Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This topic contains best practices for creating and managing background workflow processes.
Avoid infinite loops
It’s possible to create logic in a background workflow that initiates an infinite loop, which consumes server resources and affects performance. The typical situation where an infinite loop might occur is if you have a background workflow configured to start when an column is updated and then updates that column in the logic of the workflow. The update action triggers the same background workflow that updates the row and triggers the background workflow again and again.
The workflows you create include logic to detect and stop infinite loops. If a background workflow process is run more than a certain number of times on a specific row in a short period of time, the process fails with the following error: This workflow job was canceled because the workflow that started it included an infinite loop. Correct the workflow logic and try again. The limit of times is 16.
Use background workflow templates
If you have workflows that are similar and you anticipate creating more workflows that follow the same pattern, save your background workflow as a workflow template. This way, the next time you need to create a similar workflow, use the template to create the background workflow and avoid entering all the conditions and actions from scratch.
In the Create Process dialog box, choose New process from an existing template (select from list).
Use child workflows
If you apply the same logic in different workflows or in conditional branches, define that logic as a child workflow so you don’t have to replicate that logic manually in each background workflow or conditional branch. This helps make your workflows easier to maintain. Instead of examining many workflows that might apply the same logic, you can just update one workflow.
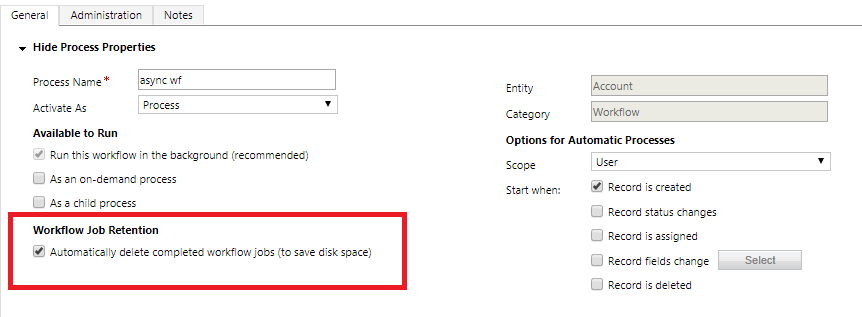
Automatically delete completed background workflow jobs
For background (asynchronous) workflows, we recommend selecting the Automatically delete completed workflow jobs (to save disk space) option in the background workflow definition. Selecting this check box allows the system to delete background workflow logs for successful executions to save space. Notice that logs from failed background workflow executions will always be saved for troubleshooting.
Limit the number of workflows that update the same table
Running more than one background workflow that updates the same table can cause resource lock issues. Imagine several workflows running where every opportunity update triggers an update to the associated account. Multiple instances of these workflows running and attempting to update the same account row at the same time can result in resource locking issues. Background workflow failures occur and an error message, such as SQL Timeout: Cannot obtain lock on resource resource name, is recorded.
Use Notes to keep track of changes
When you edit workflows you should use the Notes tab and type what you did and why. This allows others to understand the changes you made.
Next steps
Configure background workflow processes
Monitor and manage background workflow processes