Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article demonstrates using GitHub Actions and Power Automate cloud flows for extending pipelines in Power Platform. When a pipelines deployment is submitted, a cloud flow triggers the GitHub workflow to download, unpack, and commit the artifact's source code to a GitHub branch.
Workflow details
The workflow is triggered via a workflow_dispatch event. The workflow runs on ubuntu-latest and has the contents: write permission to be able to commit changes to the GitHub repository branch.
The workflow consists of the following steps:
actions/checkout@v3: Checks out the repository.create new branch if specified: Creates a new branch if atarget_branchis specified in the inputs.download solution from artifact: Downloads the solution from the artifact created by pipelines.unpack solution: Unpacks the solution.commit changes: Commits changes to the existing or new branch.push to branch: Pushes the committed changes to the source branch.
Workflow inputs
The following workflow inputs are required or optional:
artifact_url(required): The URL of the Microsoft Dataverse row (record) ID for the artifact created by the pipelines.solution_name(required): Name of the solution in the Dataverse environment.source_branch(required): Branch for the solution commit.target_branch(optional): Branch to create for the solution commit. If not specified, thesource_branchis used.commit_message(required): Message to provide for the commit.
Workflow secrets
The following secrets are required to connect to Dataverse using an Application User configured in Dataverse and in Microsoft Entra ID (AD). Configure these secrets in the GitHub repository settings.
CLIENT_ID: The client ID of the registered Microsoft Entra application.TENANT_ID: The tenant ID of the Microsoft Entra directory associated with the Microsoft Entra application.CLIENT_SECRET: The client secret of the registered Microsoft Entra application.
For more information, go to Creating and using encrypted secrets and Create an application user.
Workflow code
Listed below is the GitHub Actions workflow code.
name: Download, unpack and commit the solution to git
run-name: Getting ${{ github.event.inputs.solution_name }} from pipelines host environment and committing
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
artifact_url:
description: "The url of the Dataverse record ID for the artifact created by the pipelines (Example: https://[your-env].crm.dynamics.com/api/data/v9.0/deploymentartifacts([your-artifact-id])/artifactfile/$value)."
required: true
solution_name:
description: "Name of the Solution in Dataverse environment"
required: true
user_name:
description: "User name for the commit"
required: true
source_branch:
description: "Branch for the solution commit"
required: true
target_branch:
description: "Branch to create for the solution commit"
required: false
commit_message:
description: "Message to provide for the commit"
required: true
permissions:
contents: write
jobs:
export-unpack-commit:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
with:
ref: ${{ github.event.inputs.source_branch }}
# Commit changes to the existing or new branch
- name: create new branch if specified
shell: pwsh
run: |
if('${{ github.event.inputs.target_branch }}' -ne '') {
git checkout -b ${{ github.event.inputs.target_branch }} ${{ github.event.inputs.source_branch }}
}
# Export the solution from the artifact created by pipelines
- name: download solution from artifact
env:
CLIENT_ID: ${{secrets.CLIENT_ID}}
TENANT_ID: ${{secrets.TENANT_ID}}
CLIENT_SECRET: ${{secrets.CLIENT_SECRET}}
shell: pwsh
run: |
$aadHost = "login.microsoftonline.com"
$url = "${{ github.event.inputs.artifact_url }}"
$options = [System.StringSplitOptions]::RemoveEmptyEntries
$dataverseHost = $url.Split("://", $options)[1].Split("/")[0]
$body = @{client_id = $env:CLIENT_ID; client_secret = $env:CLIENT_SECRET; grant_type = "client_credentials"; scope = "https://$dataverseHost/.default"; }
$OAuthReq = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri "https://$aadHost/$env:TENANT_ID/oauth2/v2.0/token" -Body $body
$spnToken = $OAuthReq.access_token
$headers = New-Object "System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[[String],[String]]"
$headers.Add("Authorization", "Bearer $spnToken")
$headers.Add("Content-Type", "application/json")
# Download the managed solution
$response = Invoke-RestMethod "${{ github.event.inputs.artifact_url }}" -Method 'GET' -Headers $headers
$bytes = [Convert]::FromBase64String($response.value)
[IO.File]::WriteAllBytes("${{ github.event.inputs.solution_name }}_managed.zip", $bytes)
# Download the unmanaged solution (for now we will need to use string manipulation to get the unmanaged solution URL, until the API provides this value)
$unmanaged_artifact_url = "${{ github.event.inputs.artifact_url }}".Replace("artifactfile", "artifactfileunmanaged")
$response = Invoke-RestMethod "$unmanaged_artifact_url" -Method 'GET' -Headers $headers
$bytes = [Convert]::FromBase64String($response.value)
[IO.File]::WriteAllBytes("${{ github.event.inputs.solution_name }}.zip", $bytes)
# Unpack the solution
- name: unpack solution
uses: microsoft/powerplatform-actions/unpack-solution@v0
with:
solution-file: "${{ github.event.inputs.solution_name }}.zip"
solution-folder: "${{ github.event.repository.name }}"
solution-type: 'Both'
process-canvas-apps: false
overwrite-files: true
# Commit changes to the existing or new branch
- name: commit changes
shell: pwsh
run: |
rm -rf ${{ github.event.inputs.solution_name }}.zip
rm -rf ${{ github.event.inputs.solution_name }}_managed.zip
git config user.name ${{ github.event.inputs.user_name }}
git pull
git add --all
git commit -am "${{ github.event.inputs.commit_message }}" --allow-empty
# Push the committed changes to the source branch
- name: push to branch
shell: pwsh
run: |
if('${{ github.event.inputs.target_branch }}' -ne '') {
git push origin ${{ github.event.inputs.target_branch }}
} else {
git push origin ${{ github.event.inputs.source_branch }}
}
Note
The Dataverse web API used to download the solution artifact has a maximum file size limit of 16 MB.
Example Power Automate flow
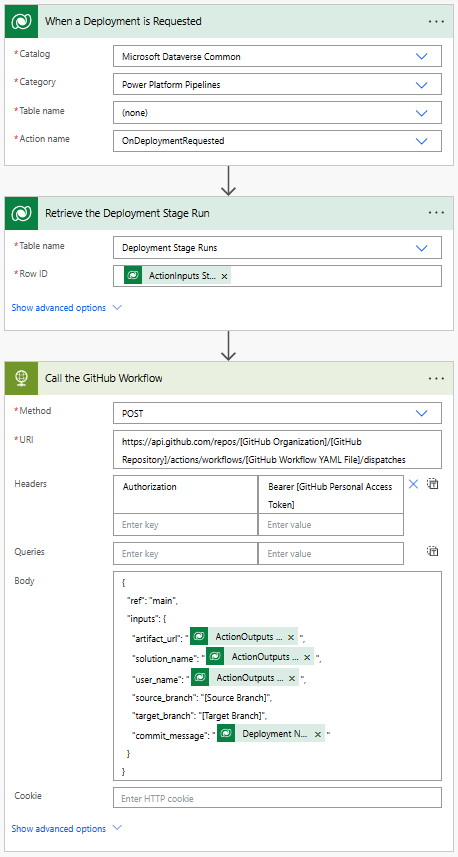
To call a GitHub workflow, you can create a Power Automate flow that is triggered when a deployment request is made in Dataverse. The flow can be configured to pass the required inputs to the GitHub workflow. For more information on how to create a Power Automate flow, go to Create a flow.
Flow details
The flow triggers when the OnDeploymentRequested action is run in Dataverse. The flow calls the HTTP connector to trigger the GitHub workflow. The flow passes the required inputs to the GitHub workflow. Include the following inputs in the request body:
artifact_url: URL of the Dataverse solution artifact created by the pipelines.solution_name: Name of the solution in the Dataverse environment.user_name: User name for the commit.source_branch: Source branch for the solution commit.target_branch: Branch to create for the solution commit.commit_message: Message to provide for the commit.
The values passed into the artifact_url, solution_name, and user_name are pulled from the outputs of the action that triggered the pipeline. The commit_message is pulled from the deployment stage run row in Dataverse.
artifact_url:@{triggerOutputs()?['body/OutputParameters/ArtifactFileDownloadLink']}solution_name:@{triggerOutputs()?['body/OutputParameters/ArtifactName']}user_name:@{triggerOutputs()?['body/OutputParameters/DeployAsUser']}commit_message:@{outputs('Retrieve_the_Deployment_Stage_Run')?['body/deploymentnotes']}
The flow also uses a personal access token (PAT) to authenticate with GitHub. For more information on how to create a GitHub personal access token, go to Creating a personal access token. The PAT is passed in the Authorization header of the HTTP request.
Update the following values in the Flow:
[GitHub Personal Access Token]- Replace with your GitHub personal access token.[GitHub Organization]- Replace with your GitHub organization name.[GitHub Repository]- Replace with your GitHub repository name.[GitHub Workflow YAML File]- Replace with your GitHub workflow YAML file name.[Source Branch]- Replace with the Git branch to commit the solution.[Target Branch]- Replace with the Git branch to create for the solution commit.Target Branchis optional. If you don't specify a target branch, then your solution is committed to theSource Branch.
Next steps
Run pipelines in Power Platform
See also
Quickstart for GitHub Actions
Extend pipelines in Power Platform
What are cloud flows?