Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Miracast over Infrastructure protocol provides the ability to transmit a multimedia data stream over a local wireless network instead of Wi-Fi Direct (WFD). The process of such transmission is called "projection".
A Miracast over Infrastructure session involves the following principals.
Miracast Source: A device that sends audio and video streams to the Miracast Sink. This device is sometimes called a "sender". Optionally, this device can also receive input signals from the Miracast Sink.
Miracast Sink: A device that receives audio and video streams from the Miracast Source. This device is sometimes called a "receiver". Optionally, this device can also send input signals back to the Miracast Source.
The following diagram illustrates the logical flow of establishing a Miracast over Infrastructure session, including successful and unsuccessful outcomes. For further details, see Protocol Details (section 3).
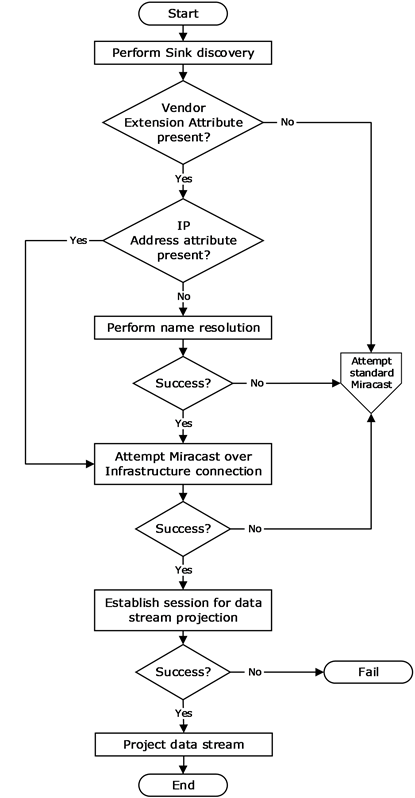
Figure 1: A Miracast over Infrastructure session
A Miracast over Infrastructure session consists of three phases: device discovery, host name resolution, and projection.
The device discovery phase starts with a Miracast Source trying to find devices capable of performing the role of Miracast Sink. Each Sink advertises its capabilities by transmitting Beacon and Probe Response frames that might include WSC IE Vendor Extension attributes (section 2.2.8).
A Sink is selected from those discovered; for example, by asking a user to pick one. If the Vendor Extension attribute from the selected Sink does not indicate support for Miracast over Infrastructure, the Source falls back to using standard Miracast [WF-WSC2.0.2].
If the Vendor Extension attribute contains one or more IP Address attributes (section 2.2.8.5), the Source optionally skips the host name resolution phase and proceeds to the projection phase.
In the host name resolution phase, name resolution is performed on the name in a Host Name attribute (section 2.2.8.2) in the Vendor Extension attribute. If name resolution is unsuccessful, the Source again falls back to using standard Miracast.
In the projection phase, the Source attempts a connection to the Sink for sending Miracast over Infrastructure messages (section 2.2). Finally, the Sink establishes a connection with the Source for streaming multimedia data. If that connection cannot be established, the entire process fails.