Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: Dynamics 365 Contact Center—standalone and Dynamics 365 Customer Service only
Setting up a comprehensive knowledge base is the key to increased customer satisfaction and improved productivity. A knowledge base is created to help you with solutions to the most common customer issues so that you can assist customers quickly. Learn how different search methods work in a knowledge base and how to get accurate results by using keywords or operators.
Dataverse search is enabled by default in all production environments, except environments that use their own encryption key. Learn more in Enable Dataverse search. When Dataverse search is enabled, knowledge management search control uses Dataverse search to search for knowledge articles. Learn more in What is Dataverse search?. If Dataverse search isn't enabled, the search mechanism switches to full-text search, which lets you run full-text queries against character-based data in SQL Server tables. Learn more in Full-text search.
Depending on the configurations made in Dataverse search through the Quick Find view columns list, you can view the information provided in search results, such as keywords, description, attachments, or article number. Learn more in Prerequisites.
How search works
By default, the search mode is "any", which means that the search results include articles that contain any of the search keywords you entered. However, if you have Dataverse search enabled along with the Knowledge search logic option in Settings, the search mode is set to "all". This means that the search results return records that contain all the search keywords you entered. Learn more in Set up knowledge search logic.
However, irrespective of your search settings, you can use the following search methods to search for your knowledge articles.
Boolean operators
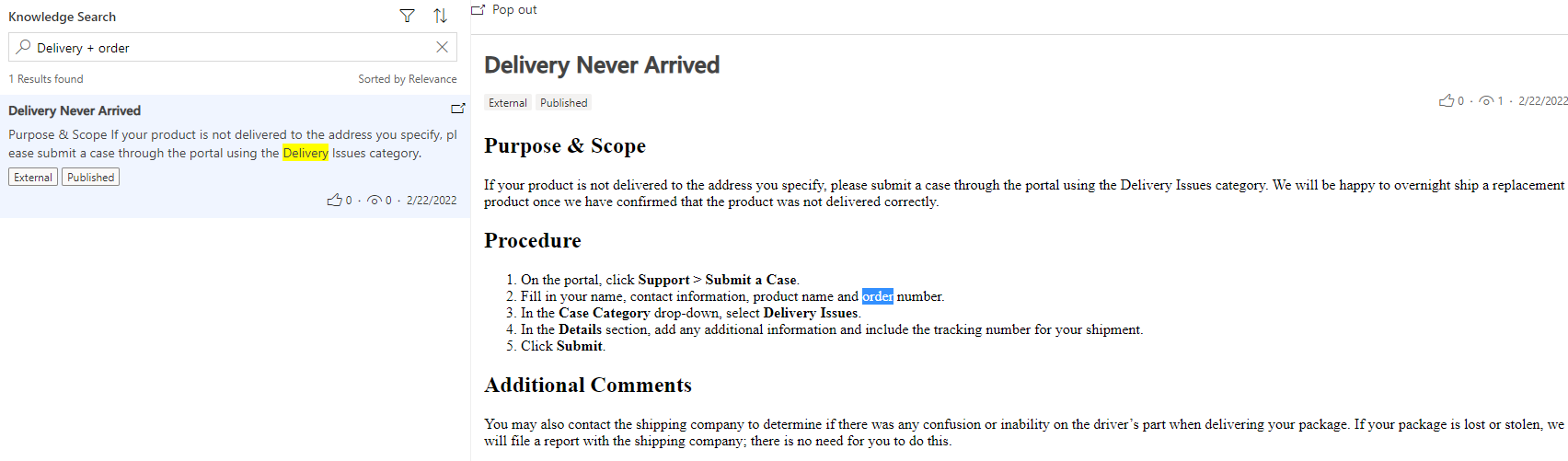
AND operator
Use the AND operator when you need to search with a combination of words. The search results only include articles that contain all the individual terms separated by (+). For example, Delivery + order returns the article Delivery Never Arrived which has Delivery and order in the article content.
- Query: AND operator; denoted by +
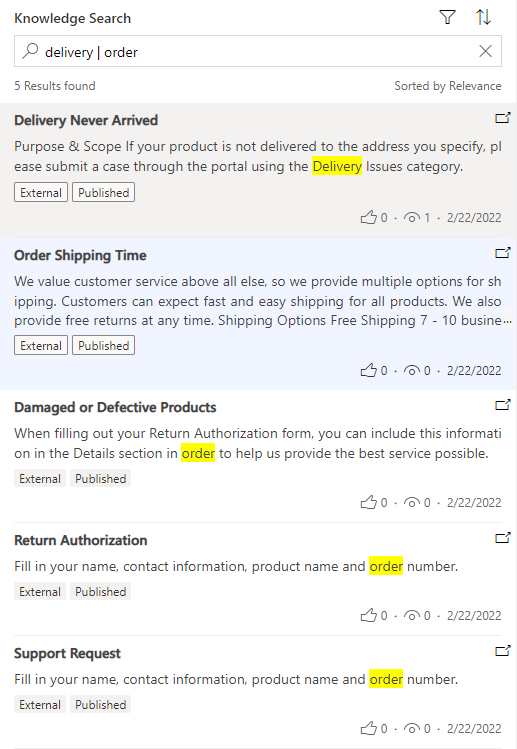
OR operator
Use the OR operator to search for either of terms. Search terms separated by a vertical bar ( | ). For example, searching for delivery | order returns records with reference to either term.
Query syntax: OR operator; denoted by |
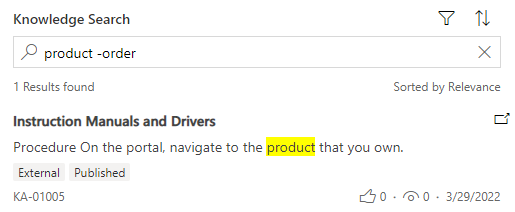
NOT operator
Use the NOT operator with a hyphen (-) before a keyword to indicate that it should be excluded from the search results. For example, when you search for product, all rows matching the term product appear in the search results. However, searching for product -order matches all rows that contain the term product but not the term order.
- Query syntax: NOT operator; denoted by -
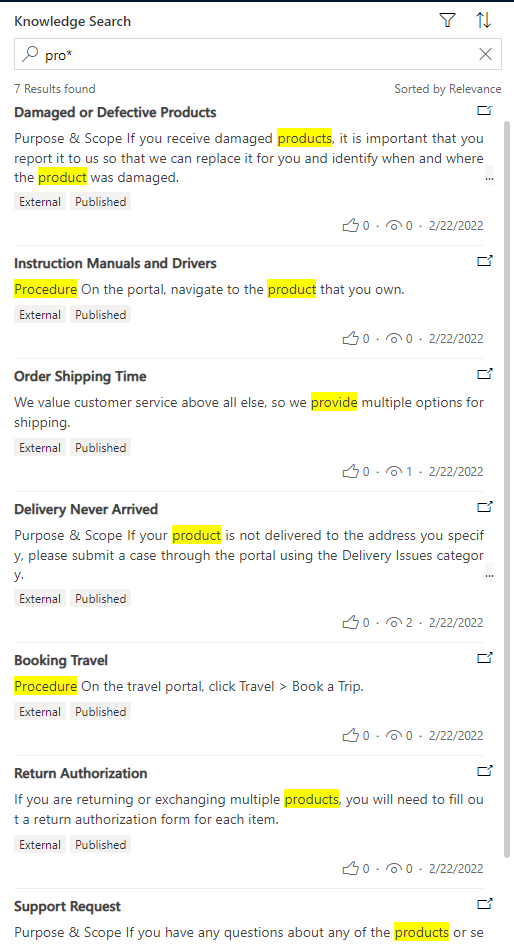
Wildcards
Use wildcards as placeholders for one or more text characters. Use an asterisk at the beginning or end of a keyword. For example, searching on pro* shows results for all records associated with a keyword that starts with pro. Pro* searches for product, products, and procedure.
- Query syntax: Search term with asterisk at the beginning or end of a keyword.
Exact matches
To search for an exact match, use double quotation marks around a keyword. For example, searching on "order shipping time" matches those exact keywords in an knowledge article. This type of search ignores commonly used words such as a, an, and the.
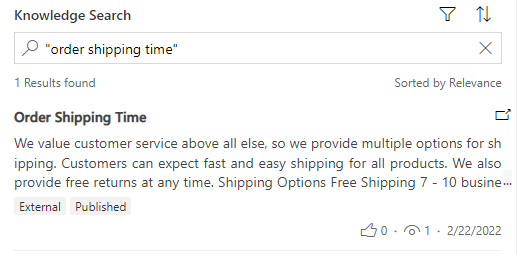
- Query syntax: Search term with double quotation marks around it.
Related information
Add the Knowledge Base Search control to forms
Create and manage knowledge articles
Understand knowledge base search mechanisms
Set up a search provider
Add a knowledge article subgrid to a form