Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Overview
The HoloLens 2 display is a combination of waveguides and light projectors. Users look through the waveguides—the lenses inside the visor—when wearing the headset. The light projectors are inside the enclosure above the brow. HoloLens 2 uses laser light to illuminate the display.
Troubleshooting
Take the following steps to ensure the highest visual quality of holograms presented in displays:
Increase brightness of the display. Holograms look best when the display is at its brightest level. When wearing the HoloLens, the brightness buttons are on the left side of the visor near your temple.
Bring visor closer to your eyes. Swing the visor down to the closest position to your eyes.
Shift visor down. Try moving the brow pad on your forehead down, which will result in the visor moving down closer to your nose.
Run eye calibration. The display uses your interpupillary distance (IPD) and eye gaze to optimize images on the display. If you don't run eye calibration, the image quality may be made worse. To run eye calibration, go to Settings > System > Calibration > Run eye calibration.
Run display color calibration. On Windows Holographic, version 21H1 and onwards, you can select an alternative color profile for your HoloLens 2 display. This may help colors appear more accurate, especially at lower display brightness levels. Display color calibration can be found in the Settings app, on the System > Calibration page.
Note
Because this setting saves a new color profile to your display firmware, it's a per-device setting (and not unique to each user account).
How to use display color calibration
Launch the Settings app and navigate to System > Calibration.
Under Display color calibration, select the Run display color calibration button.
The display color calibration experience will launch and encourage you to make sure your visor is in the correct position.
After you proceed through the instruction dialog boxes, your display will automatically be dimmed to 30% brightness.
Tip
If you're having trouble seeing the dimmed scene in your environment, you can manually adjust the brightness level of HoloLens 2 using the brightness buttons on the left side of the device.
Select buttons 1-6 to instantly try out each color profile, and find one that looks the best to your eyes (this usually means the profile that helps the scene appear most neutral, with the grayscale pattern and skin tones looking as expected.)
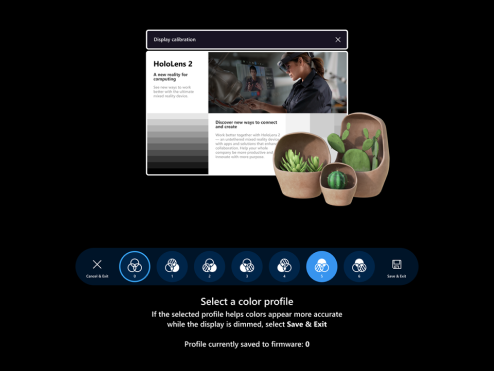
When you're happy with the selected profile, select the Save & Exit button
If you prefer not to make changes, select the Cancel & Exit button and your changes will be reverted
Tip
Here are some helpful tips to keep in mind while using the display color calibration setting:
- You can re-run display color calibration from Settings whenever you'd like
- If anyone on the device has previously used the setting to change color profiles, the date/time of the most recent change will be reflected on the Settings page
- When you re-run display color calibration, the color profile that was previously saved will be highlighted and Profile 0 won't appear (as Profile 0 represents the display's original color profile)
- If you want to revert to the display's original color profile, you can do so from the Settings page (see how to reset color profile)
How to reset color profile
If you're unhappy with the custom color profile saved to your HoloLens 2, you can restore the device's original color profile:
- Launch the Settings app and navigate to System > Calibration.
- Under Display color calibration, select the Reset to default color profile button.
- When the dialog box opens, select Restart if you're ready to restart HoloLens 2 and apply your changes.
Top display color calibration known issues
- On the Settings page, the status string that tells you when the color profile was last changed will be out of date until you reload that page of Settings
- Workaround: Select another Settings page and then re-select the Calibration page.
- If your HoloLens 2 goes to sleep while running display color calibration, it will later resume into the mixed reality home and your display brightness level will still be dimmed.
- You may need to try pressing the brightness buttons on the left side of your device up/down a few times before they work as expected.
- Localization isn't complete for all markets
FAQ
What are the patterns that occasionally flash in the bottom corners of the display?
Occasionally, your HoloLens 2 will show different patterns in the bottom left and right corners of the display. Examples are shown below (animated GIFs). This pattern is part of the normal operation of your HoloLens 2 device to calibrate the display for optimum experience.

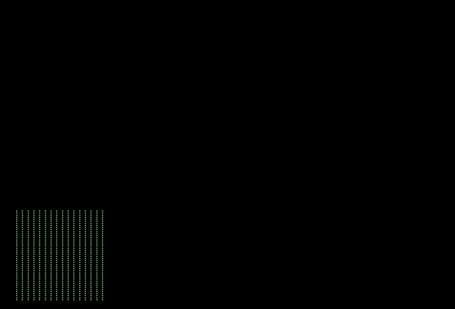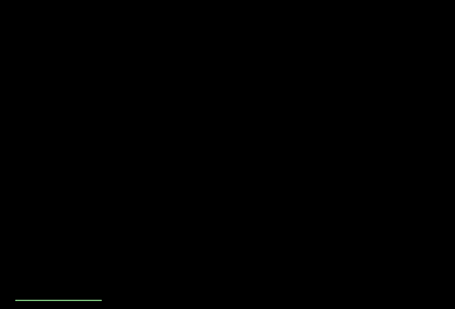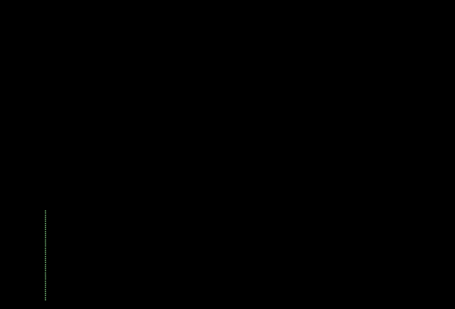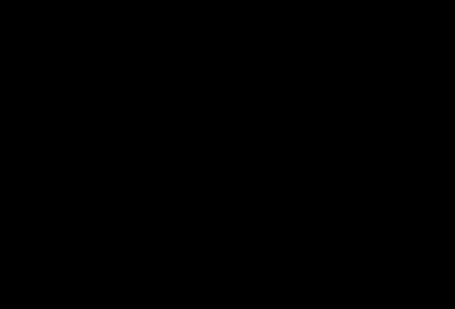
Why am I unable to take an accurate photograph of my HoloLens 2 display?
The HoloLens 2 display is designed to be viewed by the human eye. The device has an active color correction system that adapts to a user's eyes. Compared to the human eye, cameras see environments differently and below are some factors that may impact any inconsistency between what a camera captures and what a user sees.
- Eye position. The HoloLens 2 display is designed specifically for the eye position of the user. The HoloLens 2 employs eye tracking technology to adapt to the user's eye position. A camera that that is mispositioned by a few millimeters can lead to image distortion. Accurate positioning with a camera is difficult and needs to match the exact location and eye relief for which the device is performing color correction.
- Eye movement. The display adapts to the movement of a user’s eye to adjust colors. What is shown on the display may differ depending if the user is looking at the center, the edge, or the corner of the display. A single image capture could at best only show what the display looks like for the axis that matches an eye gaze direction.
- Binocular viewing. The HoloLens 2 display is designed to be viewed with both eyes. The brain adapts to seeing two images and fuses them together. Images of only one display ignore the information from the other display.
- Camera exposure time. The exposure time of the camera needs to be an exact multiple of 1/120th of a second. The HoloLens display frame rate is 120 Hz. Due to the way the HoloLens 2 draws images, capturing a single frame is also not enough to match a human's visual experience. At the same time, if the device moves at all—even micromovements—the system reprojects the image on the display to stabilize holograms. Capturing multiple frames while keeping the HoloLens from moving usually requires a laboratory setup.
- Camera aperture size. The camera's aperture size must be at least 3 mm to capture an accurate image. Cell phone cameras with small apertures integrate light from a smaller area than the human eye does. The device applies color correction for patterns observed by larger apertures. With small apertures, uniformity patterns are sharper and remain visible despite color corrections applied by the system.
- Camera entrance pupil. The entrance pupil of the camera should be at least 3 mm in diameter to capture an accurate image. Otherwise, the camera captures some high frequency patterns not visible to the eye. The position of the entrance pupil both needs to be in front of the camera and positioned at the eye relief distance to avoid introducing aberrations and other variations to the captured image.
- Camera position. Cameras that meet the requirements to view the HoloLens 2 display are larger, and it's difficult to position the camera close enough to the HoloLens 2 display to observe the color corrected image. If the camera is in the wrong place, the color correction may negatively impact the capture of the HoloLens 2 display.
- Image correction. Typical digital cameras and smartphone cameras apply a tone reproduction curve (TRC) which boosts contrast and color to provide a snappier outcome. When applied to a HoloLens 2 display, this tone curve amplifies non-uniformities.
All said, it's still possible for specialized industrial cameras to capture representative images from the HoloLens 2 display. Unfortunately, smartphone, consumer, and professional cameras won't capture images that match what a user sees on HoloLens 2.
What does eye calibration do to display image quality?
The HoloLens 2 display actively color corrects images based on the position of the user's eyes. Eye calibration provides two important inputs: (1) the user's interpupillary distance (IPD), and (2) the direction each eye is looking. Without eye calibration, the system defaults to a nominal eye position with no eye movement. The difference between active color correction versus no correction depends on the user's physiology themselves. For example, users that have the same IPD as the system default will see fewer color correction improvements. While users that have a much narrower or wider IPD than the system default will see more changes to the display image.
Note, a new feature in Windows Holographic version 20H2 will start automatically detecting eye position.
What are the display differences between HoloLens (1st gen) and HoloLens 2?
Among the top requests customers gave Microsoft after experiencing HoloLens 1 was (1) increase the field-of-view and (2) increase the brightness. Technology developments allowed Microsoft to produce waveguides that doubled the field-of-view's area and produce light projectors with a display that are up to three times brighter. The hardware sets the baseline for a trio of tradeoffs for the display image quality: (1) field-of-view, (2) brightness, and (3) color uniformity. Continued technology advancement allows improvements in all areas without sacrificing another area. In the interim, the existing technology sets the limits available for these tradeoffs.
What improvements are coming that will improve HoloLens 2 image quality?
While we have many investigations underway to improve image quality, the following areas are expected to arrive in upcoming updates:
- Automatic Eye Position. This feature will enable the eye calibration procedures to take place in the background. Users will no longer need to run eye calibration for active color correction to work. It will instead just work.
- Color Calibration Improvements. This update focuses on color values of darker colors (for example, dark gray). Right now, dimmer colors pick up a red tone. This issue also happens as the entire display is dimmed—the entire display picks up red colors. This issue is a result of too much activity in the red color channel for these darker colors. We've characterized the laser illumination curves at these dimmer colors and are working to offer a user calibration procedure. The result will be more color accuracy across the brightness spectrum. It will not change the appearance of white backgrounds at full brightness. We continue to advise use of dark mode design patterns in apps.
- Reading Mode. It's possible for app developers to tradeoff the display field-of-view to achieve higher angular resolution. App developers can override the projection matrix so that content is rendered at the display's drawing resolution. This feature results in 30% reduction in field-of-view and a corresponding increase in angular resolution. Work is underway to introduce this capability to the Mixed Reality Toolkit. When available, reading mode will work on any HoloLens 2 OS—it isn't dependent on an OS update.
Operating system updates are delivered automatically. You can also test early releases of software improvement through the insider preview program.
What guidance is available for developers to apply dark mode design principles?
Users will have the best experience when avoiding white backgrounds. Dark mode is a design principle used by apps to use black or dark colored backgrounds. The system settings default to dark mode and can be adjusted by going to Settings > System > Color.
Developers are advised to follow dark mode design guidance:
When a hologram requires a white background, keep the size of the hologram smaller than the display's full field of view. This size allows users to put the hologram in the center of the display.
How do you clean a HoloLens 2 display?
Use a microfiber cloth to gently wipe the visor. To sanitize the visor, use 70% isopropyl alcohol to lightly moisten a cloth then wipe the visor. Read full guidance in the HoloLens 2 cleaning FAQ.