the respective user interfaces while you create the Azure Key Vault secrets for them
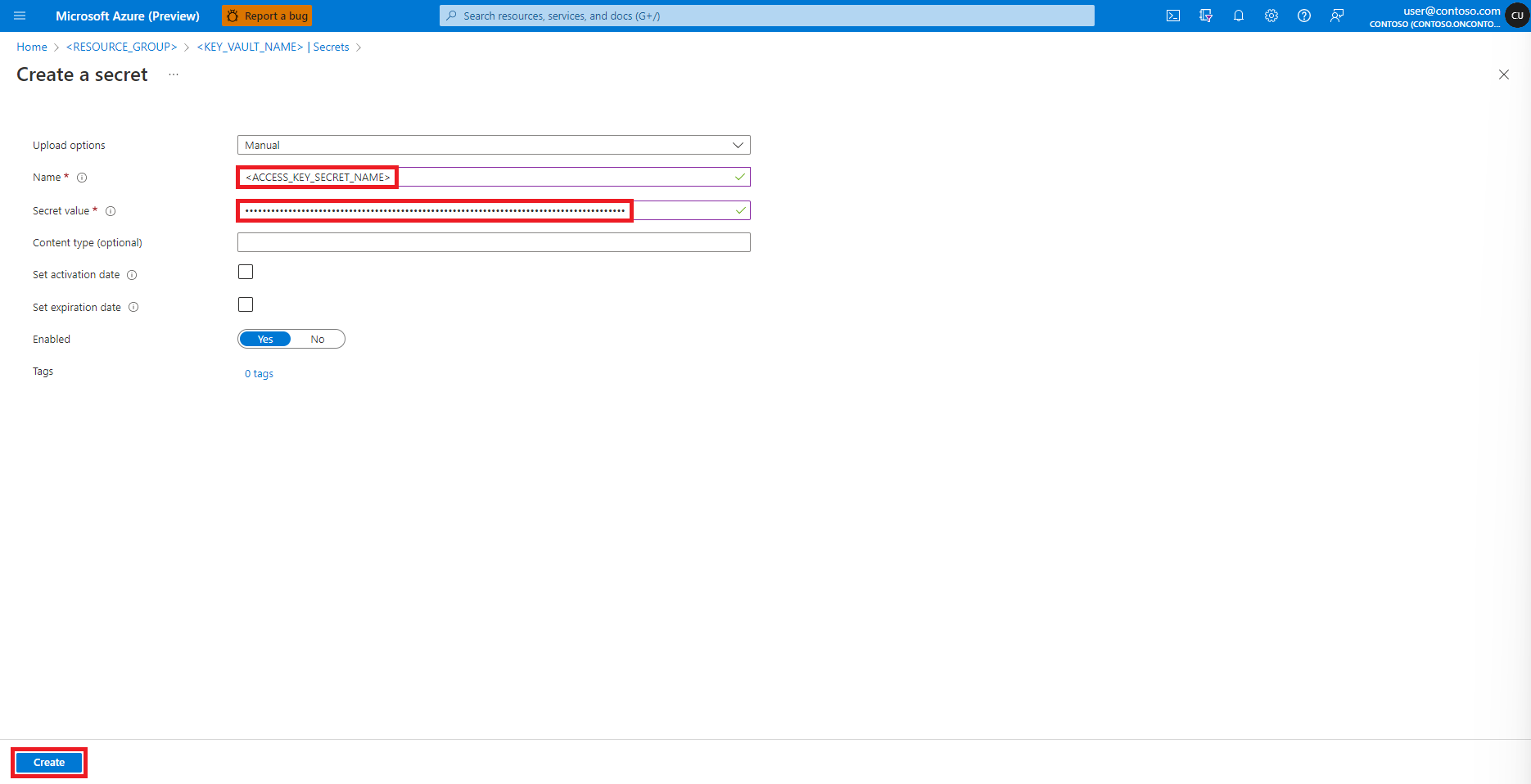
Navigate back to the Create a secret screen
In the Secret value textbox, enter the access key credential for the Azure storage account, which was copied to the clipboard in the earlier step
Select Create
Tip
Azure CLI and Azure Key Vault secret client library for Python can also create Azure Key Vault secrets.
Add role assignments in Azure storage accounts
We must ensure that the input and output data paths are accessible before we start interactive data wrangling. First, for
the user identity of the Notebooks session logged-in user
or
a service principal
assign Reader and Storage Blob Data Reader roles to the user identity of the logged-in user. However, in certain scenarios, we might want to write the wrangled data back to the Azure storage account. The Reader and Storage Blob Data Reader roles provide read-only access to the user identity or service principal. To enable read and write access, assign Contributor and Storage Blob Data Contributor roles to the user identity or service principal. To assign appropriate roles to the user identity:
Open the Microsoft Azure portal
Search and select the Storage accounts service
On the Storage accounts page, select the Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 storage account from the list. A page showing the storage account Overview opens
Select Access Control (IAM) from the left panel
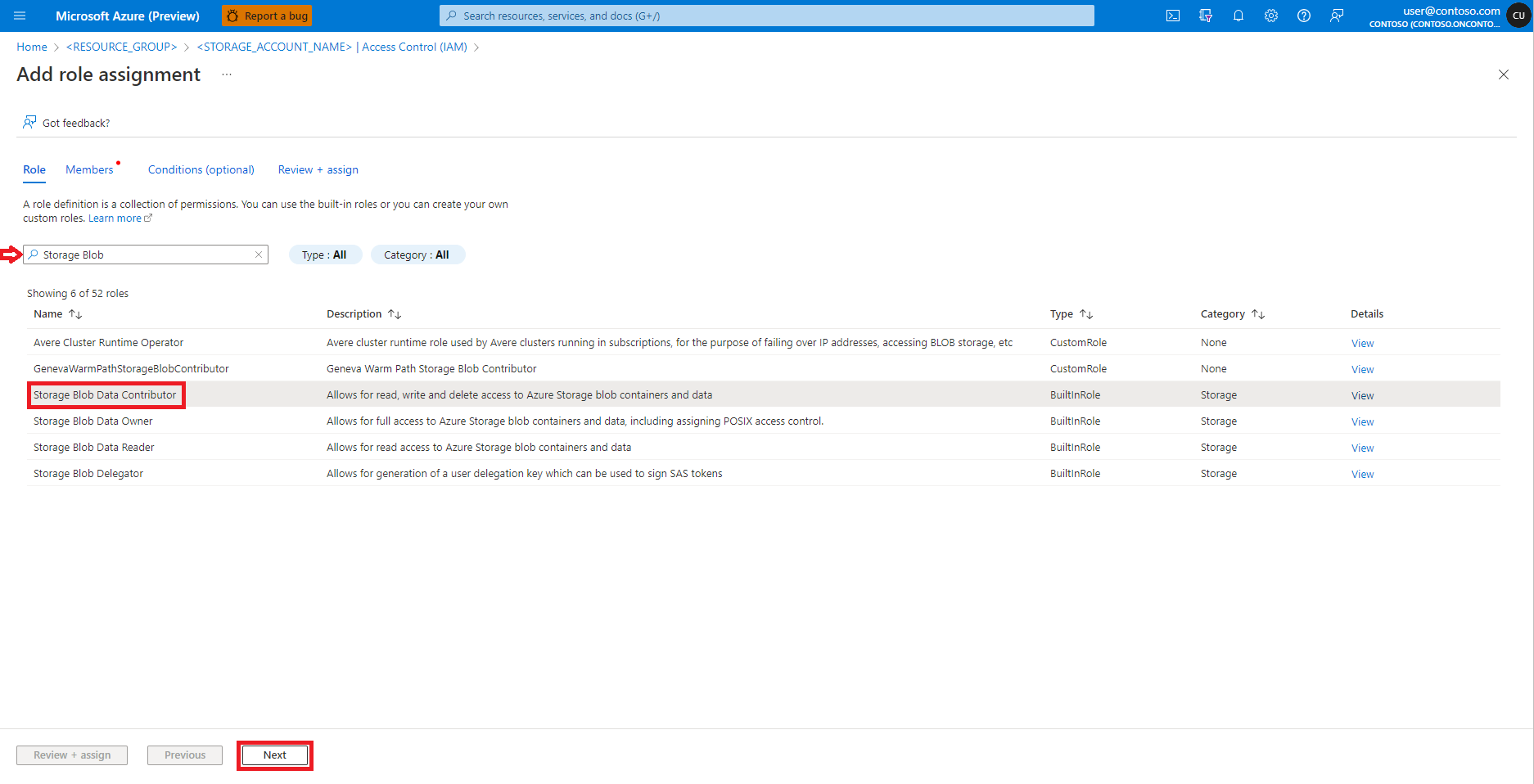
Select Add role assignment
Find and select role Storage Blob Data Contributor
Select Next
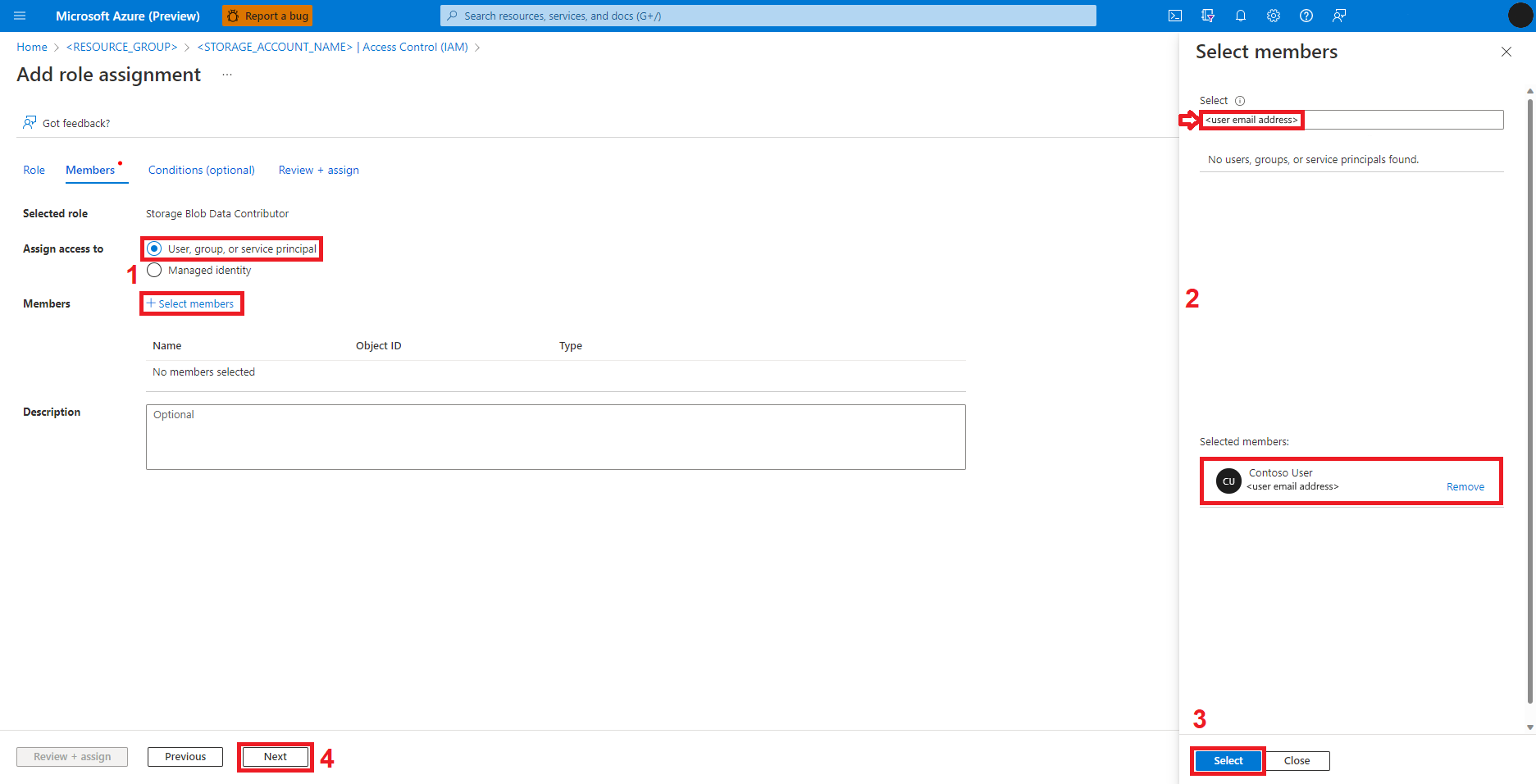
Select User, group, or service principal
Select + Select members
Search for the user identity below Select
Select the user identity from the list, so that it shows under Selected members
Select the appropriate user identity
Select Next
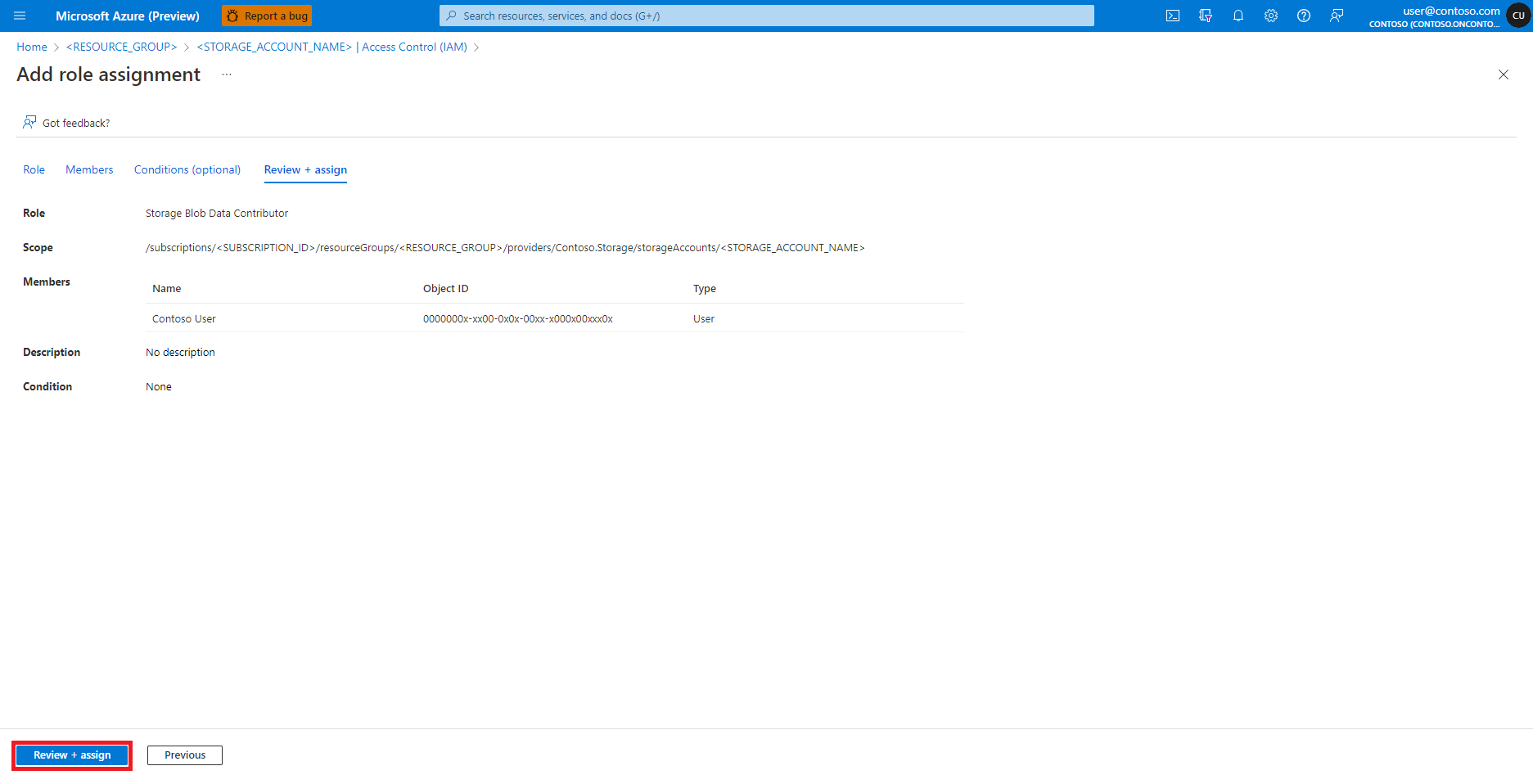
Select Review + Assign
Repeat steps 2-13 for Contributor role assignment
Once the user identity has the appropriate roles assigned, data in the Azure storage account should become accessible.
Note
If an attached Synapse Spark pool points to a Synapse Spark pool, in an Azure Synapse workspace, that has a managed virtual network associated with it, you should configure a managed private endpoint to a storage account to ensure data access.
Ensuring resource access for Spark jobs
To access data and other resources, Spark jobs can use either a managed identity or user identity passthrough. The following table summarizes the different mechanisms for resource access while you use Azure Machine Learning serverless Spark compute and attached Synapse Spark pool.
| Spark pool | Supported identities | Default identity |
|---|---|---|
| Serverless Spark compute | User identity, user-assigned managed identity attached to the workspace | User identity |
| Attached Synapse Spark pool | User identity, user-assigned managed identity attached to the attached Synapse Spark pool, system-assigned managed identity of the attached Synapse Spark pool | System-assigned managed identity of the attached Synapse Spark pool |
If the CLI or SDK code defines an option to use managed identity, Azure Machine Learning serverless Spark compute relies on a user-assigned managed identity attached to the workspace. You can attach a user-assigned managed identity to an existing Azure Machine Learning workspace with Azure Machine Learning CLI v2, or with ARMClient.
Next steps
- Apache Spark in Azure Machine Learning
- Attach and manage a Synapse Spark pool in Azure Machine Learning
- Interactive Data Wrangling with Apache Spark in Azure Machine Learning
- Submit Spark jobs in Azure Machine Learning
- Code samples for Spark jobs using Azure Machine Learning CLI
- Code samples for Spark jobs using Azure Machine Learning Python SDK