Microsoft Purview Data Catalog lineage user guide
This article provides an overview of the data lineage features in Microsoft Purview Data Catalog.
Background
One of the platform features of Microsoft Purview is the ability to show the lineage between datasets created by data processes. Systems like Data Factory, Data Share, and Power BI capture the lineage of data as it moves. Custom lineage reporting is also supported via Atlas hooks and REST API.
Lineage collection
Metadata collected in Microsoft Purview from enterprise data systems are stitched across to show an end to end data lineage. Data systems that collect lineage into Microsoft Purview are broadly categorized into following three types:
Each system supports a different level of lineage scope. Check the sections below, or your system's individual lineage article, to confirm the scope of lineage currently available.
Known limitations
- Database Views used as source of process activity(Azure Data Factory, Synapse Pipelines, Azure SQL Database, Azure Data Share) are currently captured as Database Table objects in Microsoft Purview. If the Database is also scanned, the View assets are discovered separately in Microsoft Purview. In this scenario, two assets with same name captured in Microsoft Purview, one as a Table with data lineage and another as a View.
- If a stored procedure contains drop or create statements, they are not currently captured in lineage.
Data processing systems
Data integration and ETL tools can push lineage into Microsoft Purview at execution time. Tools such as Data Factory, Data Share, Synapse, Azure Databricks, and so on, belong to this category of data processing systems. The data processing systems reference datasets as source from different databases and storage solutions to create target datasets. The list of data processing systems currently integrated with Microsoft Purview for lineage are listed in below table.
| Data processing system | Supported scope |
|---|---|
| Airflow | Airflow lineage |
| Azure Data Share | Share snapshot |
| Azure Data Factory | Copy activity Data flow activity Execute SSIS package activity |
| Azure SQL Database (Preview) | Lineage extraction for stored procedure executions |
| Azure Synapse Analytics | Copy activity Data flow activity |
Data storage systems
Databases & storage solutions such as Oracle, Teradata, and SAP have query engines to transform data using scripting language. Data lineage information from views/stored procedures/etc is collected into Microsoft Purview and stitched with lineage from other systems. Lineage is supported for the following data sources via Microsoft Purview data scan. Learn more about the supported lineage scenarios from the respective article.
| Category | Data source |
|---|---|
| Azure | Azure Databricks |
| Database | Cassandra |
| Db2 | |
| Google BigQuery | |
| Hive Metastore Database | |
| MySQL | |
| Oracle | |
| PostgreSQL | |
| Snowflake | |
| Teradata | |
| Services and apps | Erwin |
| Looker | |
| SAP ECC | |
| SAP S/4HANA |
Data analytics and reporting systems
Data analytics and reporting systems like Azure Machine Learning and Power BI report lineage into Microsoft Purview. These systems will use the datasets from storage systems and process through their meta model to create BI Dashboards, ML experiments and so on.
| Data analytics & reporting system | Supported scope |
|---|---|
| Power BI | Datasets, Dataflows, Reports & Dashboards |
Get started with lineage
Lineage in Microsoft Purview includes datasets and processes. Datasets are also referred to as nodes while processes can be also called edges:
Dataset (Node): A dataset (structured or unstructured) provided as an input to a process. For example, a SQL Table, Azure blob, and files (such as .csv and .xml), are all considered datasets. In the lineage section of Microsoft Purview, datasets are represented by rectangular boxes.
Process (Edge): An activity or transformation performed on a dataset is called a process. For example, ADF Copy activity, Data Share snapshot and so on. In the lineage section of Microsoft Purview, processes are represented by round-edged boxes.
To access lineage information for an asset in Microsoft Purview, follow the steps:
Open the Microsoft Purview governance portal by:
- Browsing directly to https://web.purview.azure.com and selecting your Microsoft Purview account.
- Opening the Azure portal, searching for and selecting the Microsoft Purview account. Selecting the the Microsoft Purview governance portal button.
On the Microsoft Purview governance portal Home page, search for a dataset name or the process name such as ADF Copy or Data Flow activity. And then press Enter.
From the search results, select the asset and select its Lineage tab.
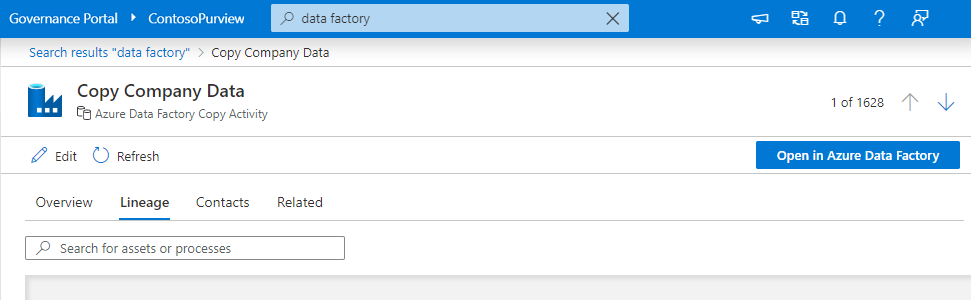
Asset-level lineage
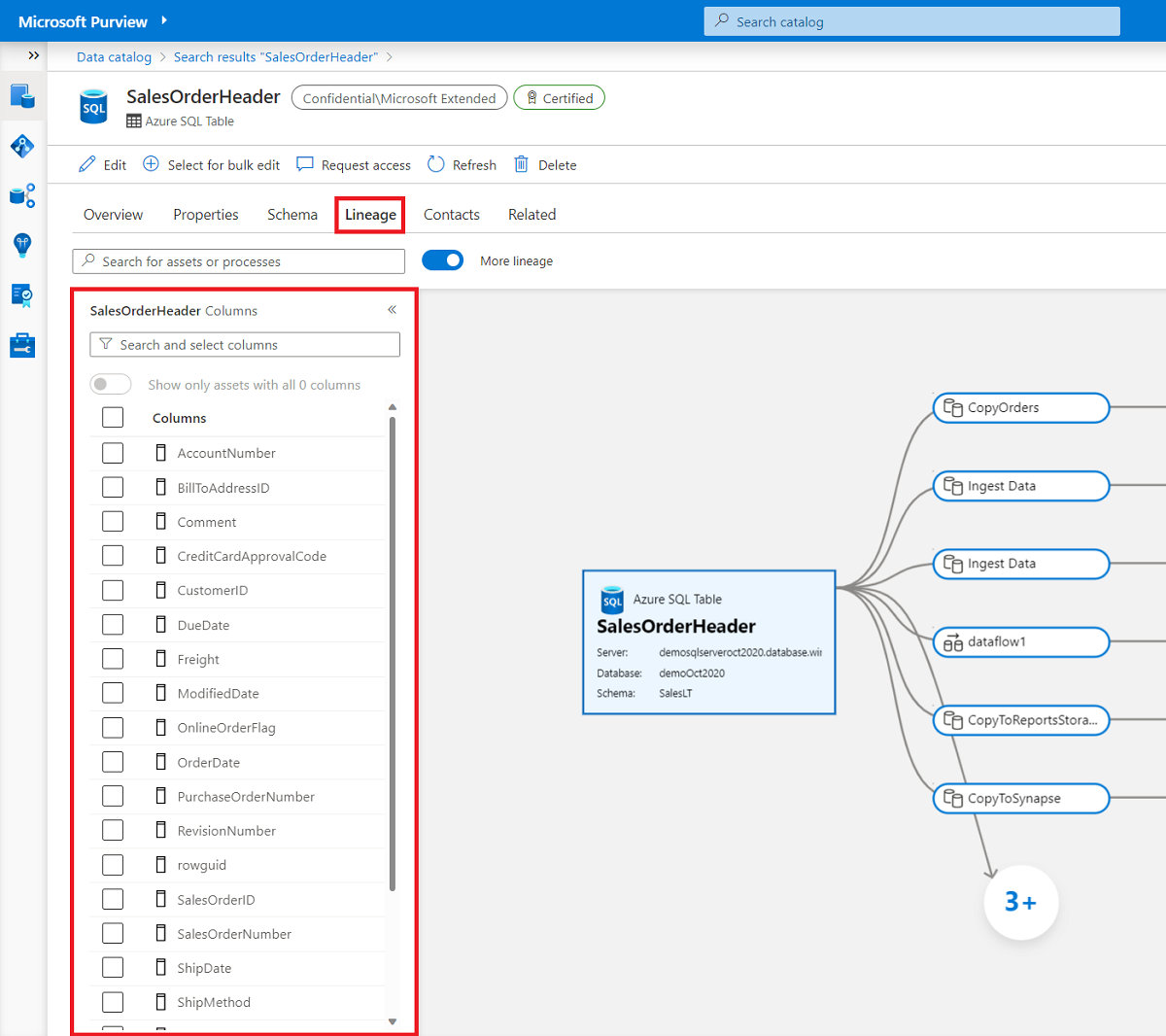
Microsoft Purview supports asset level lineage for the datasets and processes. To see the asset level lineage go to the Lineage tab of the current asset in the catalog. Select the current dataset asset node. By default the list of columns belonging to the data appears in the left pane.
Manual lineage
Data lineage in Microsoft Purview is automated for many assets in on-premises, multicloud, and SaaS environments. While we continue to add more automated sources, manual lineage allows you to document lineage metadata for sources where automation isn't yet supported, without using any code.
To add manual lineage for any of your assets, follow these steps:
Search for your asset in the data catalog and select it to view details.
Select Edit, navigate to the Lineage tab, and select Add manual lineage in the bottom panel.

To configure the asset lineage:
- Select the asset dropdown to find the asset from the suggested list or View more to search the full catalog. Select the asset you’d like to link.
- Select the swap icon to configure the relationship direction as Produces (for downstream lineage) or Consumes (for upstream lineage).
- If you want to delete a lineage, select the trash can icon.
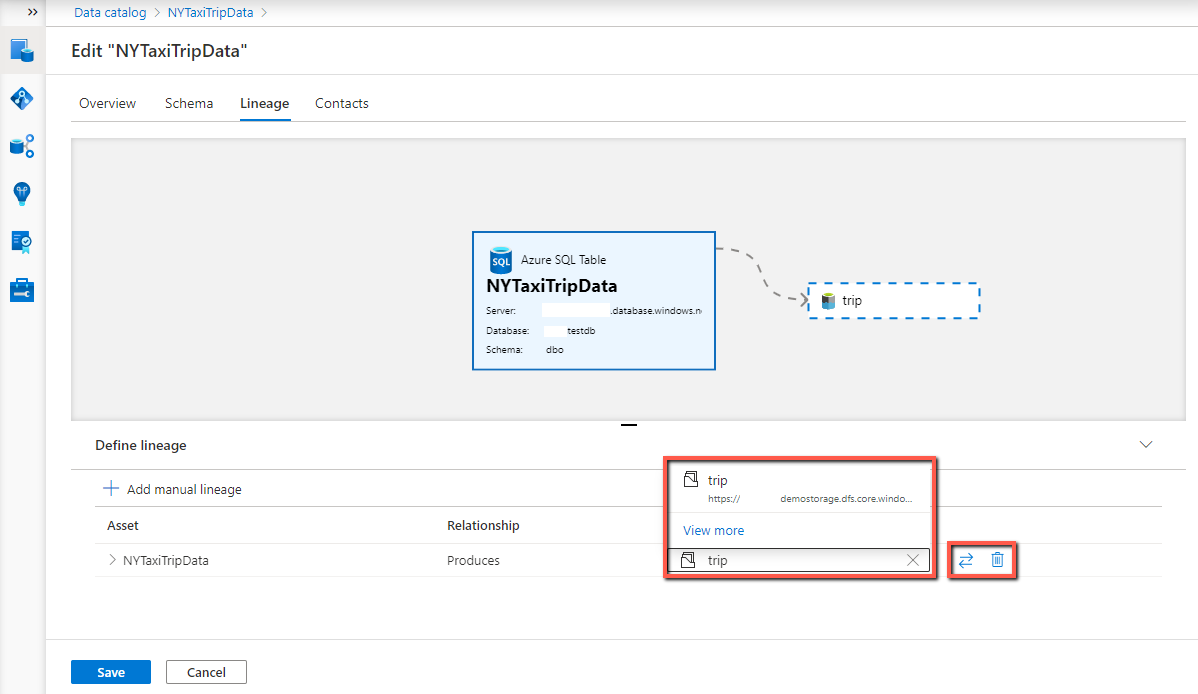
When you add lineage between two data assets, you can additionally configure the column level lineage. Select the expand icon at the beginning of the row, select the upstream and downstream columns from the corresponding dropdown lists to configure the column mapping. Select the plus icon to add more column lineage; select the trash bin icon to delete existing ones.

You can add more asset level lineage by selecting the Add manual lineage button again. When you're finished, select the Save button to save your lineage and exit edit mode.
Known limitations of manual lineage
- Current asset picker experience allows selecting only one asset at a time.
- Column level manual lineage is currently supported for lineage between two data assets, while not supported when process asset is involved in-between.
- Data curation access required for both source and target assets.
- These asset types don't currently allow manual lineage because they support automated lineage:
- Azure Data Factory
- Synapse pipelines
- Power BI datasets
- Teradata stored procedure
- Azure SQL stored procedure
Dataset column lineage
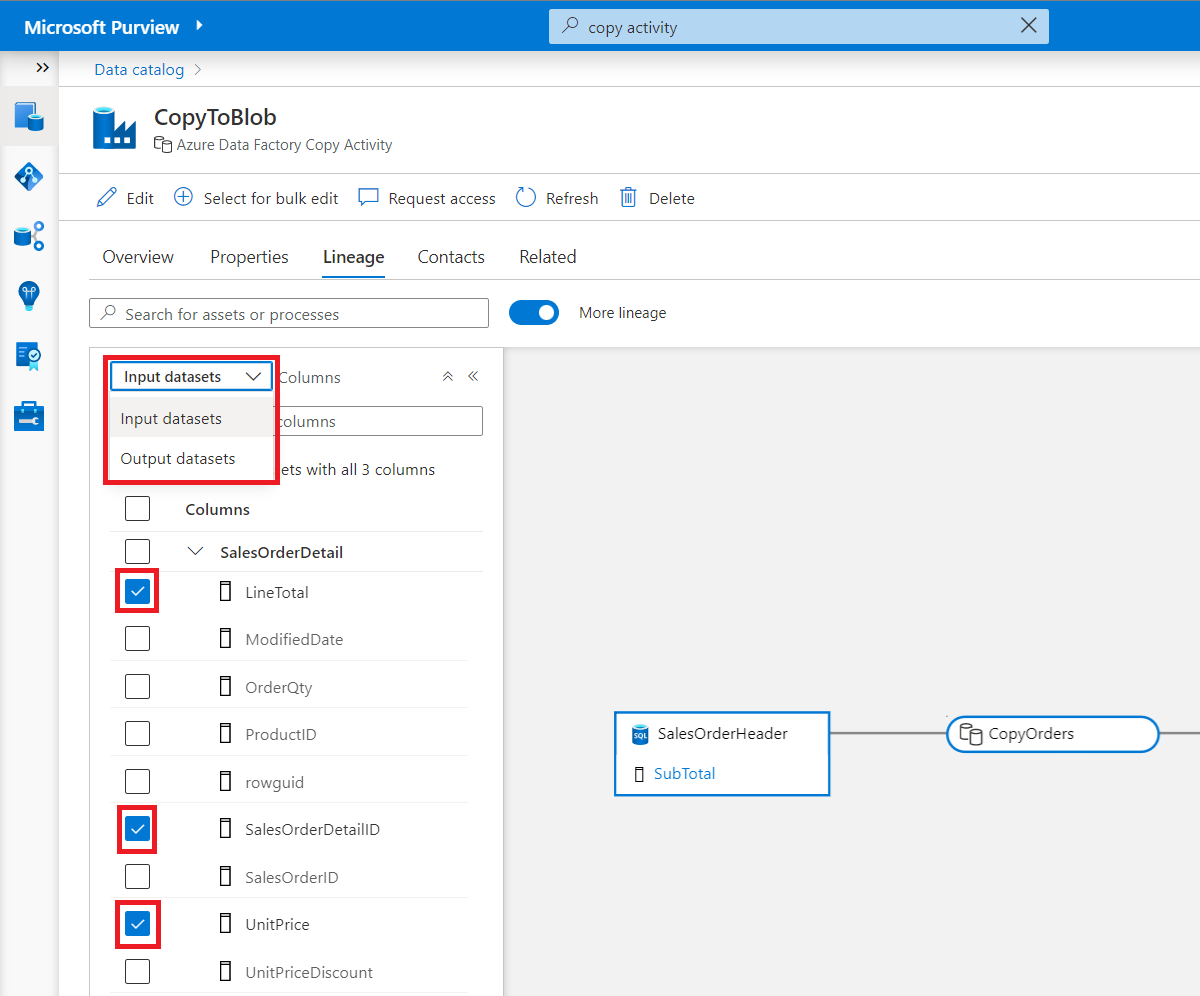
To see column-level lineage of a dataset, go to the Lineage tab of the current asset in the catalog and follow below steps:
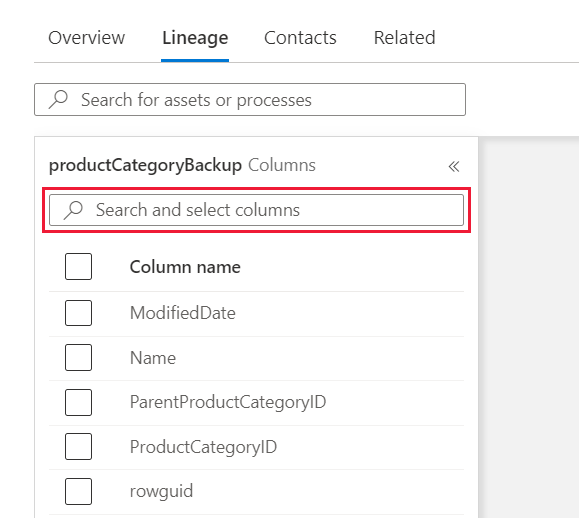
Once you are in the lineage tab, in the left pane, select the check box next to each column you want to display in the data lineage.
Hover over a selected column on the left pane or in the dataset of the lineage canvas to see the column mapping. All the column instances are highlighted.
If the number of columns is larger than what can be displayed in the left pane, use the filter option to select a specific column by name. Alternatively, you can use your mouse to scroll through the list.
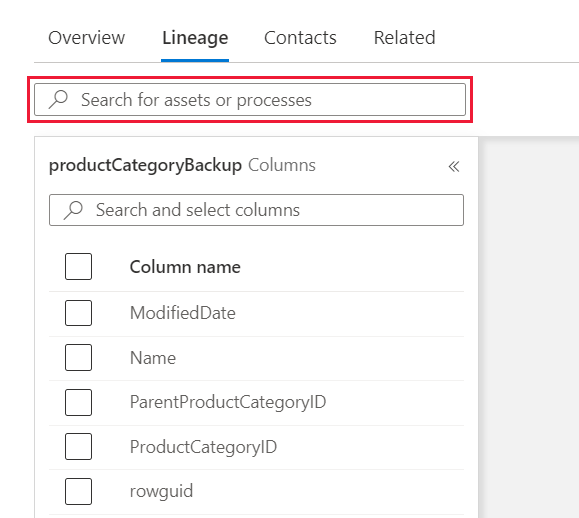
If the lineage canvas contains more nodes and edges, use the filter to select data asset or process nodes by name. Alternatively, you can use your mouse to pan around the lineage window.
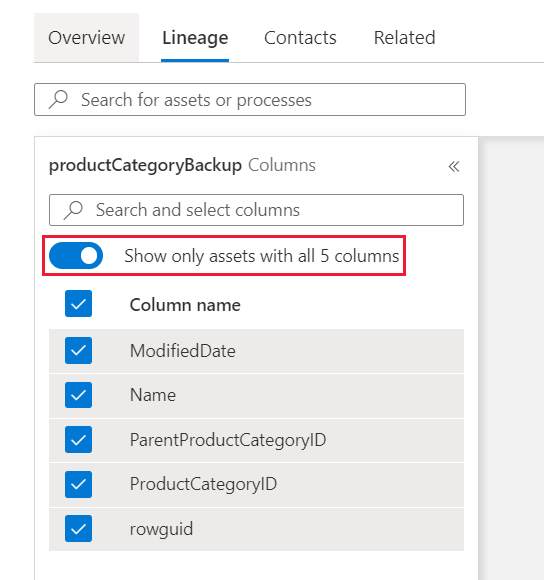
Use the toggle in the left pane to highlight the list of datasets in the lineage canvas. If you turn off the toggle, any asset that contains at least one of the selected columns is displayed. If you turn on the toggle, only datasets that contain all of the columns are displayed.
Process column lineage
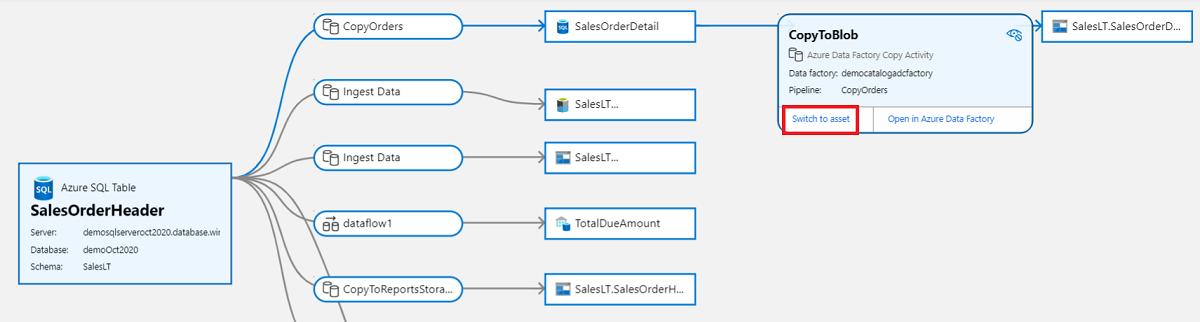
You can also view data processes, like copy activities, in the data catalog. For example, in this lineage flow, select the copy activity:
The copy activity will expand, and then you can select the Switch to asset button, which will give you more details about the process itself.
Data process can take one or more input datasets to produce one or more outputs. In Microsoft Purview, column level lineage is available for process nodes.
Switch between input and output datasets from a drop-down in the columns panel.
Select columns from one or more tables to see the lineage flowing from input dataset to corresponding output dataset.
Browse assets in lineage
Select Switch to asset on any asset to view its corresponding metadata from the lineage view. Doing so is an effective way to browse to another asset in the catalog from the lineage view.
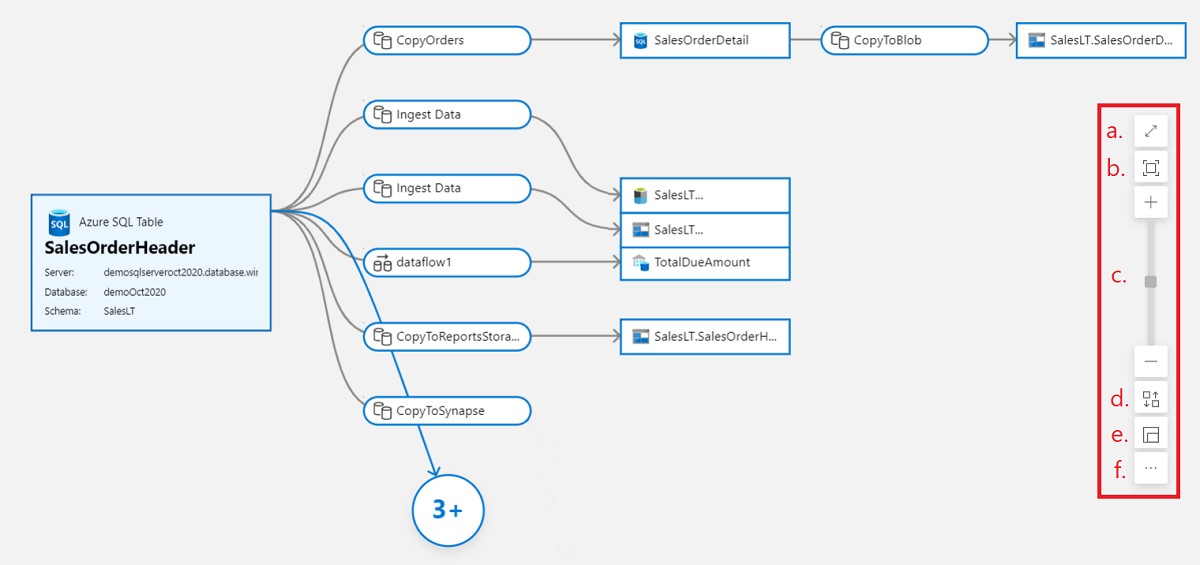
The lineage canvas could become complex for popular datasets. To avoid clutter, the default view will only show five levels of lineage for the asset in focus. The rest of the lineage can be expanded by selecting the bubbles in the lineage canvas. Data consumers can also hide the assets in the canvas that are of no interest. To further reduce the clutter, turn off the toggle More Lineage at the top of lineage canvas. This action will hide all the bubbles in lineage canvas.
Use the smart buttons in the lineage canvas to get an optimal view of the lineage:
- Full screen
- Zoom to fit
- Zoom in/out
- Auto align
- Zoom preview
- And more options:
- Center the current asset
- Reset to default view
Build custom lineage manually or with REST APIs
One of the important platform features of Microsoft Purview is the ability to show the lineage between datasets created by data processes. Systems like Data Factory, Data Share, and Power BI capture the lineage of data as it moves. In certain situations, automatically generated lineage by Purview is incomplete or missing for practical visualization and/or enterprise reporting purposes. In those scenarios, you can create custom lineage entries manually in the Microsoft Purview portal, or via Apache Atlas hooks and the REST API. Another major benefit of using REST APIs to report or build custom lineage is to overcome or mitigate the limitations of functionality exposed by Manual Lineage.
To build custom lineage manually, you can follow this user guide: Manual lineage entries in Microsoft Purview.
To build custom lineage in Microsoft Purview using the REST APIs, follow this user guide: Microsoft Purview - Building Custom Lineage using REST APIs.
Tip
In some cases, the REST APIs can provide more input and customization options than building the lineage entries manually through the portal.
Lineage best practices
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for