Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Data is an organization’s most valuable and irreplaceable asset, and encryption serves as the last and strongest line of defence in a multi-layered data security strategy. Microsoft business cloud services and products use encryption to safeguard customer data and help you maintain control over it.
At-rest data protection
Encrypting your information renders it unreadable to unauthorized persons, even if they break through your firewalls, infiltrate your network, get physical access to your devices, or bypass the permissions on your local machine. Encryption transforms data so that only someone with the decryption key can access it.
Dynamics 365 uses heterogeneous storage (Dataverse) to store the data. The data is distributed across different storage types:
- Azure SQL Database for relational data
- Azure Blob storage for binary data, such as images and documents
- Azure Search for search indexing
- Azure Cosmos DB for audit data
- Azure Data Lake for analytics
By default, Microsoft stores and manages the database encryption key for your environments using a Microsoft-managed key. However, Power Platform provides a customer-managed encryption key (CMK) for added data protection control, where you can self-manage the database encryption key. The encryption key resides in your own Azure key vault, which allows you to rotate or swap the encryption key on demand. It also allows you to prevent Microsoft's access to your customer data when you revoke the key access to our services at any time.
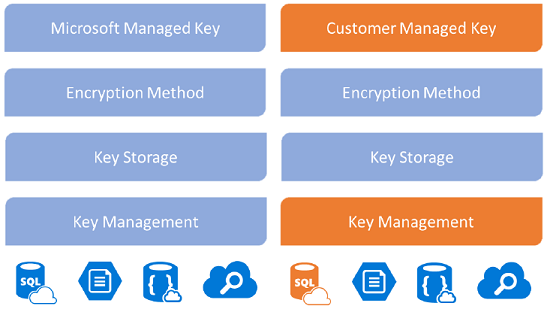
Administrators can provide their own encryption key using their own key generator hardware (HSM) or use Azure Key Vault to generate an encryption key. The key management feature takes the complexity out of encryption key management by using Azure Key Vault to securely store encryption keys. Azure Key Vault helps safeguard cryptographic keys and secrets used by cloud applications and services. Encryption keys must meet the following Azure Key Vault requirements:
- 2048-bit or 4096-bit RSA key
- HSM BYOK
- Azure Key vault Managed HSM
Administrators also can revert the encryption key back to a Microsoft managed key at any time.
In-transit data protection
Azure protects data in transit to or from outside components, as well as data in transit internally, such as between two virtual networks. Azure uses industry standard, transport protocols such as TLS between user devices and Microsoft data centers, and within data centers themselves. To protect your data even more, internal communication between Microsoft services is using Microsoft backbone network and therefore isn't exposed to the public internet.
Microsoft uses multiple encryption methods, protocols, and algorithms across its products and services to help provide a secure path for data to travel through the infrastructure, and to help protect the confidentiality of data that is stored within the infrastructure. Microsoft uses some of the strongest, most secure encryption protocols in the industry to provide a barrier against unauthorized access to your data. Proper key management is an essential element in encryption best practices, and Microsoft helps ensure that encryption keys are properly secured.
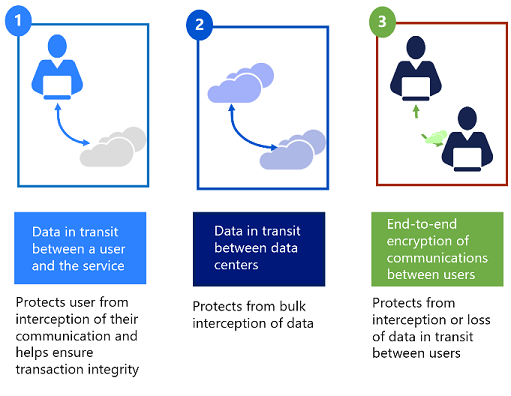
Protocols and technologies examples include:
- Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer (TLS/SSL), which uses symmetric cryptography based on a shared secret to encrypt communications as they travel over the network.
- Internet Protocol Security (IPsec), an industry-standard set of protocols used to provide authentication, integrity, and confidentiality of data at the IP packet level as it’s transferred across the network.
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)-256, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) specification for a symmetric key data encryption that was adopted by the US government to replace Data Encryption Standard (DES) and RSA 2048 public key encryption technology.