Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Database for MySQL is a managed service for running, managing, and scaling highly available MySQL servers in the cloud. This article shows you how to use the Azure portal to create an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance. You create an instance of Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server by using a defined set of compute and storage resources.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription
- Access to the Azure portal
- Basic knowledge of Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server deployment options and configurations
Sign in to the Azure portal
Enter your credentials to sign in to the Azure portal.
Create an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server
Create the server within an Azure resource group.
Complete these steps to create an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server:
In the Azure portal, search for and then select Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Servers.
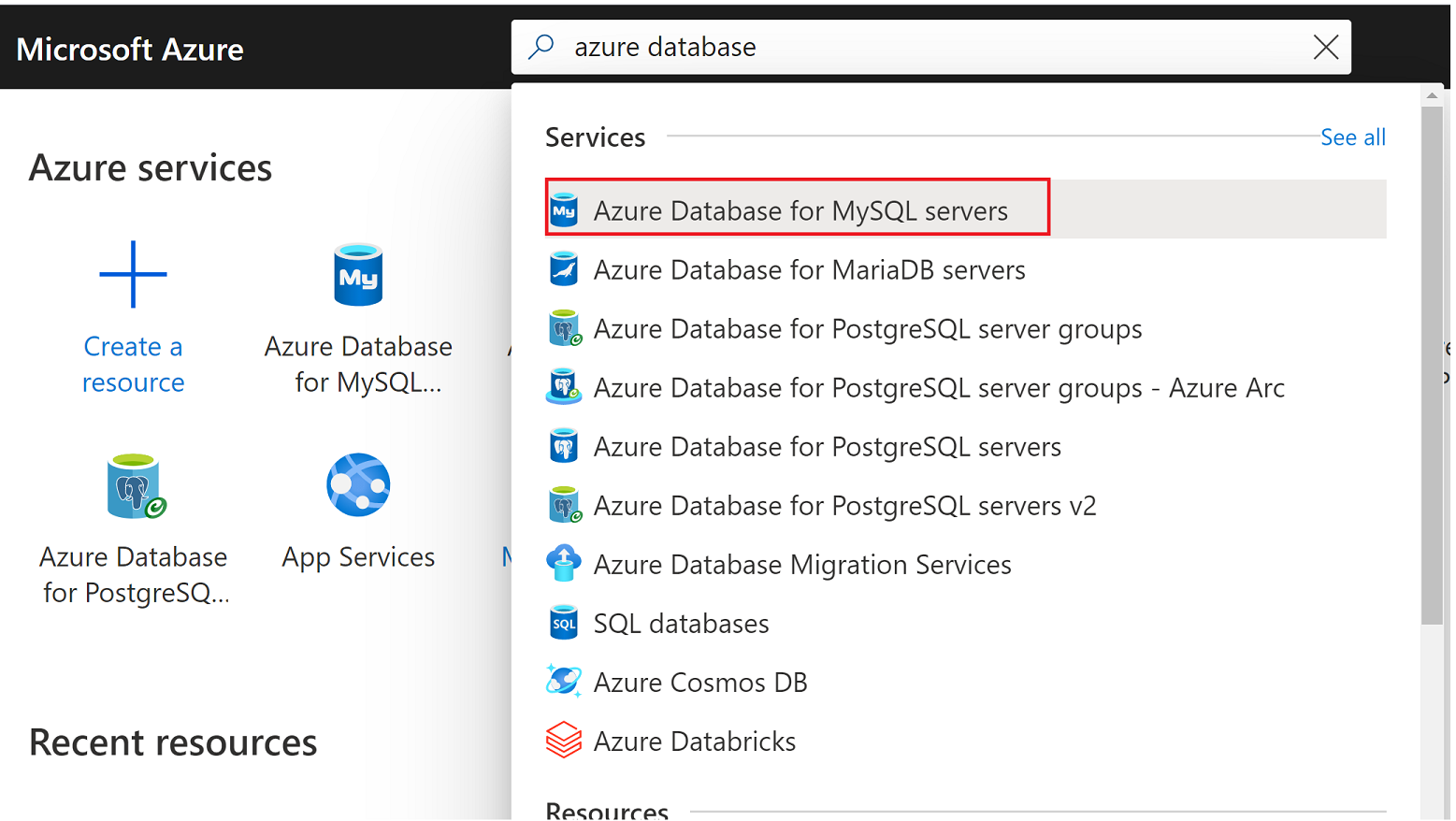
Select Create.
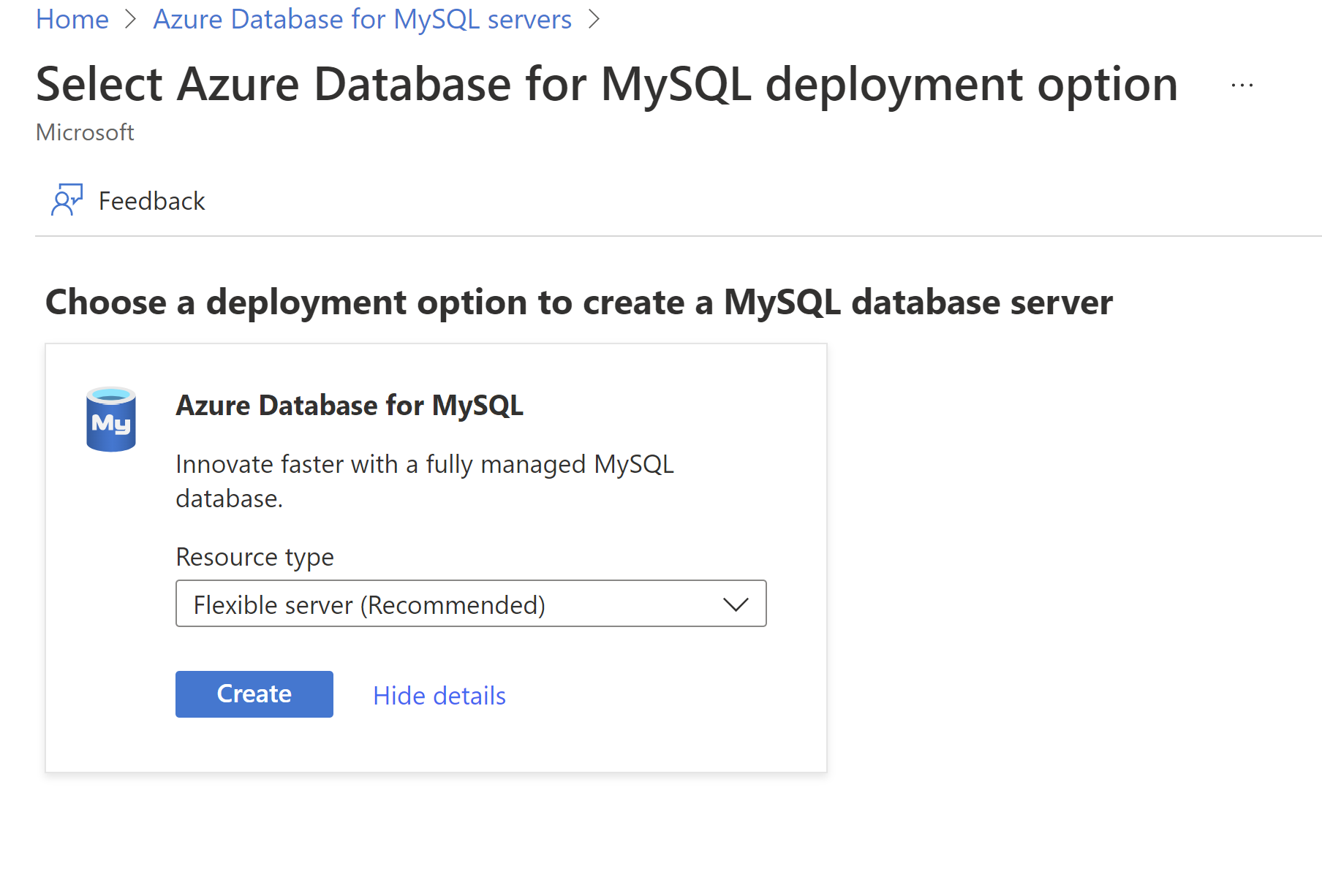
On the Select Azure Database for MySQL deployment option pane, select Flexible server as the deployment option:
On the Basics tab, enter or select the following information:
Setting Suggested value Description Subscription Your subscription name The Azure subscription you want to use for your server. Choose the subscription for which you want to be billed for the resource if you have multiple subscriptions. Resource group myresourcegroup Create a new resource group name, or select an existing resource group from your subscription. Server name mydemoserver-quickstart A unique name that identifies your instance of Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server. The domain name mysql.database.azure.comis appended to the server name you enter. The server name can contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-) character. It must contain between 3 and 63 characters.Region The region closest to your users The location closest to your users. MySQL version 8.0 The major engine version. Workload type Development For production workload, you can select Small/Medium-size or Large-size depending on max_connections requirements Compute + storage Burstable, Standard_B1ms, 10 GiB, 100 iops, 7 days The compute, storage, input/output operations per second (IOPS), and backup configurations for your new server. On the Configure server pane, the default values for Compute tier, Compute size, Storage size, iops, and Retention period (for backup) are Burstable, Standard_B1ms, 10 GiB, 100 iops, and 7 days. You can keep the default values or modify these values. For faster data loads during migration, we recommend increasing IOPS to the maximum size supported for the compute size you selected. Later, scale it back to minimize cost. To save the compute and storage selection, select Save to continue with the configuration. Availability zone No preference If your application client is provisioned in a specific availability zone, you can set your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server to the same availability zone to colocate the application and reduce network latency. High availability Cleared For production servers, choose between zone-redundant high availability and Local-redundant high availability. We recommend high availability for business continuity and protection against virtual machine (VM) failure. Authentication method MySQL and Microsoft Entra authentication Select the authentication methods you want to support for accessing this MySQL server. Admin username mydemouser Your sign-in account is to be used when you connect to the server. The admin username can't be azure_superuser, admin, administrator, root, guest, sa, or public. The maximum number of characters that are allowed is 32. Password Your password A new password for the server admin account. It must contain between 8 and 128 characters. It also must contain characters from three of the following categories: English uppercase letters, English lowercase letters, numbers (0 through 9), and nonalphanumeric characters ( !,$,#,%, and so on).Next, configure networking options.
On the Networking tab, set how your server is accessed. Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server offers two ways to connect to your server:
- Public access (allowed IP addresses)
- Private access (virtual network integration)
When you use public access, you limit access to your server to the allowed IP addresses you add to a firewall rule. This method prevents external applications and tools from connecting to the server and any databases on the server unless you create a rule to open the firewall for a specific IP address or range of IP addresses. When you select Create an azuredeploy.json file, you limit access to your server to your virtual network. For more information about private access, see the concepts article.
In this quickstart, you learn how to set public access to connect to the server. On the Networking tab, for Connectivity method, select Public access. To set firewall rules, select Add current client IP address.
You can't change the connectivity method after you create the server. For example, if you select Public access (allowed IP addresses) when you create the server, you can't change the setting to Private access (VNet Integration) after the server is deployed. We highly recommend that you create your server to use private access to help secure access to your server via virtual network integration. For more information about private access, see the concepts article.
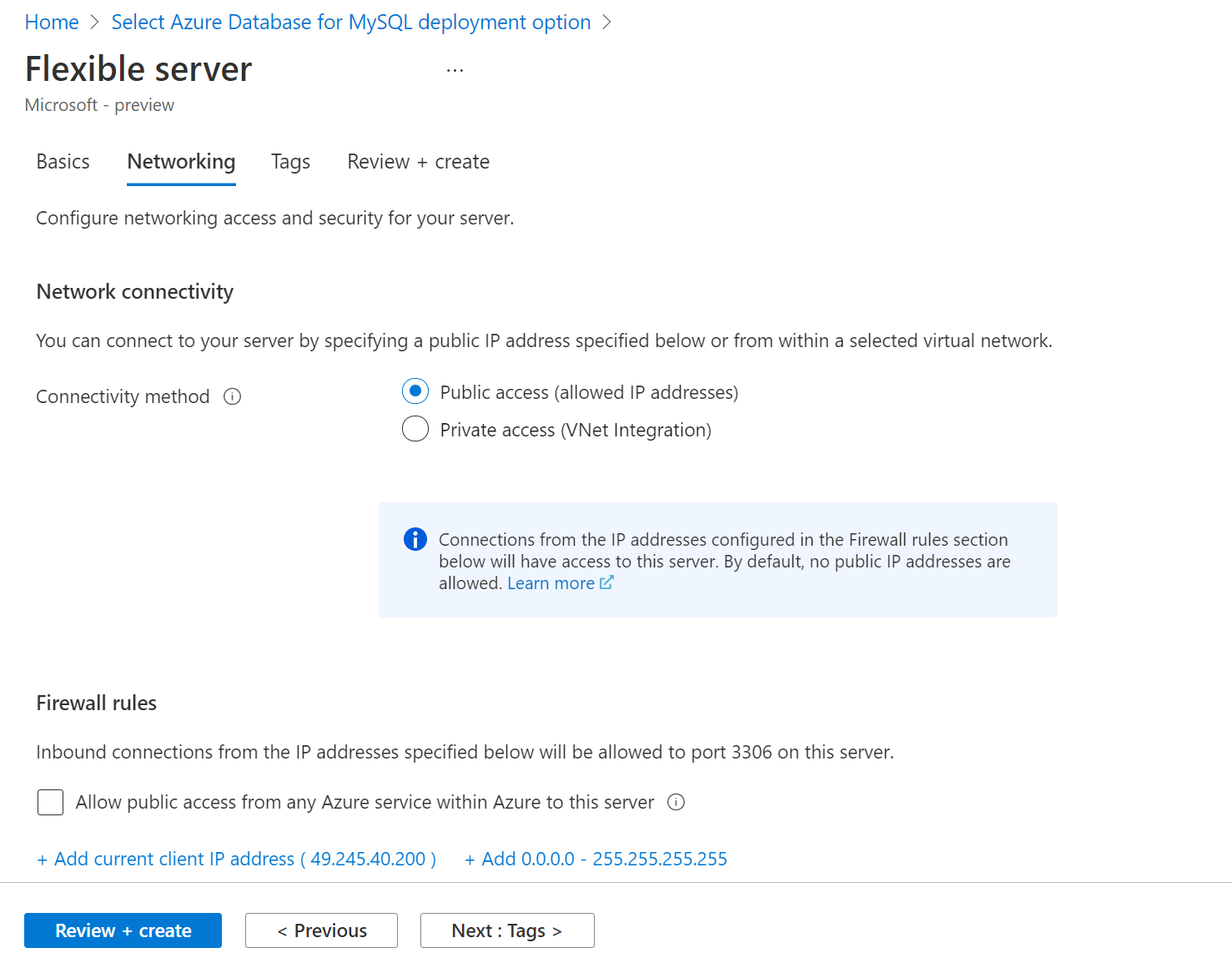
Select Review + create to review your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server configuration.
Select Create to provision the server. Provisioning might take a few minutes.
Select Notifications (the bell icon) on the toolbar to monitor the deployment process. After deployment, you can select Pin to dashboard to create a tile for the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server on your Azure portal dashboard. This tile is a shortcut to the server's Overview pane. When you select Go to resource, the Overview pane for the flexible server opens.
These databases are created by default under your server: information_schema, mysql, performance_schema, and sys.
Note
To avoid connectivity problems, check whether your network allows outbound traffic through port 3306, which Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server uses.
Connect to the server
Before you start, download the public SSL certificate for certificate authority verification.
If you deploy Azure Database for MySQL with the public access connectivity method, you can get started quickly by using the built-in MySQL command-line client tool or Azure Cloud Shell. To use the command-line tool, on the menu bar in the Overview pane, select Connect.
Note
You can also use the MySQL extension in Azure Data Studio to connect to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
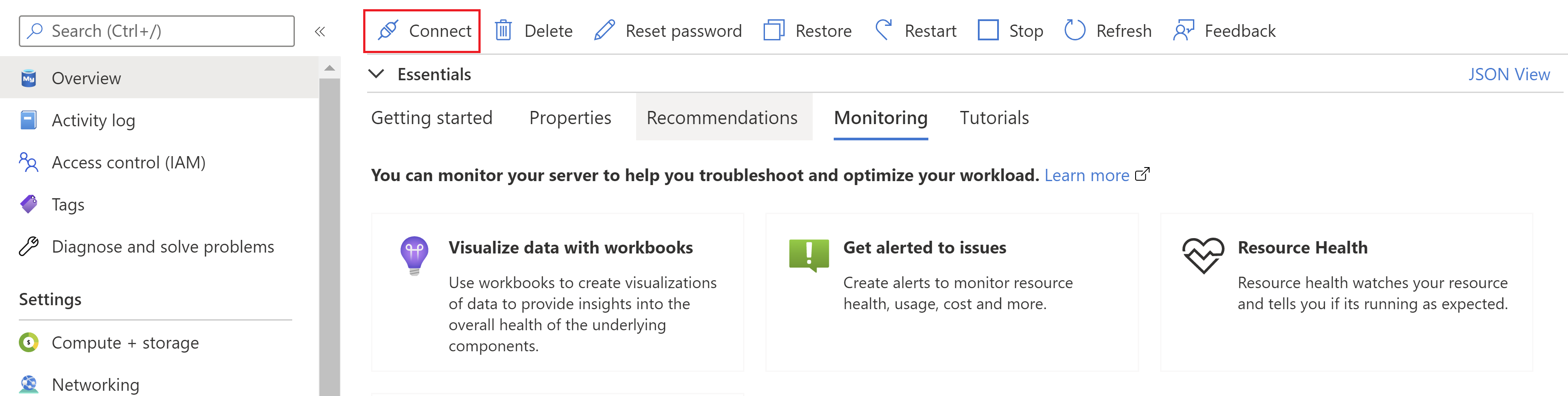
After you select Connect, you can see details about connecting locally by using the Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server client tool and how to initiate data import and export operations.
Important
If you see the following error message when you connect to your Azure Database for MySQL flexible server, either you didn't select the Allow public access from any Azure service within Azure to this server checkbox when you set up your firewall rules, or the option isn't saved. Set the firewall rules, then try again.
ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on <servername> (115)
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the resources you created for this quickstart, delete the resource group that contains the Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance. Select the resource group for the Azure Database for MySQL resource, then select Delete. Enter the name of the resource group that you want to delete.