Train with MLflow Projects in Azure Machine Learning (preview)
In this article, learn how to submit training jobs with MLflow Projects that use Azure Machine Learning workspaces for tracking. You can submit jobs and only track them with Azure Machine Learning or migrate your runs to the cloud to run completely on Azure Machine Learning Compute.
Warning
Support for MLproject files (MLflow Projects) in Azure Machine Learning will be fully retired in September 2026. MLflow is still fully supported and is still the recommended way to track machine learning workloads in Azure Machine Learning.
As you continue to use MLflow, we recommend that you transition from MLproject files to Azure Machine Learning Jobs, using either the Azure CLI or the Azure Machine Learning SDK for Python (v2). For more information on Azure Machine Learning jobs, see Track ML experiments and models with MLflow.
MLflow Projects allow for you to organize and describe your code to let other data scientists (or automated tools) run it. MLflow Projects with Azure Machine Learning enable you to track and manage your training runs in your workspace.
Important
This feature is currently in public preview. This preview version is provided without a service-level agreement, and we don't recommend it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities.
For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Learn more about the MLflow and Azure Machine Learning integration.
Prerequisites
Install the MLflow SDK package
mlflowand the Azure Machine Learning plug-in for MLflowazureml-mlflow.pip install mlflow azureml-mlflowTip
You can use the
mlflow-skinnypackage, which is a lightweight MLflow package without SQL storage, server, UI, or data science dependencies.mlflow-skinnyis recommended for users who primarily need MLflow's tracking and logging capabilities without importing the full suite of features including deployments.An Azure Machine Learning workspace. You can create one by following the Create machine learning resources tutorial.
If you're performing remote tracking (that is, tracking experiments that are running outside Azure Machine Learning), configure MLflow to point to the tracking URI of your Azure Machine Learning workspace. For more information on how to connect MLflow to your workspace, see Configure MLflow for Azure Machine Learning.
Using Azure Machine Learning as backend for MLflow projects requires the package
azureml-core:pip install azureml-core
Connect to your workspace
If you're working outside Azure Machine Learning, you need to configure MLflow to point to your Azure Machine Learning workspace's tracking URI. You can find the instructions at Configure MLflow for Azure Machine Learning.
Track MLflow Projects in Azure Machine Learning workspaces
This example shows how to submit MLflow projects and track them Azure Machine Learning.
Add the
azureml-mlflowpackage as a pip dependency to your environment configuration file in order to track metrics and key artifacts in your workspace.conda.yaml
name: mlflow-example channels: - defaults dependencies: - numpy>=1.14.3 - pandas>=1.0.0 - scikit-learn - pip: - mlflow - azureml-mlflowSubmit the local run and ensure you set the parameter
backend = "azureml", which adds support of automatic tracking, model's capture, log files, snapshots, and printed errors in your workspace. In this example we assume the MLflow project you are trying to run is in the same folder you currently are,uri=".".mlflow run . --experiment-name --backend azureml --env-manager=local -P alpha=0.3View your runs and metrics in the Azure Machine Learning studio.
Train MLflow projects in Azure Machine Learning jobs
This example shows how to submit MLflow projects as a job running on Azure Machine Learning compute.
Create the backend configuration object, in this case we are going to indicate
COMPUTE. This parameter references the name of your remote compute cluster you want to use for running your project. IfCOMPUTEis present, the project will be automatically submitted as an Azure Machine Learning job to the indicated compute.backend_config.json
{ "COMPUTE": "cpu-cluster" }Add the
azureml-mlflowpackage as a pip dependency to your environment configuration file in order to track metrics and key artifacts in your workspace.conda.yaml
name: mlflow-example channels: - defaults dependencies: - numpy>=1.14.3 - pandas>=1.0.0 - scikit-learn - pip: - mlflow - azureml-mlflowSubmit the local run and ensure you set the parameter
backend = "azureml", which adds support of automatic tracking, model's capture, log files, snapshots, and printed errors in your workspace. In this example we assume the MLflow project you are trying to run is in the same folder you currently are,uri=".".mlflow run . --backend azureml --backend-config backend_config.json -P alpha=0.3Note
Since Azure Machine Learning jobs always run in the context of environments, the parameter
env_manageris ignored.View your runs and metrics in the Azure Machine Learning studio.
Clean up resources
If you don't plan to use the logged metrics and artifacts in your workspace, the ability to delete them individually is currently unavailable. Instead, delete the resource group that contains the storage account and workspace, so you don't incur any charges:
In the Azure portal, select Resource groups on the far left.
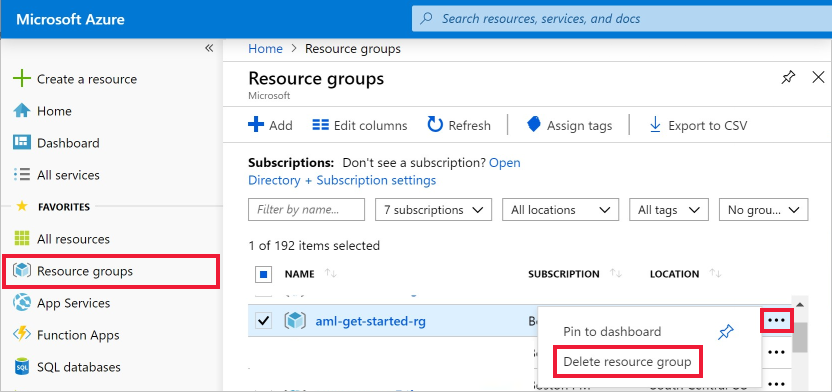
From the list, select the resource group you created.
Select Delete resource group.
Enter the resource group name. Then select Delete.
Example notebooks
The MLflow with Azure Machine Learning notebooks demonstrate and expand upon concepts presented in this article.
Note
A community-driven repository of examples using mlflow can be found at https://github.com/Azure/azureml-examples.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for