Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This tutorial guides you through converting Oracle database schemas to Azure Database for PostgreSQL using the Visual Studio PostgreSQL extension with Azure OpenAI to automate and validate schema translation
It covers connecting to your Oracle source and Azure Database for PostgreSQL target, configuring Azure OpenAI, running the Migration Wizard, and reviewing generated PostgreSQL artifacts. Before you begin, ensure you have network access and credentials for both servers and an Azure OpenAI deployment.
Here's what you can expect during the conversion:
- Schema Discovery: The tool analyzes your Oracle schema objects
- AI Processing: Azure OpenAI processes and converts compatible objects
- Validation: Converted objects are validated in the scratch database
- Review Tasks: Objects requiring manual attention are flagged
- Output Generation: Successfully converted objects are saved as PostgreSQL files
Prerequisites
This section describes the prerequisites for using the Oracle to Azure Database for PostgreSQL schema conversion feature in Visual Studio Code before starting a conversion.
System requirements
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Visual Studio Code version | 1.95.2 or higher |
| GitHub Copilot subscription | Pro+, Business, Enterprise |
Operating system support
| Operating System | Support Details |
|---|---|
| Windows | x64 architecture only |
| Linux | x64 architecture |
| macOS | macOS 13+ |
PostgreSQL version support
| Component | Version Requirement |
|---|---|
| Azure Database for PostgreSQL | PostgreSQL version 15 or higher |
| Scratch database | Azure Database for PostgreSQL |
AI model requirements
You need one of the following AI components configured:
| AI Component | Model Version |
|---|---|
| Azure OpenAI | GPT-4.1 deployment |
Azure OpenAI deployment configuration
You must configure the Azure OpenAI deployment with the model name gpt-4.1.
Example endpoint format:
https://{your-resource}.openai.azure.com/openai/deployments/gpt-4.1/chat/completions?api-version=2025-01-01-preview
Required database privileges
Before running the schema conversion, ensure the accounts, you use have the minimum privileges required on both the source Oracle database and the scratch Azure Database for PostgreSQL. The Oracle account needs read access to data and dictionary views so the tool can analyze schema and code. The PostgreSQL scratch account must be able to create schemas, tables, and other objects for validation. Use a dedicated service account where possible. Follow the principle of least privilege. Coordinate with your DBAs to grant any temporary elevated rights and to validate connectivity and access before starting the conversion.
Source Oracle privileges
The following minimum privileges are required on the source Oracle database:
| Privilege | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CONNECT | Basic database connection |
| SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE | Access to data dictionary views |
| SELECT ANY DICTIONARY | Read system metadata and dictionary objects |
SELECT SYS.ARGUMENT$ |
Access to procedure and function argument information |
Scratch database privileges
The following privileges are required on the Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server (Scratch DB):
| Privilege | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CREATE SCHEMA | Create validation schemas |
| CREATE ON DATABASE | Create database objects for validation |
| GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE | Connection permissions for validation processes |
Network requirements
- Outbound connectivity to Azure OpenAI endpoints
- Database connectivity to both source Oracle and target PostgreSQL databases
- HTTPS access for Visual Studio Code extension marketplace and GitHub Copilot services
- GitHub repository access to https://github.com/microsoft/pgsql-tools/
Migration process
This section walks through the complete migration workflow: install the PostgreSQL extension, create, and test connections to your Oracle source and Azure Database for PostgreSQL target, open and initialize a migration project, configure Azure OpenAI for schema translation, run the Migration Wizard to discover and convert schemas, validate converted objects in a scratch database, and review or fix any flagged items before applying the generated PostgreSQL artifacts to your target.
Step 1: Install the PostgreSQL Visual Studio Code extension
Open Visual Studio.
Go to the Extensions view (Ctrl+Shift+X).
Search for PostgreSQL and install the PostgreSQL extension.
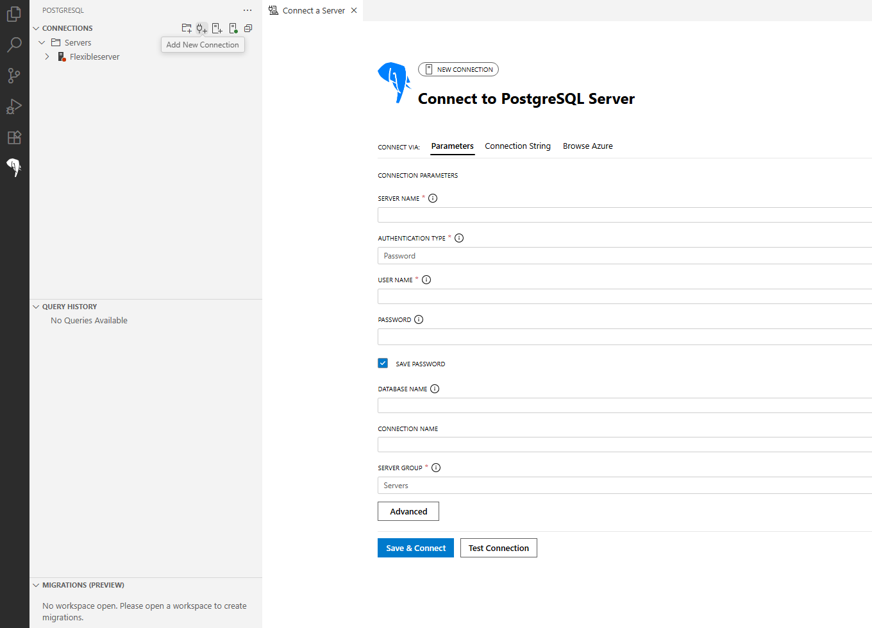
Step 2: Create PostgreSQL connection
In the PostgreSQL extension panel, create a connection to your Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
Enter the necessary connection details (host, database, username, password).
Test and save the connection.
Step 3: Open new workspace
Create a new folder on your local machine for the migration project.
Open a new workspace in Visual Studio Code.

Step 4: Initialize migration project
Go to the PostgreSQL extension.
Navigate to the Migrations (preview) panel.
Select on Create Migration Project.

Step 5: Configure project settings
In the Migration Wizard, enter your project name.
Select Next to proceed to the next step.

Step 6: Configure Oracle connection
Enter your Oracle connection details including:
- Host or server name
- Port number
- Database or service name
- Username and password
Select Load Schemas.
The system Tests the Oracle connection.
If successful, it Lists all user-defined schemas available in Oracle.
Choose one or multiple schemas that you want to convert to PostgreSQL.
Select Next to continue.

Step 7: Configure a PostgreSQL scratch database
Select the Azure Database for PostgreSQL connection that you defined in the PostgreSQL extension
Select the target database from the dropdown list
Select Next to proceed

Step 8: Configure an Azure OpenAI language model
Enter your Azure OpenAI details including:
- Endpoint URL
- API key
- Deployment name (must be gpt-4.1)
Select Test Connection to verify the configuration
Once the connection is successful, select Create Migration Project

Step 9: Execute schema conversion
The system navigates to the main Migration Wizard
Select Migrate to initiate the Schema Conversion process
Monitor the conversion progress in the Visual Studio interface

Step 10: Review schema conversion report
- Once the schema conversion is completed, a schema conversion report is generated.
- Review the objects that were converted successfully or skipped.
- The report displays the success percentage of the conversion.
Step 11: Review and refine conversion tasks
- Once the schema conversion is completed, Review tasks are created for objects requiring attention.
- Use GitHub Copilot agents or manually convert schemas to PostgreSQL.
- Review and compare the previous and new converted schema conversion statements.
Step 12: Validate converted objects before deployment
- Independently validate all converted objects in a nonproduction environment.
- Confirm dependencies, constraints, and representative workloads behave as expected.
- Review resolutions for all Review tasks and re-test after changes.
Important
Customer validation responsibility: The same AI engine used for schema conversion can also assist with validation and review. AI systems can occasionally confirm their own mistakes. To prevent data loss, functional regressions, or security issues, independently validate all converted objects and review-task resolutions before deploying to production. As part of your controls, consider enabling Azure AI Foundry content filtering to help reduce harmful or undesired outputs. For guidance, see Content filtering in Azure AI Foundry.
For more information about the Visual Studio Code extension, visit PostgreSQL extension for Visual Studio Code.