Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Configure Microsoft Office macro settings
This article walks IT administrators through meeting the Essential Eight mitigation strategy for configuring Microsoft Office macro settings. The outlined controls are aligned to the intent of Essential Eight Maturity Level 3. Applying the recommended policies to harden Microsoft 365 Apps meets certain controls for User Application Hardening.
Note
Guidance for enabling Office macro execution from Trusted Locations is outside the scope of this article. It is recommended to use a Trusted Publisher instead.
References
The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) provides multiple guidance documents on hardening Microsoft 365 Apps and the recommended policies for configuring macros. All policies in this article are based off the following references:
- Guidelines for System Hardening
- Hardening Microsoft 365, Office 2021, Office 2019, and Office 2016
- Microsoft Office Macro Security
Deploying Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise & ACSC Hardening Guidance for Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise
Intune has a feature called Policy Sets. Policy Sets provide the ability to combine applications, configuration policies, and other objects into a single deployable entity. The deployment of Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise should always be accompanied by the recommended ACSC Office Hardening policies. This ensures that all users of the Office suite of apps have the appropriate ACSC Office hardening policies applied.
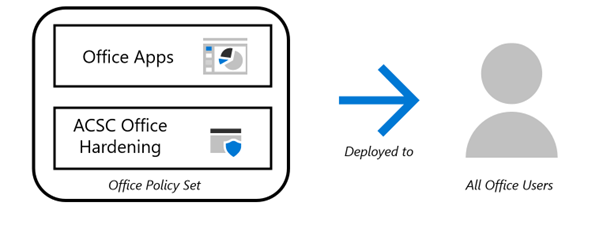
Implementation details
To apply the policy set, the administrator needs to complete three stages:
- Create the policy that targets the desired users.
- Import the ACSC Hardening Guideline policy.
- Create the policy set combining Microsoft 365 Apps and ACSC Hardening Guideline policy.
Stage 1: To create the policy to target desired users
- Create a policy to be used to contain users that are targeted with the Office apps and the Office hardening policies. For the rest of this article, this group is referred to as All Office Users.
- Create the Microsoft 365 Apps for Windows 10 or later app, under Apps > Windows > Add > Microsoft 365 Apps.
- Include the Microsoft 365 Apps as required by your organization.
- Set the architecture to: 64-bit (recommended).
- Set the Update Channel to: Semi-Annual Enterprise Channel (recommended).
Note
Don't assign the application. This is done in a later step.
Stage 2: To import the ACSC hardening guideline policy
- Save the ACSC Office Hardening Guidelines policy to your local device.
- Navigate to the Microsoft Intune console.
- Import a policy, under Devices > Windows > Configuration profiles > Create > Import Policy.
- Name the policy, select Browse for files under Policy file and navigate to the saved policy from step 1.
- Select Save.
Import script to prevent activation of Object Linking and Embedding packages
- Navigate to Devices > Scripts and create a new PowerShell script.
- Import the PowerShell script to prevent activation of Object Linking and Embedding packages.
- Run this script using the logged on credentials: Yes.
- Enforce script signature check: No.
-
- Run script in 64-bit PowerShell Host: No.
- Assign the PowerShell script to: All Office Users (created in Stage 1).
Note
This PowerShell script is specifically for Office 2016 and later. A script to prevent the activation of OLE for Office 2013 is provided here: OfficeMacroHardening-PreventActivationofOLE-Office2013.ps1.
Stage 3: Creation of the policy set combining Microsoft 365 Apps and ACSC Hardening Guideline policy
- Navigate to Devices > Policy sets > Create.
- Under Application Management > Apps, select Microsoft 365 Apps (for Windows 10 and later) (created in Stage 1).
- Under Device Management > Device Configuration Profiles, select ACSC Office Hardening (created in Stage 2).
- Under Assignments select All Office Users (created in Stage 1).
- Import the Endpoint Security Attack Surface Reduction policy.
- Navigate to Graph Explorer and authenticate.
- Create a POST request, using the beta schema to the Attack Surface Reduction policy endpoint:
https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/templates/0e237410-1367-4844-bd7f-15fb0f08943b/createInstance. - Copy the JSON in the ACSC Windows Hardening Guidelines-Attack Surface Reduction policy and paste it in the request body.
- (Optional) modify the name value if necessary.
- Assign the policy to: All Office Users (created in Stage 1).
Note
This Attack Surface Reduction (ASR) policy configures each of the ASR rules recommended by the ACSC in audit mode. ASR rules should be tested for compatibility issues in any environment before enforcement.
By following the document up to this point, the following additional mitigations are made:
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|
| 1488 | Microsoft Office macros in files originating from the internet are blocked. | For each Office application, the following policy has been configured (via theACSC Office Hardening policy): Block macros from running in Office files from the internet: Enabled |
| 1675 | Microsoft Office macros digitally signed by an untrusted publisher can't be enabled via the Message Bar or Backstage View. | For each Office application, the following policy has been configured (via the ACSC Office Hardening policy): Disable Trust Bar Notification for unsigned application: Enabled |
| 1672 | Microsoft Office macro antivirus scanning is enabled. | The following policies have been configured (via the ACSC Office Hardening Guidelines policy): Force Runtime AV Scan: Enabled Macro Runtime Scan Scope: Enabled for all documents Note: This requires Windows Defender to be running on the device. |
| 1673 | Microsoft Office macros are blocked from making Win32 API calls. | The following Attack Surface reduction rule has been configured (via the ASR policy): Block Win32 API calls from Office macro (92E97FA1-2EDF-4476-BDD6-9DD0B4DDDC7B) |
Controlling macro execution
The policy to block macros isn't included in the Policy Set. This provides the ability to selectively exempt groups of users that have a demonstrated business need to execute macros. All other users who don't have a demonstrated need are blocked from executing macros.
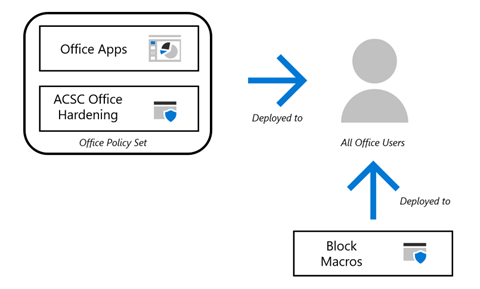
Implementation details
To facilitate a later step, which enables the execution of macros that are signed by Trusted Publishers, a new group must be created. This group is excluded from other Office macro policies to avoid conflicts and is allowed to execute macros that are signed by a Trusted Publisher. All other users are targeted with a policy to disable the execution of all macros.
To only allow macros that are signed by a Trusted Publisher:
- Create a group that contains users that are able to run Office macros if they're signed by a Trusted Publisher. This group is referred to as: Allow macro execution - Trusted Publisher.
- Save the All Macros Disabled policy policy to your local device.
- Navigate to the Microsoft Intune console..
- Import a policy, under Devices > Windows > Configuration profiles > Create > Import Policy.
- Name the policy, select Browse for files under Policy file and navigate to the saved policy (from step 2).
- Select Save
- Assign the All Macros Disabled policy to All Office Users (that was created at the start of this document).
- Exclude the Allow macro execution - Trusted Publisher group (from step 1).
By following the document up to this point, the following extra mitigations have been made:
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|
| 1671 | Microsoft Office macros are disabled for users that don't have a demonstrated business requirement. | All Office users by default are targeted with a policy that blocks the execution of macros (policies differ per Office application): Disable VBA for Office applications: Enabled |
| 1489 | Microsoft Office macro security settings can't be changed by users. | Policies configured and deployed via Intune can't be changed by standard users. The policies for hardening Office and disabling macros aren't able to be changed by end users. Ensure users that are exempted from the Block macros policy are targeted with a policy that only allows the running of macros from a trusted publisher. |
Trusted Publisher
For standard users, it's recommended to use Trusted Publisher whenever possible over allowing the execution of macros from a Trusted Location. Using a Trusted Location requires each macro to be thoroughly vetted before being placed into the Trusted Location. The reason for using a trusted publisher is because by choosing a Trusted Publisher, there's a demonstrated commitment to security with their products, reducing the risk of using their Macros compared to a location or website. Users exempted from the policy that blocks macros from the previous step are targeted with a policy that limits the execution of the macros to a curated list of Trusted Publishers.
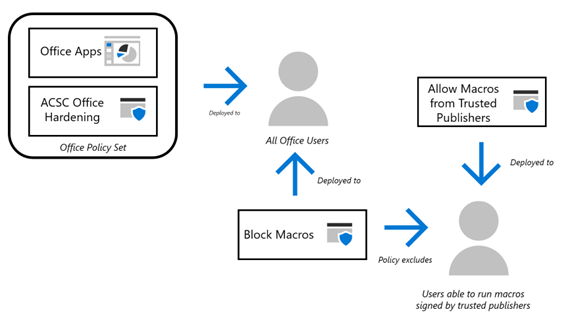
Microsoft Office macros are checked to ensure they're free of malicious code before being digitally signed or placed within Trusted Locations
By implementing the ACSC Office Hardening Guidelines, macros are scanned by Microsoft Defender before execution (see above with meeting ISM-1672). Before signing any macros, an administrator should execute the macros on a disconnected device (with the ACSC Office Hardening policies applied), dedicated for the use of determining the safety of the macros.
Third party tools are also available and can provide automated scanning and signing for submitted macros.
Implementation details
To import the Macros Enabled for Trusted Publishers policy, complete the following steps:
- Save the Macros Enabled for Trusted Publishers policy to your local device.
- Navigate to the Microsoft Intune console.
- Import a policy, under Devices > Windows > Configuration profiles > Create > Import Policy
- Name the policy, select Browse for files under Policy file and navigate to the saved policy (from step 2)
- Select Save
- Assign the policy to the group: Allow macro execution - Trusted Publisher
After importing the Trusted Publisher policy, you'll need to specify one or more Trusted Publishers. To add a Trusted Publisher, follow the instructions for adding a certificate to the Trusted Publishers certificate store using Intune: Adding a Certificate to Trusted Publishers using Intune - Microsoft Tech Community.
Create a new policy for each Trusted Publisher, rather than bundling multiple Publishers in the same policy. This simplifies identification of deployed Trusted Publishers and eases the removal of any Trusted Publishers that are no longer required. Deploy any Trusted Publishers certificate policies to the same group: Allow macro execution – Trusted Publisher.
Note
When signing macros, use the more secure version of the VBS project signature scheme: V3 signature.
By only allowing the execution of macros signed by a Trusted Publisher, the following additional mitigations are met:
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|
| 1674 | Only Microsoft Office macros running from within a sandboxed environment, a Trusted Location or that are digitally signed by a Trusted Publisher are allowed to execute. | For each Office app, the following setting has been configured (via the Macros Enabled for Trusted Publishers policy): Disable all except digitally signed macros: Enabled |
| 1487 | Only privileged users responsible for checking that Microsoft Office macros are free of malicious code can write to and modify content within Trusted Locations. | Not applicable. Only macros signed by a Trusted Publisher are allowed to execute for select users. |
| 1890 | Microsoft Office macros are checked to ensure they're free of malicious code before being digitally signed or placed within Trusted Locations. | An administrator launches macros on a device that has the ACSC Office Hardening policies applied, that is disconnected from the production environment and dedicated for the purpose of determining the safety of the macros prior to signing. |
Office macro execution logging
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) uses the following combination of technology, built with Microsoft's robust cloud service:
- Endpoint behavioral sensors: Embedded in Windows, these sensors collect and process behavioral signals from the operating system and send this sensor data to your private, isolated, cloud instance of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
- Cloud security analytics: Using big-data, device learning, and unique Microsoft optics across the Windows ecosystem, enterprise cloud products (such as Office 365), and online assets, behavioral signals are translated into insights, detections, and recommended responses to advanced threats.
- Threat intelligence: Generated by Microsoft hunters, security teams, and augmented by threat intelligence provided by partners, threat intelligence enables Defender for Endpoint to identify attacker tools, techniques, and procedures, and generate alerts when they're observed in collected sensor data.
MDE can be used to obtain and retain logs from endpoints that can then be used for detection of cyber security events.
The integration between Microsoft Intune and MDE allows easy onboarding into MDE for Intune managed devices.
Implementation details – onboarding endpoints into Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Create a new Windows Configuration Profile with a type of Template > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (desktop devices running Windows 10 or later)
- Set Expedite telemetry reporting frequency to Enable
- Assign the policy to a deployment group.
Once devices are onboarded to MDE, certain actions are captured for review and action can be taken if necessary. Fore more information, see Take response actions on a device in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
By onboarding devices to MDE, processes executed by macros that match deployed Attack Surface Reduction (ASR) rules are logged in Defender for Endpoint. Executions that match an indication of attack or compromise will generate an alert for review.
Validating list of trusted publishers
Validate the list of Trusted Publishers on a device with a user that has been allowed to execute macros from Trusted Publishers. In the Trusted Publishers certificate store, verify that each of the Trusted Publisher certificates:
- Is still required for macros in use in your organization.
- Is still within its validity period.
- Still has a valid chain of trust.
Remove any certificates that don't meet the previous criteria.
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|
| 1676 | Microsoft Office’s list of trusted publishers is validated on an annual or more frequent basis. | An administrator verifies the certificates in the Trusted Publishers certificate store, ensuring that all certificates are still required and within their validity period. Remove any certificates and associated policies that are no longer required. |