Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Summary
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Release State | General Availability |
| Products | Excel Power BI (Semantic models) Power BI (Dataflows) Fabric (Dataflow Gen2) Power Apps (Dataflows) Dynamics 365 Customer Insights Analysis Services |
| Authentication Types Supported | Anonymous Basic (Web only) Organizational Account Web API (Web only) Windows |
| Function Reference Documentation | Json.Document |
Note
Some capabilities might be present in one product but not others due to deployment schedules and host-specific capabilities.
Capabilities supported
- Import
Load a local JSON file from Power Query Desktop
To load a local JSON file:
Select the JSON option in the Get Data selection. This selection launches a local file browser where you can select your JSON file.
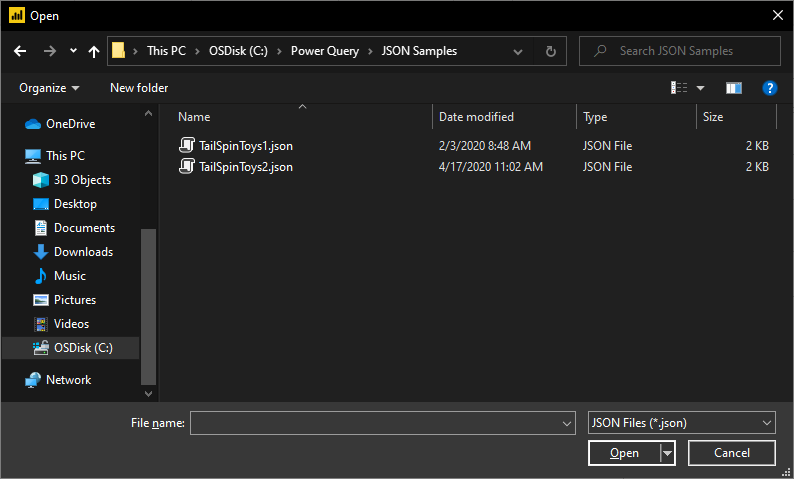
Select Open to open the file.
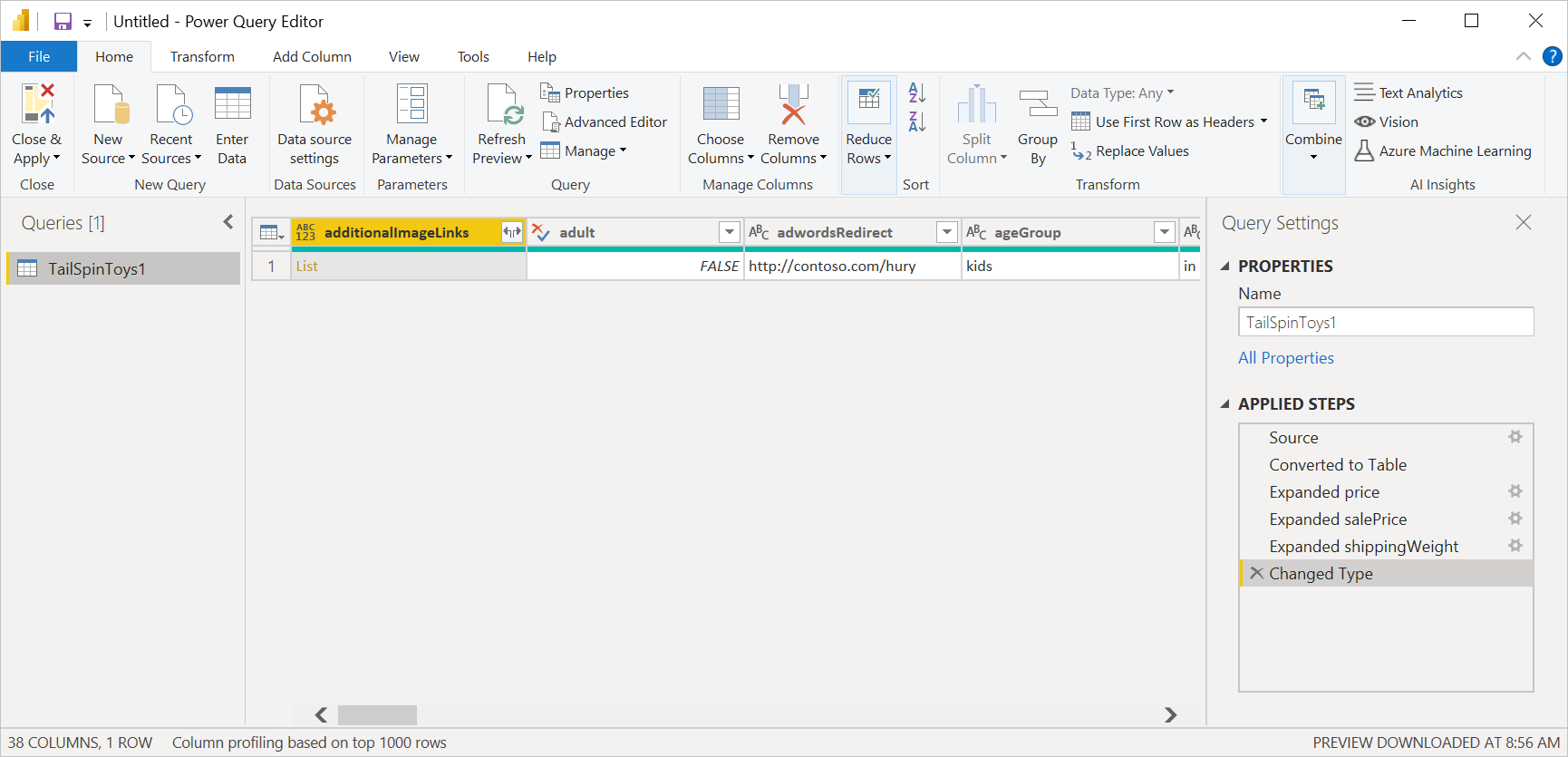
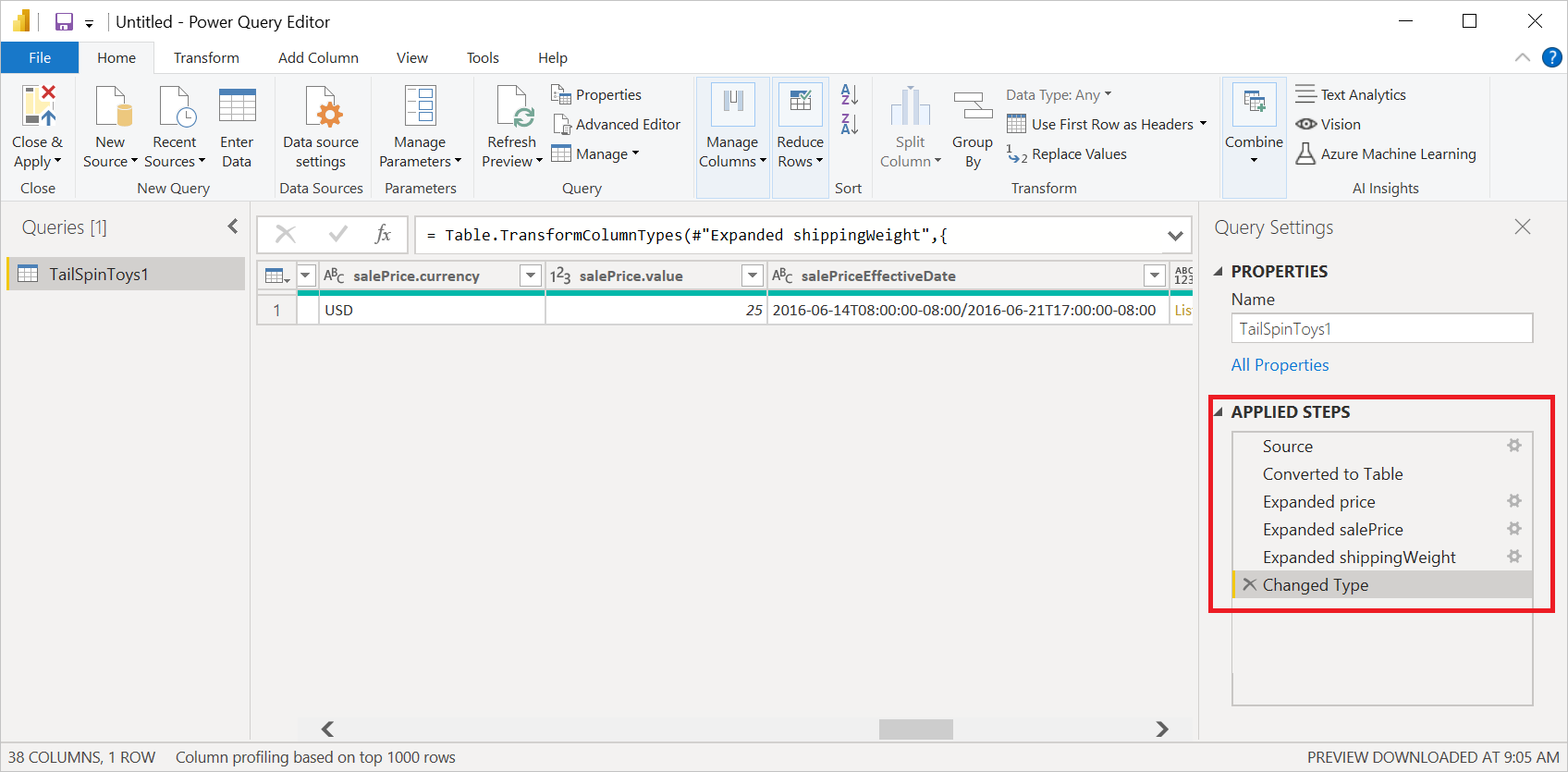
Loading the JSON file automatically launches the Power Query editor. Power Query uses automatic table detection to seamlessly flatten the JSON data into a table. From the editor, you can then continue to transform the data if you want, or you can just close and apply. More information: Automatic table detection from JSON files
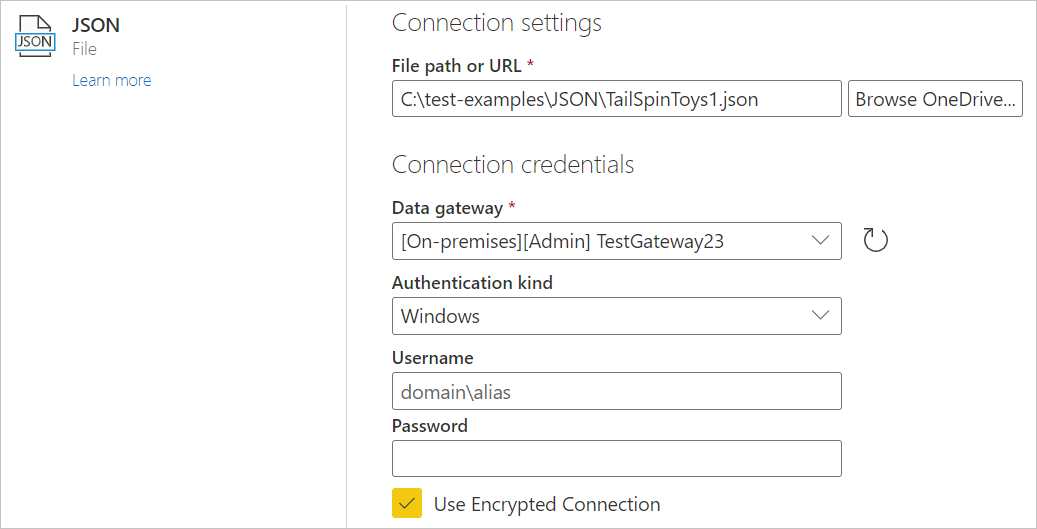
Load a local JSON file from Power Query Online
To load a local JSON file:
From the Data sources page, select JSON.
Enter the path to the local JSON file.
Select an on-premises data gateway from Data gateway.
If authentication is required, enter your credentials.
Select Next.
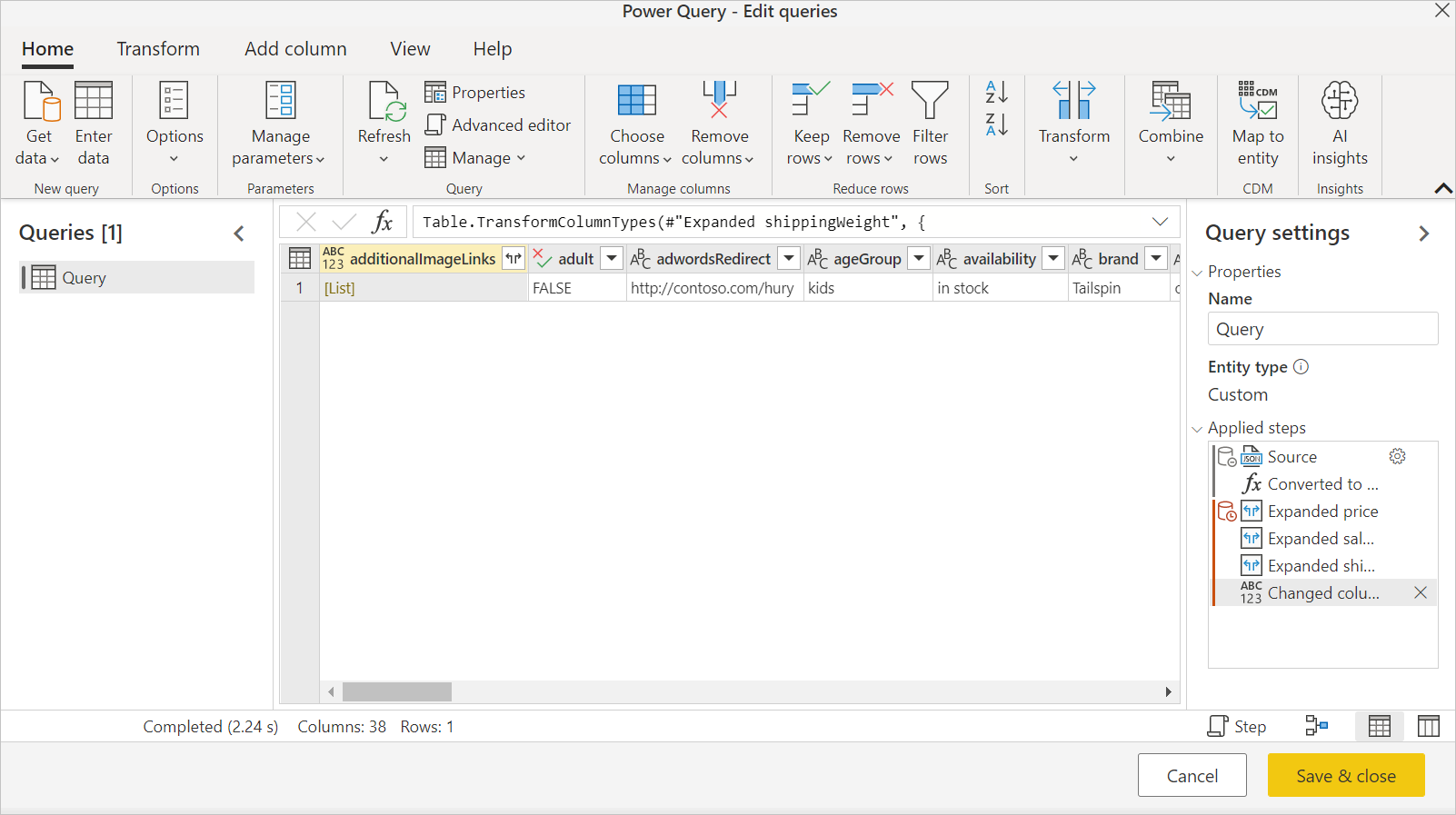
Loading the JSON file automatically launches the Power Query editor. Power Query uses automatic table detection to seamlessly flatten the JSON data into a table. From the editor, you can then continue to transform the data if you want, or you can just save and close to load the data. More information: Automatic table detection from JSON files
Load from the web
To load a JSON file from the web, select the Web connector, enter the web address of the file, and follow any credential prompts.
Automatic table detection from JSON files
Importing data from JSON files (or Web APIs) can be challenging for end users. Here's an example of JSON file with multiple levels of nested data.
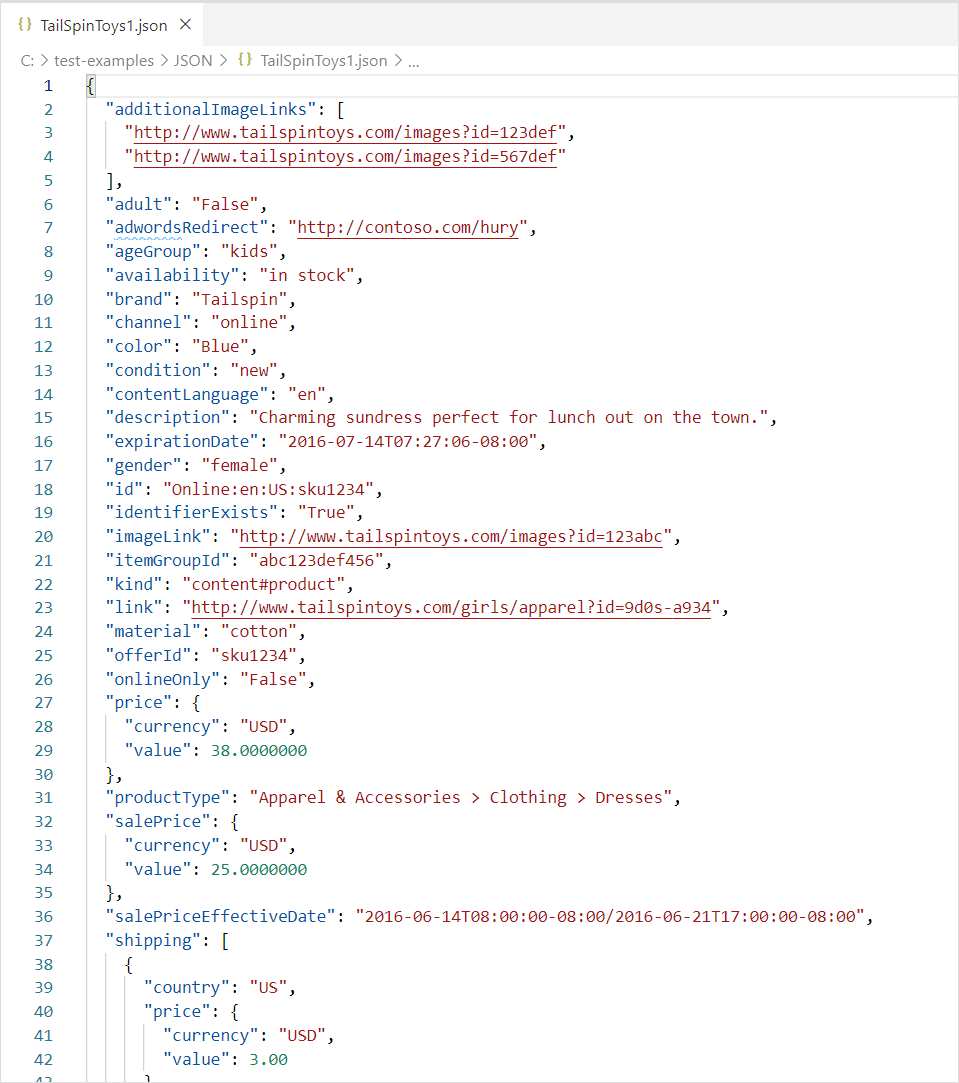
With the addition of automatic table detection capabilities, using the JSON connector in Power Query automatically applies transformation steps to flatten the JSON data into a table. Previously, users had to flatten records and lists manually.
Troubleshooting
If you see the following message, it might be because the file is invalid. For example, it's not really a JSON file, or is malformed, or you might be trying to load a JSON Lines file.
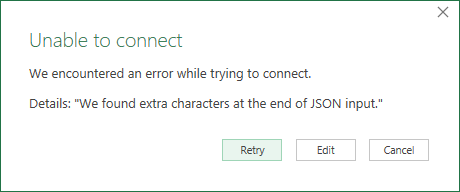
If you're trying to load a JSON Lines file, the following sample M code converts all JSON Lines input to a single flattened table automatically:
let
// Read the file into a list of lines
Source = Table.FromColumns({Lines.FromBinary(File.Contents("C:\json-lines-example.json"), null, null)}),
// Transform each line using Json.Document
#"Transformed Column" = Table.TransformColumns(Source, {"Column1", Json.Document})
in
#"Transformed Column"
Then you need to use an Expand operation to combine the lines together.