Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can quickly create a Power BI semantic model directly from a SharePoint list. The semantic model will be full-fledged Power BI semantic model that you can use to create reports, analyze in Excel, and more.
Creating a semantic model directly from a SharePoint list is an easy and quick way to share a semantic model, because if you save it to a shared workspace, everyone with the sufficient permissions in the workspace can use it. You can also use semantic model sharing to share it with other users who don’t have a role in the workspace.
To keep the data fresh after you've created the semantic model, either refresh the data manually or set up scheduled refresh.
This feature creates a semantic model in the Power BI service directly from a SharePoint list. If you need to model or transform the data in ways that aren't available in the service, you can also connect to the SharePoint list from Power BI Desktop. For more information, see Create a report on a SharePoint List in Power BI Desktop.
Prerequisites
You must have a Power BI account to be able to use this functionality.
Create a semantic model from a SharePoint list
To create a Power BI semantic model from a SharePoint list:
Open your SharePoint list.
In the actions bar, select Export > Export to Power BI.
Power BI will open and a dialog will ask you to name the semantic model and choose a workspace to save it in. By default the semantic model will be given the same name as the SharePoint list and saved to My workspace. You can choose your own name and destination workspace. If you're a free user in Power BI, you'll only be able to save to My workspace.
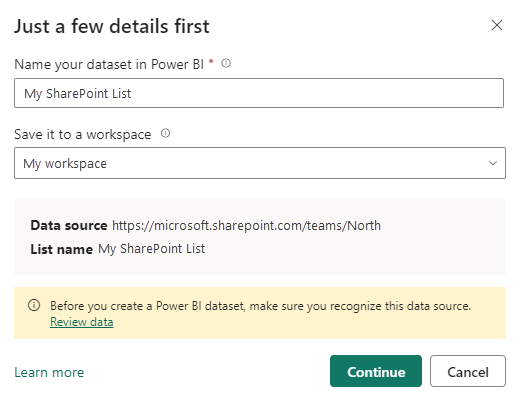
The dialog also shows the URL of the data source (SharePoint site) and name of the SharePoint list. To prevent inadvertently exposing sensitive data, make sure that you recognize the data source and are familiar with the data. Select Review data if you want to check the SharePoint list before allowing export to continue. For more information about when reviewing the data might be a good idea, see Reviewing the SharePoint list data.
Select Continue. Your semantic model will be created, and you'll be taken to the details page of the new semantic model. From there you can do all the things you can do with a regular Power BI semantic model - refresh the data, share the semantic model, create new reports, and more. See semantic model details for more information.
Note
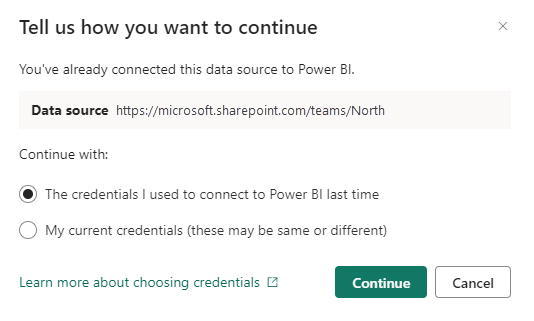
If you've connected to the SharePoint site from Power BI before, you'll be asked to choose which credentials to use to for the connection between Power BI and the Sharepoint site before being taken to the semantic model details page. For help deciding which credentials to choose, see Choosing which credentials to authenticate with.
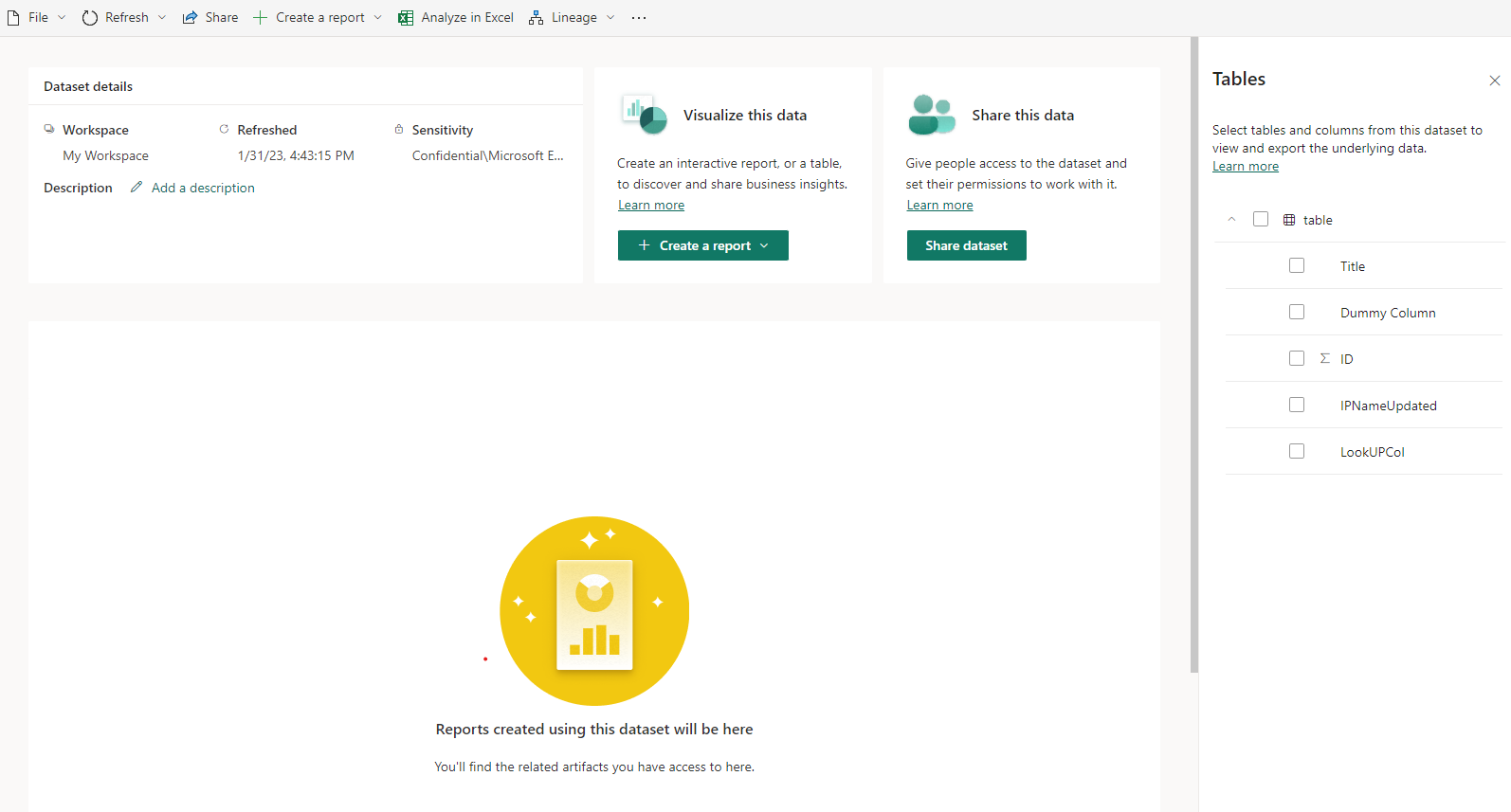
To keep the data fresh after you've created the semantic model, either refresh the data manually or set up scheduled refresh.
Reviewing the SharePoint list data
When you export a SharePoint list to Power BI, a redirect URL is created that includes all the parameters needed to launch the create semantic model process in Power BI. If you're the person who selected Export to BI in your SharePoint list, you probably don't need to worry about reviewing the data because you most likely are familiar with the data you're exporting.
Reviewing the data is important if you weren't the one who exported the SharePoint list, but rather received a link from someone for creating a semantic model from a SharePoint list. In such a case, you might not be familiar with the data that is being exported, and hence it's important to review it to make sure that no sensitive data is inadvertently being exposed.
Choosing which credentials to authenticate with
When you export a SharePoint list to Power BI, Power BI connects to the SharePoint site to get the data from the list. In order to connect, it needs to authenticate with SharePoint.
If you get the following dialog, it means that you've already established a connection to the SharePoint site in the past. The credentials you used at that time may or may not be different than the credentials of your current sign in. You need to choose whether to continue using the sign-in details you used the last time you connected (The credentials I used to connect to Power BI last time), or whether the connection should use your current sign-in credentials from now on (My current credentials (these may be the same or different)).
Why is this important?
The Power BI view of the SharePoint list data is determined by the permissions of the account used to establish the Power BI connection to the SharePoint data source (that is, the SharePoint site).
If you let Power BI use the sign-in details you used last time for the connection, the data you'll see in the semantic model you're creating may differ from what you see in the SharePoint list. This is because the data that is shown in the semantic model is what the account with the credentials you used last time can see in the SharePoint list.
If you replace the credentials you used last time with your current sign-in credentials, the data you see in the semantic model you're creating will be exactly the same as what you see in the SharePoint list. However, since the connection now uses your current login credentials, views of the data in semantic models you might have created previously from that SharePoint site might also change, and this could affect reports and other downstream items that users might have created based on those semantic models.
Take the above considerations into account when you make your choice.
If you've never previously connected to the SharePoint site from Power BI, Power BI will automatically use your current credentials to establish the connection, and you won't see this dialog.
Considerations and limitations
- The semantic model won't be created if the SharePoint list contains values with more than four digits after a decimal place (".")
- The sensitivity label (if any) of the SharePoint list isn't inherited by the semantic model that is created.
- This flow does not support business-to-business (B2B) scenarios or scenarios where authentication takes place against a service principal.
- If the SharePoint service is configured to use multi-factor authentication, then in order for this flow to work, Power BI must also be configured to use multi-factor authentication. Consult your organization's IT support if you encounter a problem related to this consideration.