Events
Take the Microsoft Learn AI Skills Challenge
Sep 24, 11 PM - Nov 1, 11 PM
Elevate your skills in Microsoft Fabric and earn a digital badge by November 1.
Register nowThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
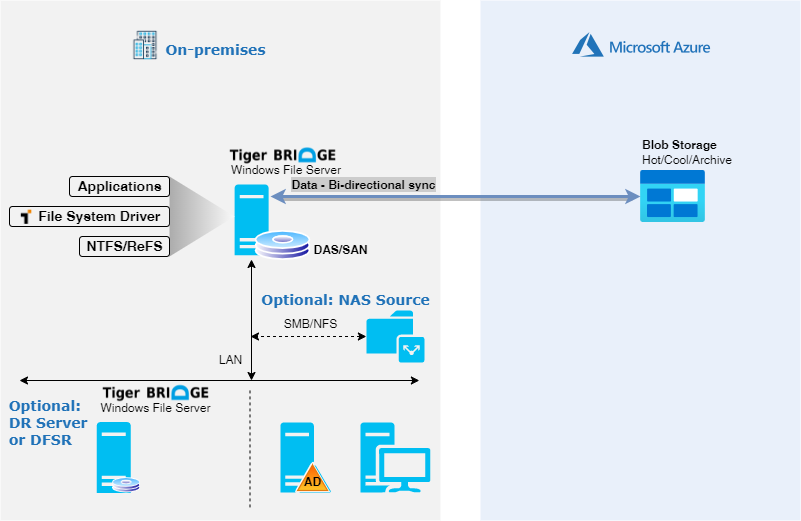
This article describes how to set up Tiger Bridge data management system with Azure Blob Storage. Tiger Bridge is fully integrated with NTFS, or ReFS file systems on windows platform. It can also manage volumes via SMB/NFS. Tiger Bridge is a connector that creates a single name-space between different sources, and Azure Blob Storage. It allows replication, tiering, and collaboration of unstructured data with file-locking capabilities between different file systems. Data is stored in Azure Blob Storage in native format, which makes it open to Azure, and third-party services (like AI/ML). Tiger Bridge can be deployed on physical or virtual infrastructure, and can easily be integrated within existing environment. Main features of the solution are:
Optional analytics component helps in assessing data sets, and recommends Azure Blob storage tiers.
Tiger Bridge can be deployed in two configurations:
Standalone hybrid configuration
Multi-site configuration
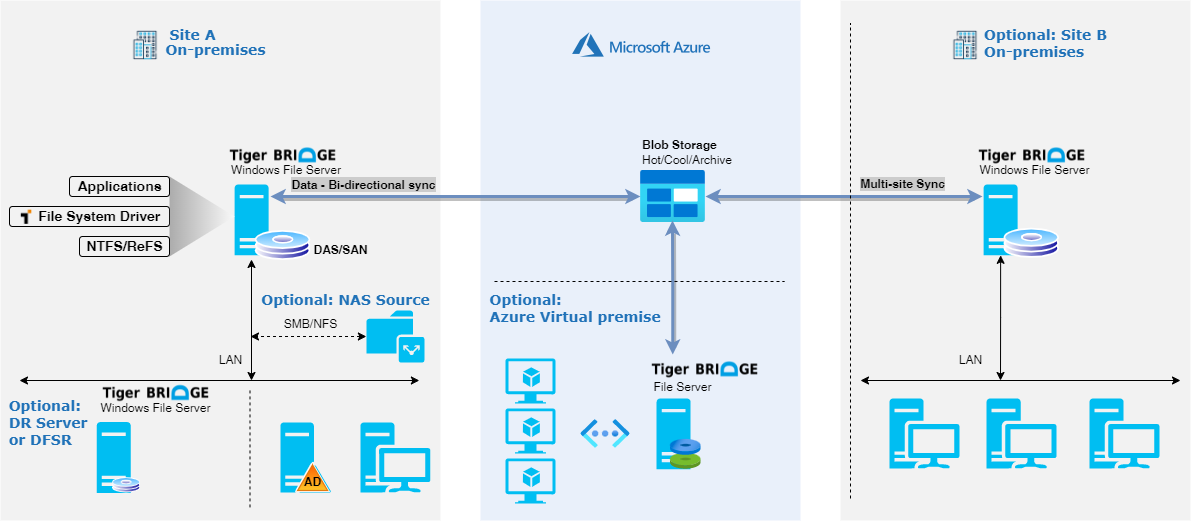
Upfront planning will help in seamless deploy for Tiger Bridge.
Microsoft offers a framework to follow to get you started with Azure. The Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF) is a detailed approach to enterprise digital transformation and comprehensive guide to planning a production grade cloud adoption. The CAF includes a step-by-step Azure setup guide to help you get up and running quickly and securely. You can find an interactive version in the Azure portal. You'll find sample architectures, specific best practices for deploying applications, and free training resources to put you on the path to Azure expertise.
Several aspects are important when considering hybrid deployment with Tiger Bridge on-premises.
Most important aspect is available network bandwidth. You will require enough network bandwidth to support initial replication, and any incremental change without impacting production applications. This section outlines the tools and techniques that are available to assess your network needs.
It's important to know how much typically unutilized bandwidth (or headroom) you have available on a day-to-day basis. To help you assess whether you can meet your goals for:
Use the following methods to identify the bandwidth headroom to Azure that is free to consume.
Before you begin the deployment, we recommend you plan your Tiger Bridge use case:
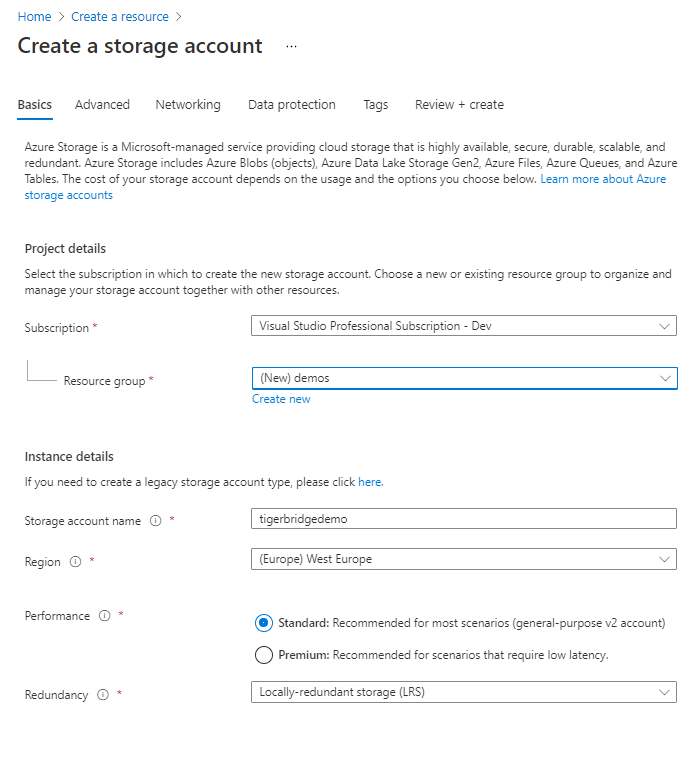
Before Tiger Bridge can be deployed, you need to create a Storage Account. Storage account will be used as a repository for data that is tiered, or replicated from Tiger Bridge solution. Tiger Bridge supports all Azure Storage services, including Archive Tier for Azure Storage Block blobs. That support allows to store less frequently data in cost-effective way but still access it through the well-known pane of glass. For additional information on Tiger Bridge, visit our comparison of ISV solutions.
Create a storage account
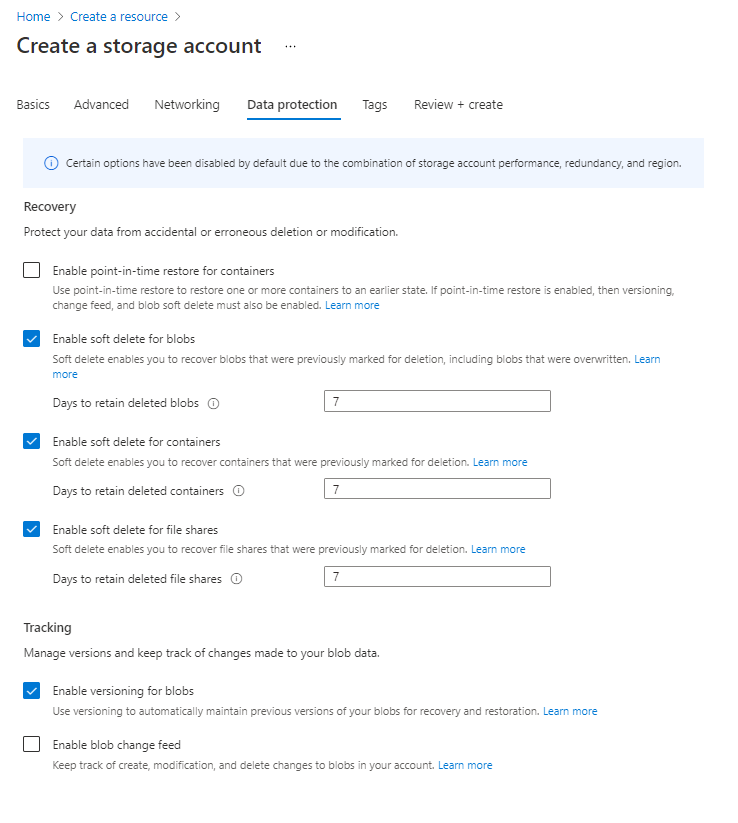
Choose data protection for the storage account
Create a container within storage account
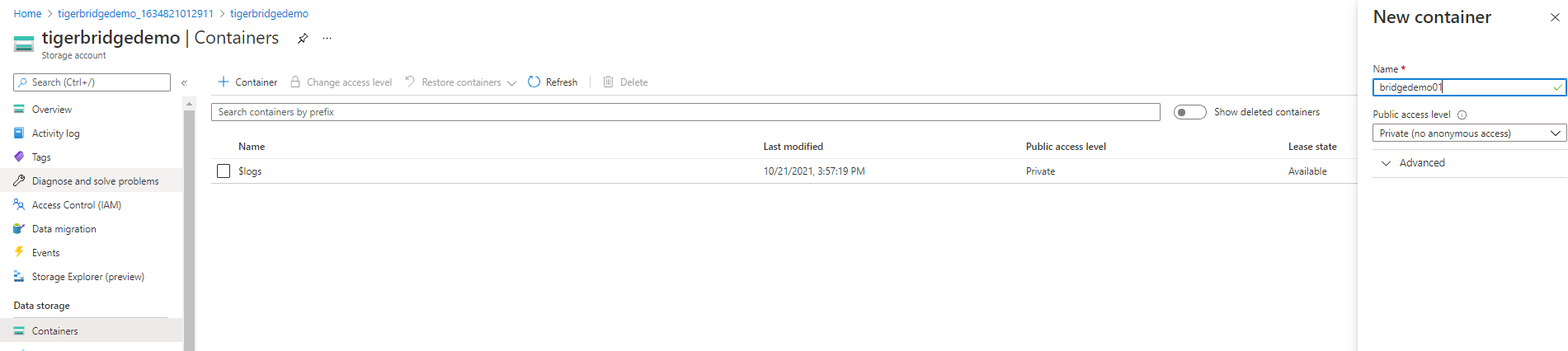
Before you can install Tiger Bridge, you need to have a Windows file server installed and fully configured. Windows server must have access to a storage account prepared in previous step.
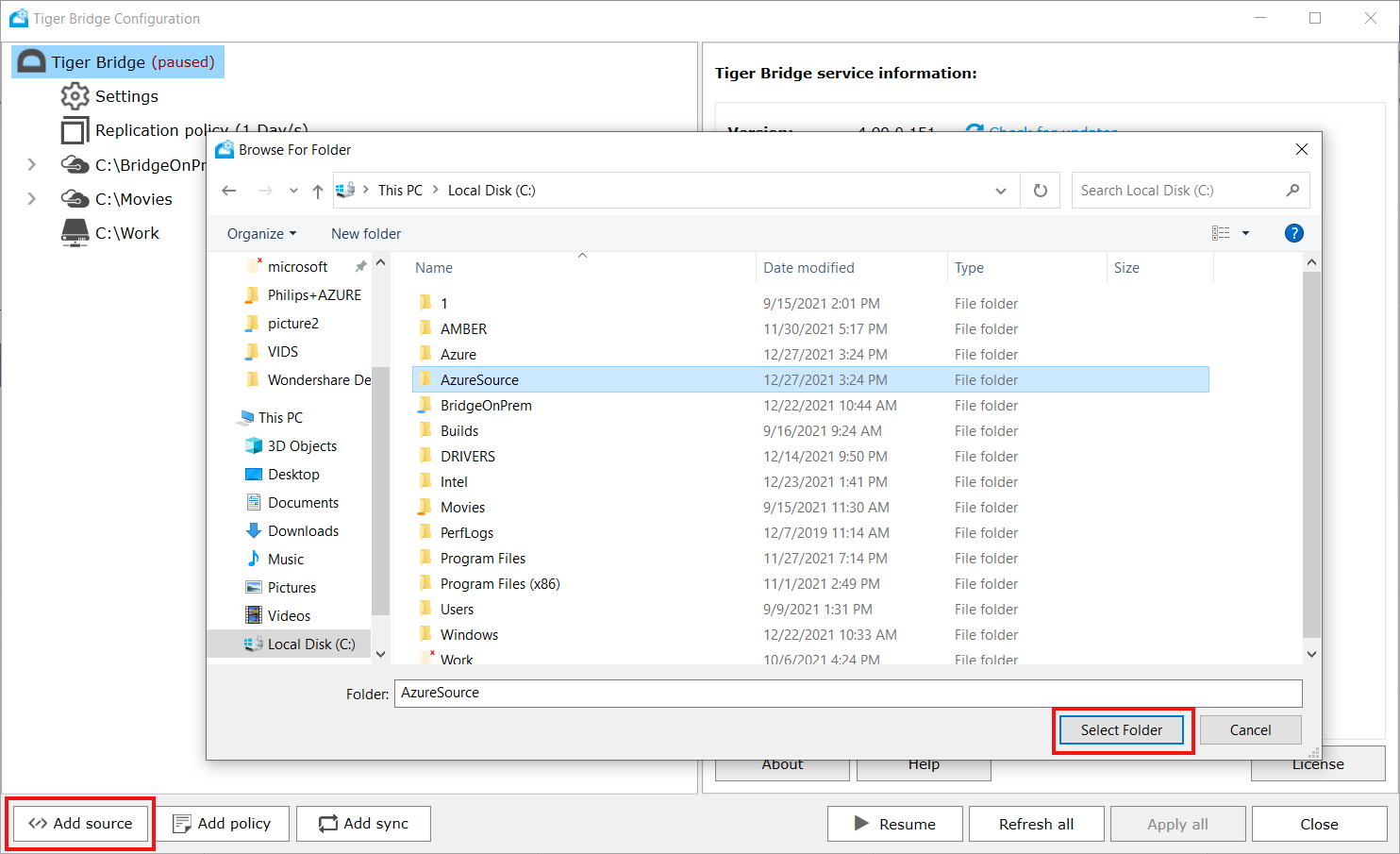
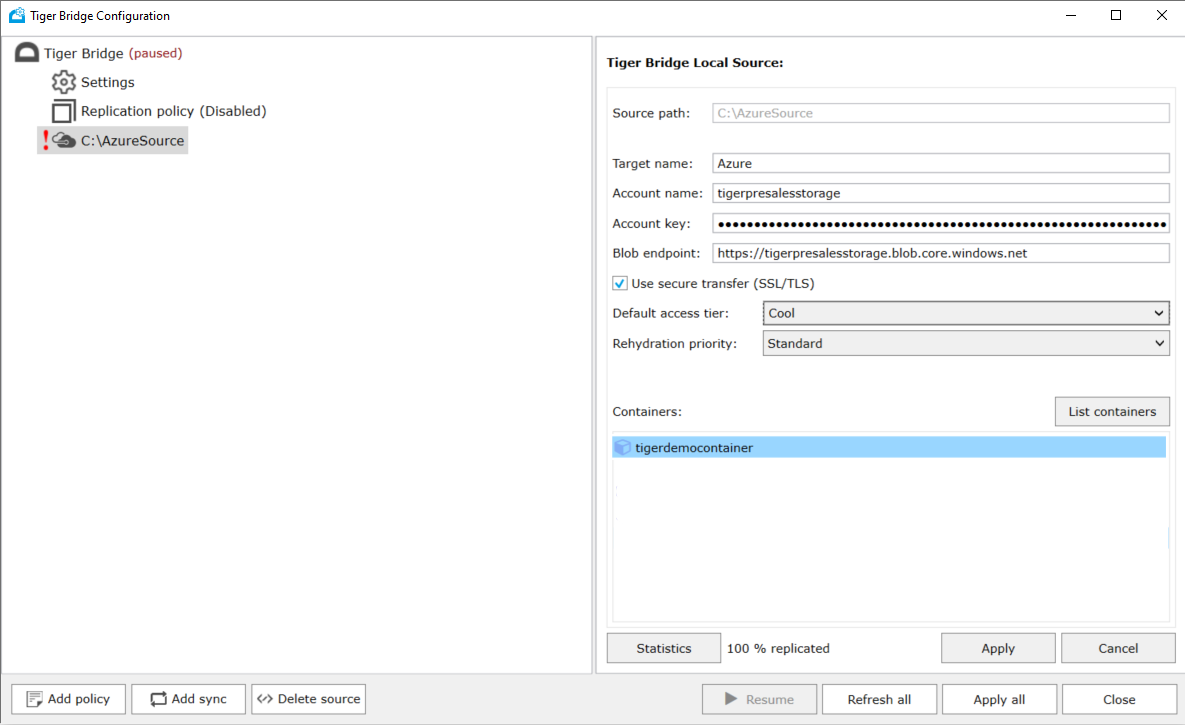 C:\AzureSource in the screenshot is a folder selected in the previous step.
C:\AzureSource in the screenshot is a folder selected in the previous step.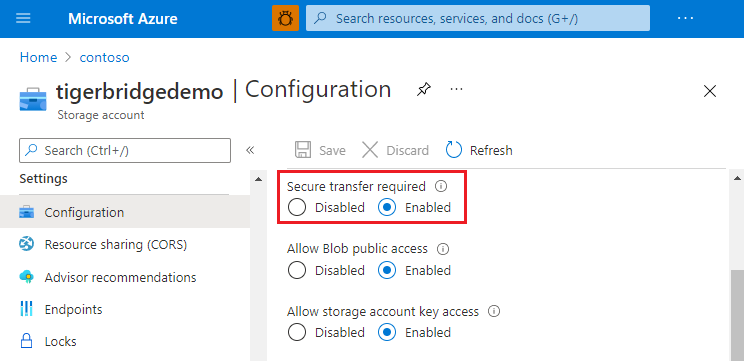
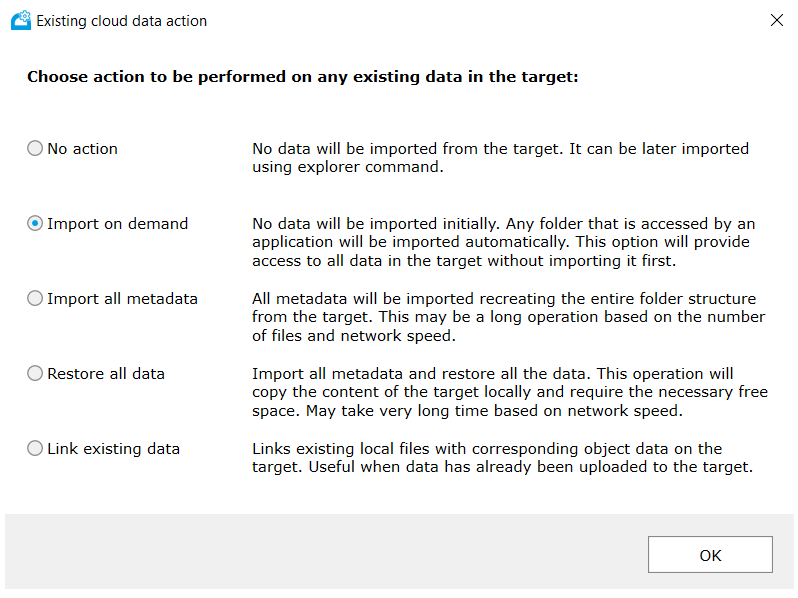
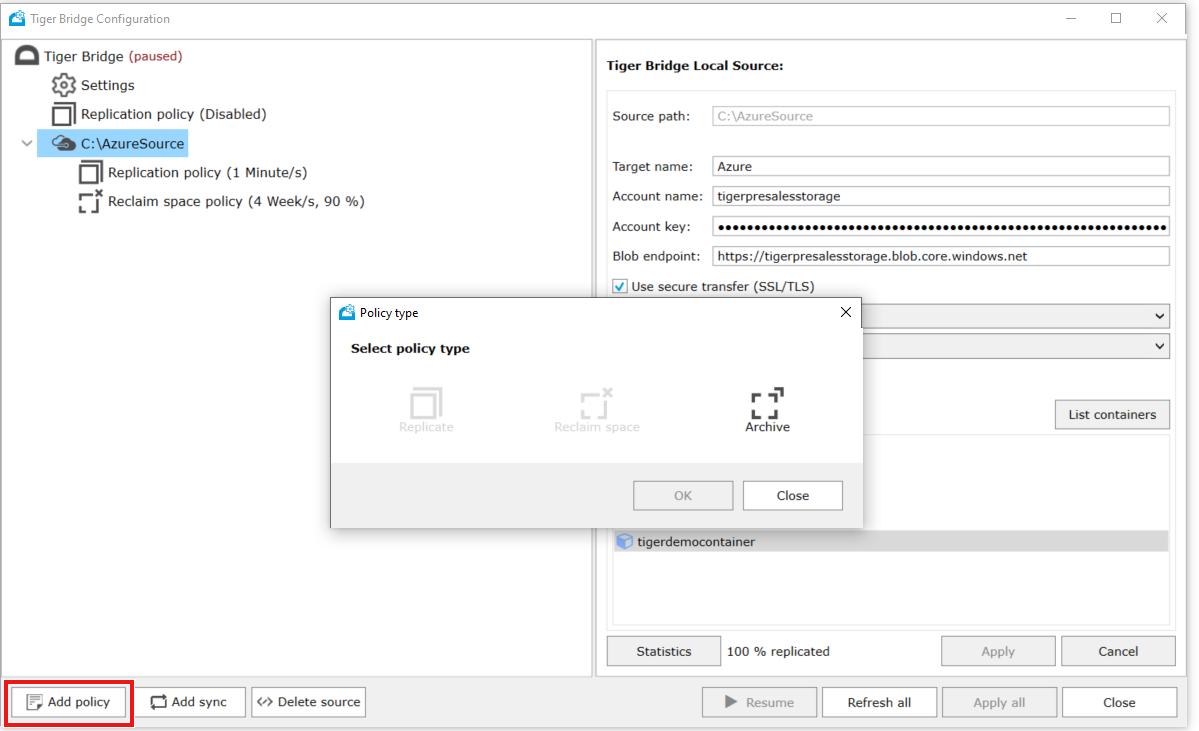
To deploy Tiger Bridge in multi-site configuration, follow the steps from deploying standalone hybrid configuration. These steps must be run on all Tiger Bridge servers you want to use in multi-site configuration. Servers must use the same storage accounts and same containers. Once done, do the following extra steps on all Tiger Bridge servers
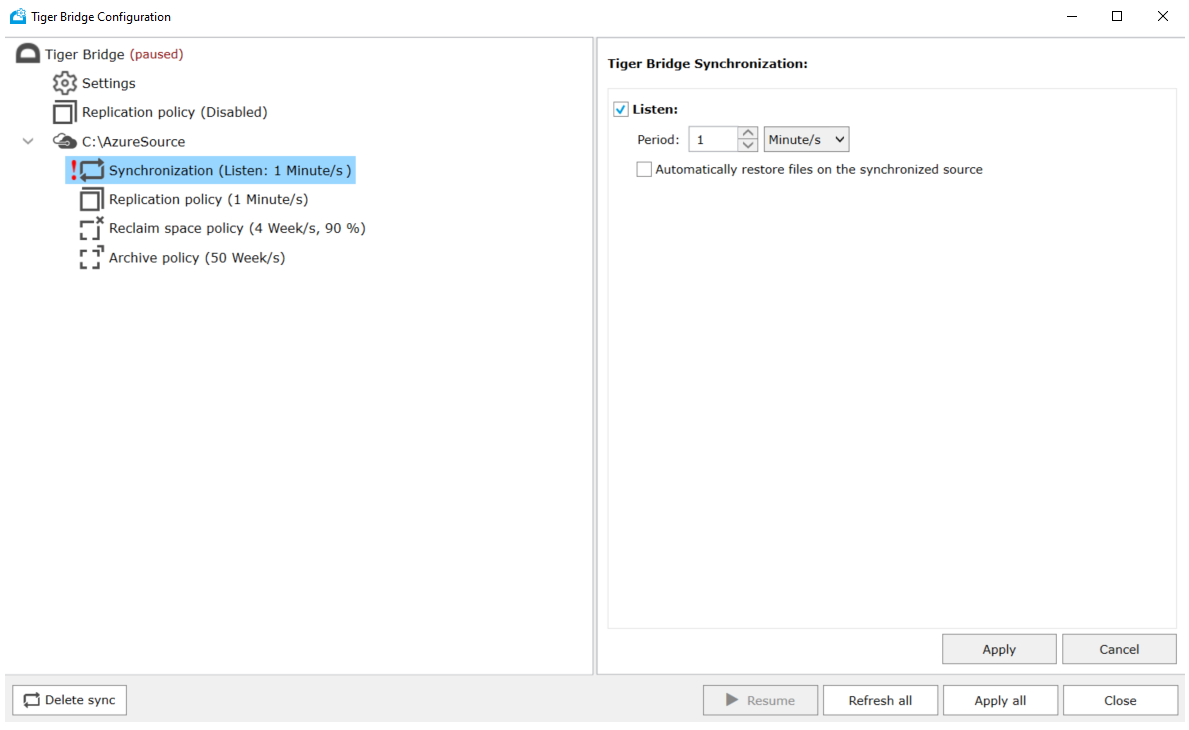
Tip
Tiger Bridge Policies and Synchronization can be defined as global (applied to all Tiger Bridge servers), or can be defined per Tiger Bridge server.
In the Azure portal search for support in the search bar at the top. Select Help + support -> New Support Request.
Tiger Technology provides 365x24x7 support for Tiger Bridge. To contact support, create a support ticket.
Events
Take the Microsoft Learn AI Skills Challenge
Sep 24, 11 PM - Nov 1, 11 PM
Elevate your skills in Microsoft Fabric and earn a digital badge by November 1.
Register nowTraining
Module
Configure Azure Blob Storage - Training
Learn how to configure Azure Blob Storage, including tiers and object replication.
Certification
Microsoft Certified: Azure Database Administrator Associate - Certifications
Administer an SQL Server database infrastructure for cloud, on-premises and hybrid relational databases using the Microsoft PaaS relational database offerings.