Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: ✅ Microsoft Fabric ✅ Azure Data Explorer
The function series_fit_lowess_fl() is a user-defined function (UDF) that applies a LOWESS regression on a series. This function takes a table with multiple series (dynamic numerical arrays) and generates a LOWESS Curve, which is a smoothed version of the original series.
Prerequisites
- The Python plugin must be enabled on the cluster. This is required for the inline Python used in the function.
- The Python plugin must be enabled on the database. This is required for the inline Python used in the function.
Syntax
T | invoke series_fit_lowess_fl(y_series, y_fit_series, [ fit_size ], [ x_series ], [ x_istime ])
Learn more about syntax conventions.
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| y_series | string |
✔️ | The name of the input table column containing the dependent variable. This column is the series to fit. |
| y_fit_series | string |
✔️ | The name of the column to store the fitted series. |
| fit_size | int |
For each point, the local regression is applied on its respective fit_size closest points. The default is 5. | |
| x_series | string |
The name of the column containing the independent variable, that is, the x or time axis. This parameter is optional, and is needed only for unevenly spaced series. The default value is an empty string, as x is redundant for the regression of an evenly spaced series. | |
| x_istime | bool |
This boolean parameter is needed only if x_series is specified and it's a vector of datetime. The default is false. |
Function definition
You can define the function by either embedding its code as a query-defined function, or creating it as a stored function in your database, as follows:
Define the function using the following let statement. No permissions are required.
Important
A let statement can't run on its own. It must be followed by a tabular expression statement. To run a working example of series_fit_lowess_fl(), see Examples.
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
// Write your query to use the function here.
Examples
The following examples use the invoke operator to run the function.
LOWESS regression on regular time series
To use a query-defined function, invoke it after the embedded function definition.
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
//
// Apply 9 points LOWESS regression on regular time series
//
let max_t = datetime(2016-09-03);
demo_make_series1
| make-series num=count() on TimeStamp from max_t-1d to max_t step 5m by OsVer
| extend fnum = dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_lowess_fl('num', 'fnum', 9)
| render timechart
Output

Test irregular time series
To use a query-defined function, invoke it after the embedded function definition.
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
let max_t = datetime(2016-09-03);
demo_make_series1
| where TimeStamp between ((max_t-1d)..max_t)
| summarize num=count() by bin(TimeStamp, 5m), OsVer
| order by TimeStamp asc
| where hourofday(TimeStamp) % 6 != 0 // delete every 6th hour to create irregular time series
| summarize TimeStamp=make_list(TimeStamp), num=make_list(num) by OsVer
| extend fnum = dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_lowess_fl('num', 'fnum', 9, 'TimeStamp', True)
| render timechart
Output

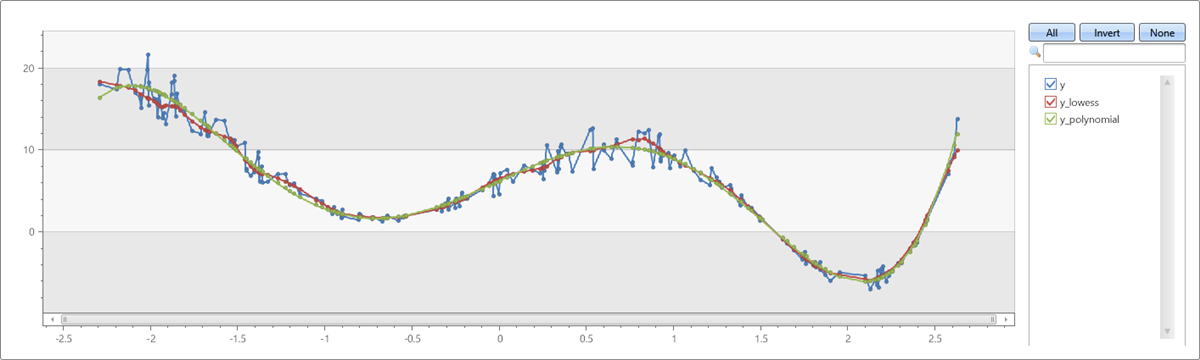
Compare LOWESS versus polynomial fit
To use a query-defined function, invoke it after the embedded function definition.
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
range x from 1 to 200 step 1
| project x = rand()*5 - 2.3
| extend y = pow(x, 5)-8*pow(x, 3)+10*x+6
| extend y = y + (rand() - 0.5)*0.5*y
| summarize x=make_list(x), y=make_list(y)
| extend y_lowess = dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_lowess_fl('y', 'y_lowess', 15, 'x')
| extend series_fit_poly(y, x, 5)
| project x, y, y_lowess, y_polynomial=series_fit_poly_y_poly_fit
| render linechart
Output