Microsoft Defender for Endpoint plug-in for Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Overview
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 2, which replaces the previous version of WSL (supported by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint without a plug-in), provides a Linux environment that is seamlessly integrated with Windows yet isolated using virtualization technology. The Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL) plug-in enables Defender for Endpoint to provide more visibility into all running WSL containers, by plugging into the isolated subsystem.
Known issues and limitations
Be aware of the following before you start:
The plug-in does not currently support automatic updates. When a new version is released, a new MSI package needs to be applied to perform the update. This can be done through any of the software deployment tools. Updates will come through Microsoft updates.
As it takes a few minutes for the plug-in to fully instantiate and up to 30 minutes for a WSL2 instance to onboard itself, short-lived WSL container instances might result in the WSL2 instance not showing up in the Microsoft Defender portal (https://security.microsoft.com). Once a (any) distribution has been running long enough (at least 30 minutes), it does show up.
The use of a custom kernel in combination with the plug-in isn't supported. When you attempt to launch WSL with the plugin installed, you'll encounter the error A fatal error was returned by plugin 'DefenderforEndpointPlug-in'. Error message: 'Custom Kernel/Configuration not supported.'.
Software prerequisites
WSL version 2.0.7 or later must be running with at least one active distro.
Run
wsl --updateto make sure you are on the latest version. Ifwsl -–versionshows a version older than 2.0.7, runwsl -–update –pre-releaseto get the latest update.Defender for Endpoint must be onboarded and running on the Windows host OS.
The host OS must be running Windows 10 Client, version 2004 and higher (build 19044 and higher) or Windows 11 Client to support the Windows Subsystem for Linux versions that can work with the plug-in.
Software components and installer file names
Installer: DefenderPlugin-x64-0.23.1102.4.msi. You can download it from the onboarding page in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Installation directories:
C:\Program Files\C:\ProgramData\
Components installed:
DefenderforEndpointPlug-in.dll. This DLL is the library to load Defender for Endpoint to work within WSL. You can find it at C:\Program Files\Microsoft Defender for Endpoint plug-in for WSL\plug-in.healthcheck.exe. This program checks the health status of Defender for Endpoint and enables you to see the installed versions of WSL, plug-in, and Defender for Endpoint. You can find it at C:\Program Files\Microsoft Defender for Endpoint plug-in for WSL\tools.
Installation steps
If your Windows Subsystem for Linux isn't installed yet, follow these steps:
Open Terminal or Command Prompt. (In Windows, go to Start > Command Prompt. Or, right-click the start button and then select Terminal.)
Run the command
wsl -–install.1. Confirm WSL is installed and running
Using Terminal or Command Prompt, run
wsl –updateto make sure you have the latest version.Run the
wslcommand to ensure WSL is running before testing.
2. Install the plug-in
After WSL is running and fully up to date, follow these steps to install the plug-in:
Install the MSI file downloaded from the onboarding section in the Microsoft Defender portal (Settings > Endpoints > Onboarding > Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (plug-in).)
Open a command prompt/terminal and run
wsl.
Note
If WslService is running, it stops during the installation process. You do not need to onboard the subsystem separately; instead, the plug-in automatically onboards to the tenant the Windows host is onboarded to.
Installation validation checklist
After update or installation, wait for at least five minutes for the plug-in to fully initialize and write log output.
Open Terminal or Command Prompt. (In Windows, go to Start > Command Prompt. Or, right-click the start button and then select Terminal.)
Run the command:
cd "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Defender for Endpoint plug-in for WSL\tools".Run the command
.\healthcheck.exe.Review the details of Defender and WSL and make sure they match or exceed the following requirements:
- Defender Plug-in Version:
0.23.1102.4 - WSL Version:
2.0.7.0or later - WSL Defender Version:
101.23092.0011 - WSL Defender Health:
Healthy
- Defender Plug-in Version:
Setting a proxy for Defender running in WSL
This section describes how to configure proxy connectivity for the Defender for Endpoint plug-in. If your enterprise uses a proxy to provide connectivity to Defender for Endpoint running on the Windows host, continue reading to determine whether you need to configure it for the plug-in.
If you want to use the host windows EDR telemetry proxy configuration for MDE for the WSL plug-in, nothing more is required. This configuration is adopted by the plug-in automatically.
If you want to use the host winhttp proxy configuration for MDE for WSL plug-in, nothing more is required. This configuration is adopted by the plug-in automatically.
If you want to use the host network and network proxy setting for MDE for WSL plug-in, nothing more is required. This configuration is adopted by the plug-in automatically.
Plug-in Proxy selection
If your host machine contains multiple proxy settings, the plug-in selects the proxy configurations with the following hierarchy:
Defender for Endpoint static proxy setting (
TelemetryProxyServer).Winhttpproxy (configured throughnetshcommand).Network & Internet proxy settings.
Example: If your host machine has both Winhttp proxy and Network & Internet proxy, the plug-in selects Winhttp proxy as the proxy configuration.
Note
The DefenderProxyServer registry key is no longer supported. Follow the above mentioned steps to configure proxy in plug-in.
Connectivity test for Defender running in WSL
The following procedure describes how to confirm that Defender in Endpoint in WSL has internet connectivity.
Open Registry Editor as an administrator.
Create a registry key with the following details:
- Name:
ConnectivityTest - Type:
REG_DWORD - Value:
Number of seconds plug-in must wait before running test. (Recommended: 60 seconds) - Path:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Lxss\Plugins\DefenderPlug-in
- Name:
Once the registry is set, restart wsl using the following steps:
Open Command Prompt and run the command,
wsl --shutdown.Run the command
wsl.
Wait for 5 minutes and then run
healthcheck.exe(located atC:\Program Files\Microsoft Defender for Endpoint plug-in for WSL\toolsfor the results of the connectivity test).If successful, you can see that the connectivity test was successful.
Note
To set a proxy for use in WSL containers (the distributions running on the subsystem), see Advanced settings configuration in WSL.
Verifying functionality and SOC analyst experience
After installing the plug-in, the subsystem and all its running containers are onboarded to the Microsoft Defender portal.
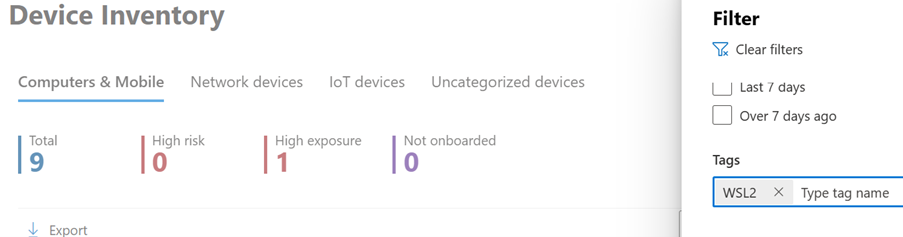
Sign into the Microsoft Defender portal, and open the Devices view.
Filter using the tag WSL2.
You can see all WSL instances in your environment with an active Defender for Endpoint plug-in for WSL. These instances represent all distributions running inside WSL on a given host. The hostname of a device matches that of the Windows host. However, it's represented as a Linux device.
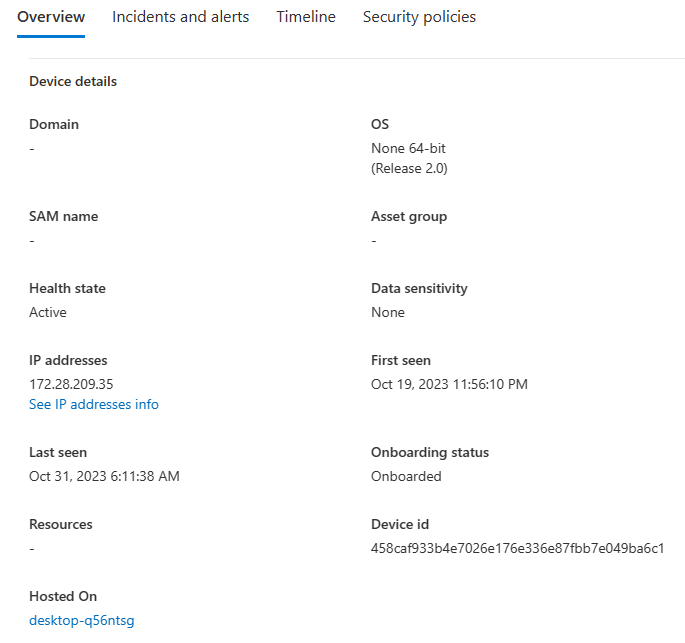
Open the device page. In the Overview pane, there's a link for where the device is hosted. The link enables you to understand that the device is running on a Windows host. You can then pivot to the host for further investigation and/or response.
The timeline is populated, similar to Defender for Endpoint on Linux, with events from inside the subsystem (file, process, network). You can observe activity and detections in the timeline view. Alerts and incidents are generated as appropriate as well.
Test the plug-in
To test the plug-in after installation, follow these steps:
Open Terminal or Command Prompt. (In Windows, go to Start > Command Prompt. Or, right-click the start button and then select Terminal.)
Run the command
wsl.Download and extract the script file from https://aka.ms/LinuxDIY.
At the Linux prompt, run the command
./mde_linux_edr_diy.sh.An alert should appear in the portal after a few minutes for a detection on the WSL2 instance.
Note
It takes about 5 minutes for the events to appear on the Microsoft Defender portal
Treat the machine as if it were a regular Linux host in your environment to perform testing against. In particular, we would like to get your feedback on the ability to surface potentially malicious behavior using the new plug-in.
Advanced hunting
In the Advanced Hunting schema, under the DeviceInfo table, there's a new attribute called HostDeviceId that you can use to map a WSL instance to its Windows host device. Here are a few sample hunting queries:
Get all WSL device IDs for the current organization/tenant
Get all WSL device ids for the current organization/tenant
let wsl_endpoints = DeviceInfo
| where OSPlatform == "Linux" and isempty(HostDeviceId) != true
| distinct DeviceId;
wsl_endpoints
Get WSL device IDs and their corresponding host device IDs
Get WSL device ids and their corresponding host device ids
DeviceInfo
| where OSPlatform == "Linux" and isempty(HostDeviceId) != true
| distinct WSLDeviceId=DeviceId, HostDeviceId
Get a list of WSL device IDs where curl or wget was run
Get a list of WSL device ids where curl or wget was run
let wsl_endpoints = DeviceInfo
| where OSPlatform == "Linux" and isempty(HostDeviceId) != true
| distinct DeviceId;
DeviceProcessEvents
| where FileName == "curl" or FileName == "wget"
| where DeviceId in (wsl_endpoints)
| sort by Timestamp desc
Troubleshooting
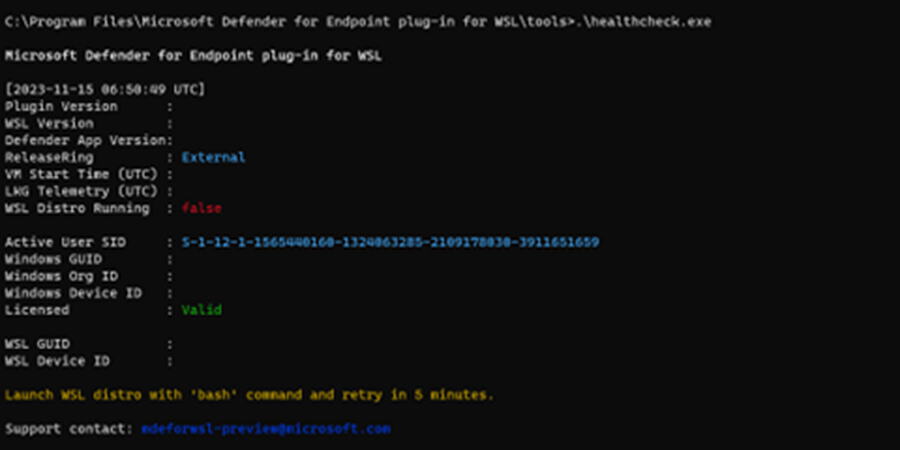
The command
healthcheck.exeshows the output, "Launch WSL distro with 'bash' command and retry in 5 minutes."If the previously mentioned error occurs, take the following steps:
Open a terminal instance and run the command
wsl.Wait for at least 5 minutes before rerunning the health check.
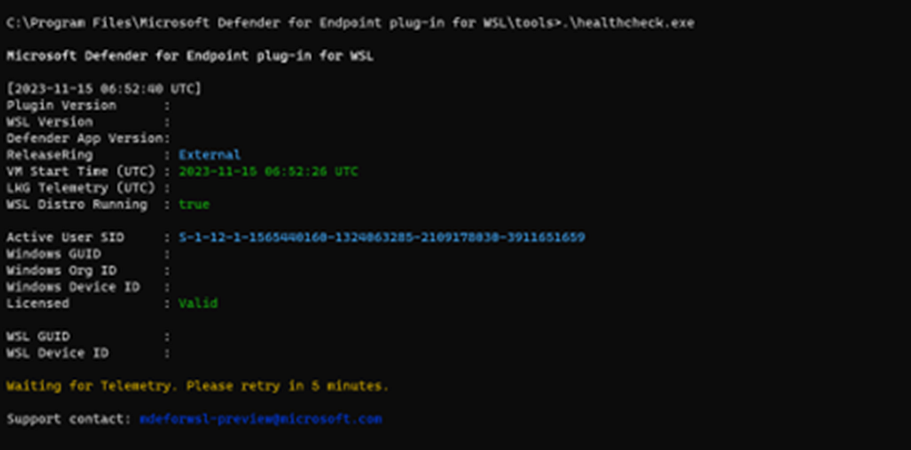
The
healthcheck.execommand might show the output, "Waiting for Telemetry. Please retry in 5 minutes."If that error occurs, wait for 5 minutes and rerun
healthcheck.exe.If you don't see any devices in the Microsoft Defender portal, or you don't see any events in the timeline, check these things:
If you aren't seeing a machine object, make sure sufficient time has passed for onboarding to complete (typically up to 10 minutes).
Make sure to use the right filters, and that you have the appropriate permissions assigned to view all device objects. (For example, is your account/group is restricted to a specific group?)
Use the health check tool to provide an overview of overall plug-in health. Open Terminal, and run the
healthcheck.exetool fromC:\Program Files\Microsoft Defender for Endpoint plug-in for WSL\tools.
- Enable the connectivity test and check for Defender for Endpoint connectivity in WSL. If the connectivity test fails, provide the output of the health check tool to mdeforwsl-preview@microsoft.com.
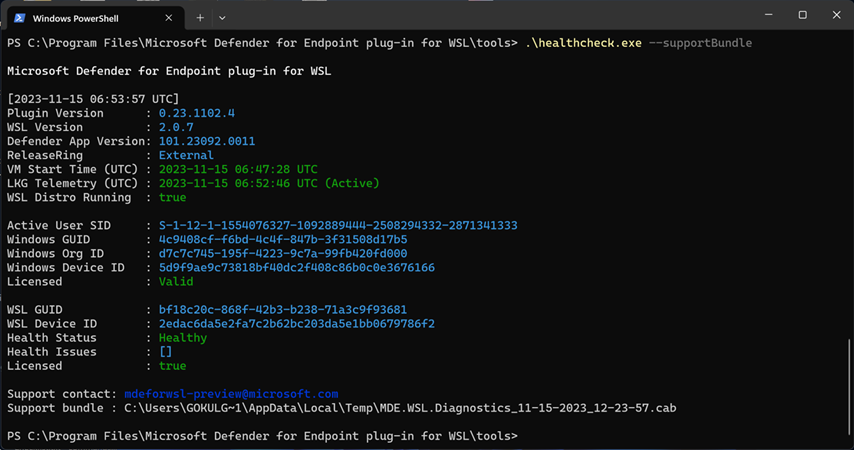
In case you face any other challenges or issues, open the terminal and run the following commands to generate the support bundle:
cd "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Defender for Endpoint plug-in for WSL\tools".\healthcheck.exe --supportBundleThe support bundle can be found in the path provided by the previous command.
Microsoft Defender Endpoint for WSL supports Linux distributions running on WSL 2. If they're associated with WSL 1, you might encounter issues. Therefore, it is advised to disable WSL 1. To do so with the Intune policy, perform the following steps :
Navigate to your Microsoft Intune admin center portal.
Go to Devices > Configuration Profiles > Create > New Policy.
Select Windows 10 and later > Settings catalog.
Create a name for the new profile, and search for Windows Subsystem for Linux to see and add the full list of available settings.
Set the Allow WSL1 setting to Disabled, to ensure that only WSL 2 distributions can be used.
Alternately, if you want to keep using WSL 1, or not use the Intune Policy, you can selectively associate your installed distributions to run on WSL 2, by running the command in PowerShell:
wsl --set-version <YourDistroName> 2To have WSL 2 as your default WSL version for new distributions to be installed in the system, run the following command in PowerShell:
wsl --set-default-version 2
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for