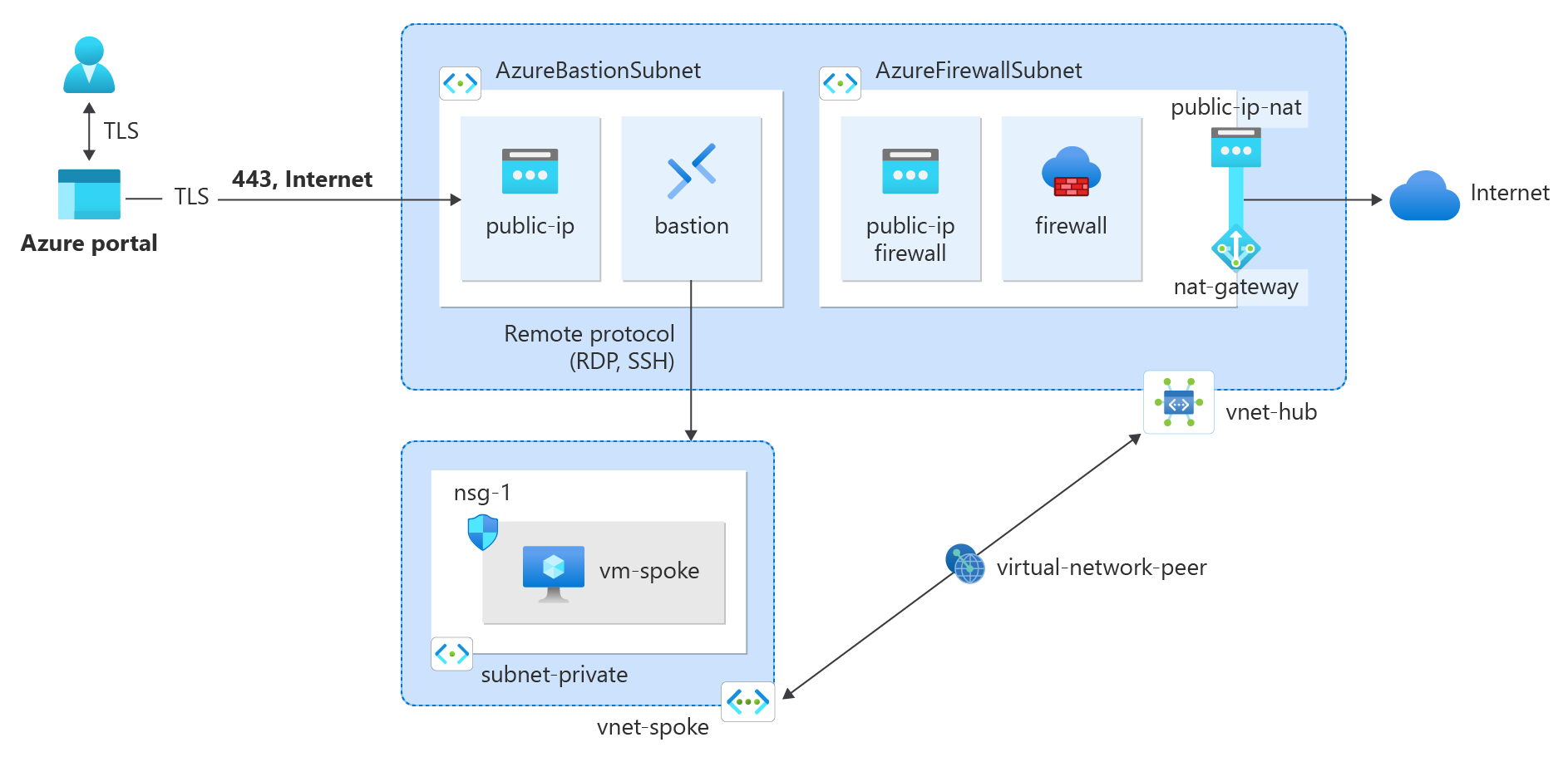
Tutorial: Integrate NAT gateway with Azure Firewall in a hub and spoke network for outbound connectivity
In this tutorial, you learn how to integrate a NAT gateway with an Azure Firewall in a hub and spoke network
Azure Firewall provides 2,496 SNAT ports per public IP address configured per backend Virtual Machine Scale Set instance (minimum of two instances). You can associate up to 250 public IP addresses to Azure Firewall. Depending on your architecture requirements and traffic patterns, you may require more SNAT ports than what Azure Firewall can provide. You may also require the use of fewer public IPs while also requiring more SNAT ports. A better method for outbound connectivity is to use NAT gateway. NAT gateway provides 64,512 SNAT ports per public IP address and can be used with up to 16 public IP addresses.
NAT gateway can be integrated with Azure Firewall by configuring NAT gateway directly to the Azure Firewall subnet in order to provide a more scalable method of outbound connectivity. For production deployments, a hub and spoke network is recommended, where the firewall is in its own virtual network. The workload servers are peered virtual networks in the same region as the hub virtual network where the firewall resides. In this architectural setup, NAT gateway can provide outbound connectivity from the hub virtual network for all spoke virtual networks peered.
Note
Azure NAT Gateway is not currently supported in secured virtual hub network (vWAN) architectures. You must deploy using a hub virtual network architecture as described in this tutorial. For more information about Azure Firewall architecture options, see What are the Azure Firewall Manager architecture options?.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create a hub virtual network and deploy an Azure Firewall and Azure Bastion during deployment
- Create a NAT gateway and associate it with the firewall subnet in the hub virtual network
- Create a spoke virtual network
- Create a virtual network peering
- Create a route table for the spoke virtual network
- Create a firewall policy for the hub virtual network
- Create a virtual machine to test the outbound connectivity through the NAT gateway
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Create the hub virtual network
The hub virtual network contains the firewall subnet that is associated with the Azure Firewall and NAT gateway. Use the following example to create the hub virtual network.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual network. Select Virtual networks in the search results.
Select + Create.
In the Basics tab of Create virtual network, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select Create new.
Enter test-rg.
Select OK.Instance details Name Enter vnet-hub. Region Select (US) South Central US. Select Next to proceed to the Security tab.
Select Enable Azure Bastion in the Azure Bastion section of the Security tab.
Azure Bastion uses your browser to connect to VMs in your virtual network over secure shell (SSH) or remote desktop protocol (RDP) by using their private IP addresses. The VMs don't need public IP addresses, client software, or special configuration. For more information about Azure Bastion, see Azure Bastion
Enter or select the following information in Azure Bastion:
Setting Value Azure Bastion host name Enter bastion. Azure Bastion public IP address Select Create a public IP address.
Enter public-ip-bastion in Name.
Select OK.Select Enable Azure Firewall in the Azure Firewall section of the Security tab.
Azure Firewall is a managed, cloud-based network security service that protects your Azure Virtual Network resources. It's a fully stateful firewall as a service with built-in high availability and unrestricted cloud scalability. For more information about Azure Firewall, see Azure Firewall.
Enter or select the following information in Azure Firewall:
Setting Value Azure Firewall name Enter firewall. Tier Select Standard. Policy Select Create new.
Enter firewall-policy in Name.
Select OK.Azure Firewall public IP address Select Create a public IP address.
Enter public-ip-firewall in Name.
Select OK.Select Next to proceed to the IP addresses tab.
Select Review + create.
Select Create.
It takes a few minutes for the bastion host and firewall to deploy. When the virtual network is created as part of the deployment, you can proceed to the next steps.
Create the NAT gateway
All outbound internet traffic traverses the NAT gateway to the internet. Use the following example to create a NAT gateway for the hub and spoke network and associate it with the AzureFirewallSubnet.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter NAT gateway. Select NAT gateways in the search results.
Select + Create.
In the Basics tab of Create network address translation (NAT) gateway enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select test-rg. Instance details NAT gateway name Enter nat-gateway. Region Select South Central US. Availability zone Select a Zone or No zone. TCP idle timeout (minutes) Leave the default of 4. For more information about availability zones, see NAT gateway and availability zones.
Select Next: Outbound IP.
In Outbound IP in Public IP addresses, select Create a new public IP address.
Enter public-ip-nat in Name.
Select OK.
Select Next: Subnet.
In Virtual Network select vnet-hub.
Select AzureFirewallSubnet in Subnet name.
Select Review + create.
Select Create.
Create spoke virtual network
The spoke virtual network contains the test virtual machine used to test the routing of the internet traffic to the NAT gateway. Use the following example to create the spoke network.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual network. Select Virtual networks in the search results.
Select + Create.
In the Basics tab of Create virtual network, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select test-rg. Instance details Name Enter vnet-spoke. Region Select South Central US. Select Next to proceed to the Security tab.
Select Next to proceed to the IP addresses tab.
In the IP Addresses tab in IPv4 address space, select Delete address space to delete the address space that is auto populated.
Select + Add IPv4 address space.
In IPv4 address space enter 10.1.0.0. Leave the default of /16 (65,536 addresses) in the mask selection.
Select + Add a subnet.
In Add a subnet enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Subnet purpose Leave the default Default. Name Enter subnet-private. IPv4 IPv4 address range Leave the default of 10.1.0.0/16. Starting address Leave the default of 10.1.0.0. Size Leave the default of /24(256 addresses). Select Add.
Select Review + create.
Select Create.
Create peering between the hub and spoke
A virtual network peering is used to connect the hub to the spoke and the spoke to the hub. Use the following example to create a two-way network peering between the hub and spoke.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual network. Select Virtual networks in the search results.
Select vnet-hub.
Select Peerings in Settings.
Select + Add.
Enter or select the following information in Add peering:
Setting Value Remote virtual network summary Peering link name Enter vnet-spoke-to-vnet-hub. Virtual network deployment model Leave the default of Resource manager. Subscription Select your subscription. Virtual network Select vnet-spoke (test-rg). Remote virtual network peering settings Allow 'vnet-spoke' to access 'vnet-hub' Leave the default of Selected. Allow 'vnet-spoke' to receive forwarded traffic from 'vnet-hub' Select the checkbox. Allow gateway or route server in 'vnet-spoke' to forward traffic to 'vnet-hub' Leave the default of Unselected. Enable 'vnet-spoke' to use 'vnet-hub's' remote gateway or route server Leave the default of Unselected. Local virtual network summary Peering link name Enter vnet-hub-to-vnet-spoke. Local virtual network peering settings Allow 'vnet-hub' to access 'vnet-spoke-2' Leave the default of Selected. Allow 'vnet-hub' to receive forwarded traffic from 'vnet-spoke' Select the checkbox. Allow gateway or route server in 'vnet-hub' to forward traffic to 'vnet-spoke' Leave the default of Unselected. Enable 'vnet-hub' to use 'vnet-spoke's' remote gateway or route server Leave the default of Unselected. Select Add.
Select Refresh and verify Peering status is Connected.
Create spoke network route table
A route table forces all traffic leaving the spoke virtual network to the hub virtual network. The route table is configured with the private IP address of the Azure Firewall as the virtual appliance.
Obtain private IP address of firewall
The private IP address of the firewall is needed for the route table created later in this article. Use the following example to obtain the firewall private IP address.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Firewall. Select Firewalls in the search results.
Select firewall.
In the Overview of firewall, note the IP address in the field Firewall private IP. The IP address in this example is 10.0.1.68.
Create route table
Create a route table to force all inter-spoke and internet egress traffic through the firewall in the hub virtual network.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Route table. Select Route tables in the search results.
Select + Create.
In Create Route table enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select test-rg. Instance details Region Select South Central US. Name Enter route-table-spoke. Propagate gateway routes Select No. Select Review + create.
Select Create.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Route table. Select Route tables in the search results.
Select route-table-spoke.
In Settings select Routes.
Select + Add in Routes.
Enter or select the following information in Add route:
Setting Value Route name Enter route-to-hub. Destination type Select IP Addresses. Destination IP addresses/CIDR ranges Enter 0.0.0.0/0. Next hop type Select Virtual appliance. Next hop address Enter 10.0.1.68. Select Add.
Select Subnets in Settings.
Select + Associate.
Enter or select the following information in Associate subnet:
Setting Value Virtual network Select vnet-spoke (test-rg). Subnet Select subnet-private. Select OK.
Configure firewall
Traffic from the spoke through the hub must be allowed through and firewall policy and a network rule. Use the following example to create the firewall policy and network rule.
Configure network rule
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Firewall. Select Firewall Policies in the search results.
Select firewall-policy.
Expand Settings then select Network rules.
Select + Add a rule collection.
In Add a rule collection enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Name Enter spoke-to-internet. Rule collection type Select Network. Priority Enter 100. Rule collection action Select Allow. Rule collection group Select DefaultNetworkRuleCollectionGroup. Rules Name Enter allow-web. Source type IP Address. Source Enter 10.1.0.0/24. Protocol Select TCP. Destination Ports Enter 80,443. Destination Type Select IP Address. Destination Enter * Select Add.
Create test virtual machine
An Ubuntu virtual machine is used to test the outbound internet traffic through the NAT gateway. Use the following example to create an Ubuntu virtual machine.
The following procedure creates a test virtual machine (VM) named vm-spoke in the virtual network.
In the portal, search for and select Virtual machines.
In Virtual machines, select + Create, then Azure virtual machine.
On the Basics tab of Create a virtual machine, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select test-rg. Instance details Virtual machine name Enter vm-spoke. Region Select (US) South Central US. Availability options Select No infrastructure redundancy required. Security type Leave the default of Standard. Image Select Ubuntu Server 24.04 LTS - x64 Gen2. VM architecture Leave the default of x64. Size Select a size. Administrator account Authentication type Select Password. Username Enter azureuser. Password Enter a password. Confirm password Reenter the password. Inbound port rules Public inbound ports Select None. Select the Networking tab at the top of the page or select Next:Disks, then Next:Networking.
Enter or select the following information in the Networking tab:
Setting Value Network interface Virtual network Select vnet-spoke. Subnet Select subnet-private (10.1.0.0/24). Public IP Select None. NIC network security group Select Advanced. Configure network security group Select Create new.
Enter nsg-1 for the name.
Leave the rest at the defaults and select OK.Leave the rest of the settings at the defaults and select Review + create.
Review the settings and select Create.
Wait for the virtual machine to finishing deploying before proceeding to the next steps.
Note
Virtual machines in a virtual network with a bastion host don't need public IP addresses. Bastion provides the public IP, and the VMs use private IPs to communicate within the network. You can remove the public IPs from any VMs in bastion hosted virtual networks. For more information, see Dissociate a public IP address from an Azure VM.
Test NAT gateway
You connect to the Ubuntu virtual machines you created in the previous steps to verify that the outbound internet traffic is leaving the NAT gateway.
Obtain NAT gateway public IP address
Obtain the NAT gateway public IP address for verification of the steps later in the article.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Public IP. Select Public IP addresses in the search results.
Select public-ip-nat.
Make note of value in IP address. The example used in this article is 203.0.113.0.25.
Test NAT gateway from spoke
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual machine. Select Virtual machines in the search results.
Select vm-spoke.
In Overview, select Connect then Connect via Bastion.
Enter the username and password entered during VM creation. Select Connect.
In the bash prompt, enter the following command:
curl ifconfig.meVerify the IP address returned by the command matches the public IP address of the NAT gateway.
azureuser@vm-1:~$ curl ifconfig.me 203.0.113.0.25Close the Bastion connection to vm-spoke.
When you finish using the resources that you created, you can delete the resource group and all its resources.
In the Azure portal, search for and select Resource groups.
On the Resource groups page, select the test-rg resource group.
On the test-rg page, select Delete resource group.
Enter test-rg in Enter resource group name to confirm deletion, and then select Delete.
Next steps
Advance to the next article to learn how to integrate a NAT gateway with an Azure Load Balancer: