React single-page application using MSAL React to authenticate users with Azure AD for Customers and call a protected ASP.NET Core web API
- Overview
- Scenario
- Contents
- Prerequisites
- Setup the sample
- Explore the sample
- Troubleshooting
- About the code
- How to deploy this sample to Azure
- Contributing
- Learn More
Overview
This sample demonstrates a React single-page application (SPA) that lets users sign-in with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Consumers Identity and Access Management (CIAM) using the Microsoft Authentication Library for React (MSAL React).
Here you'll learn about access tokens, token validation, CORS configuration, silent requests and more.
ℹ️ To learn how to integrate a JavaScript React application with Azure AD, consider going through the recorded session: Deep dive on using MSAL.js to integrate React single-page applications with Azure Active Directory
Scenario
- The client React SPA uses the to sign-in a user and obtain a JWT ID Token and an Access Token from Azure AD for Customers.
- The access token is used as a bearer token to authorize the user to call the ASP.NET Core web API protected by Azure AD for Customers.
- The service uses the Microsoft.Identity.Web to protect the Web api, check permissions and validate tokens.
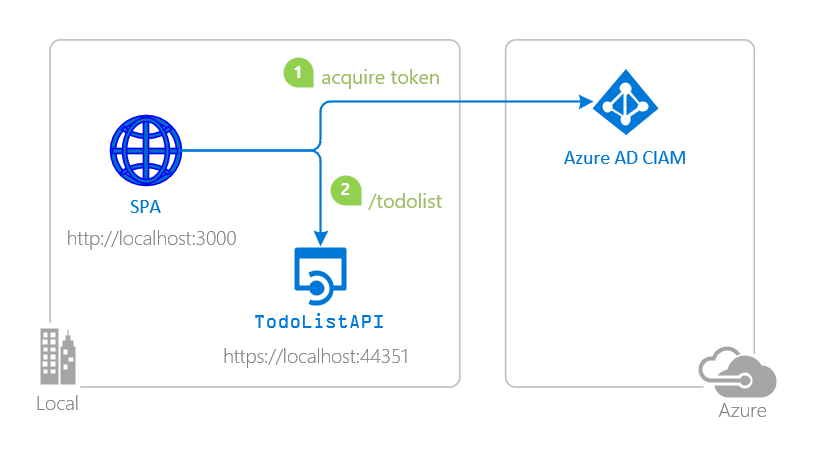
Contents
| File/folder | Description |
|---|---|
SPA/App.jsx |
Main application logic resides here. |
SPA/hooks/useFetchWithMsal.jsx |
Custom hook to make fetch calls with bearer tokens. |
SPA/authConfig.js |
Contains authentication parameters for SPA project. |
API/ToDoListAPI/appsettings.json |
Authentication parameters for the API reside here. |
API/ToDoListAPI/Startup.cs |
Microsoft.Identity.Web is initialized here. |
Prerequisites
- Either Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code and .NET Core SDK
- An Azure AD for Customers tenant. For more information, see: How to get an Azure AD for Customers tenant
- A user account in your Azure AD for Customers tenant.
Setup the sample
Step 1: Clone or download this repository
From your shell or command line:
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/ms-identity-ciam-javascript-tutorial.git
or download and extract the repository .zip file.
⚠️ To avoid path length limitations on Windows, we recommend cloning into a directory near the root of your drive.
Step 2: Navigate to project folder
cd 2-Authorization\1-call-api-react\SPA
npm install
Step 3: Register the sample application(s) in your tenant
There are two projects in this sample. Each needs to be separately registered in your Azure AD tenant. To register these projects, you can:
- follow the steps below for manually register your apps
- or use PowerShell scripts that:
- automatically creates the Azure AD applications and related objects (passwords, permissions, dependencies) for you.
- modify the projects' configuration files.
Expand this section if you want to use this automation:
⚠️ If you have never used Microsoft Graph PowerShell before, we recommend you go through the App Creation Scripts Guide once to ensure that your environment is prepared correctly for this step.
Ensure that you have PowerShell 7 or later which can be installed at here.
Run the script to create your Azure AD application and configure the code of the sample application accordingly.
For interactive process -in PowerShell, run:
cd .\AppCreationScripts\ .\Configure.ps1 -TenantId "[Optional] - your tenant id" -AzureEnvironmentName "[Optional] - Azure environment, defaults to 'Global'"
Other ways of running the scripts are described in App Creation Scripts guide. The scripts also provide a guide to automated application registration, configuration and removal which can help in your CI/CD scenarios.
Choose the Azure AD for Customers tenant where you want to create your applications
To manually register the apps, as a first step you'll need to:
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- If your account is present in more than one Azure AD for Customers tenant, select your profile at the top right corner in the menu on top of the page, and then switch directory to change your portal session to the desired Azure AD for Customers tenant.
Create User Flows
Please refer to: Tutorial: Create user flow in Azure Active Directory CIAM
ℹ️ To enable password reset in Customer Identity Access Management (CIAM) in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), please refer to: Tutorial: Enable self-service password reset
Add External Identity Providers
Please refer to:
Register the service app (ciam-msal-dotnet-api)
- Navigate to the Azure portal and select the Azure AD for Customers service.
- Select the App Registrations blade on the left, then select New registration.
- In the Register an application page that appears, enter your application's registration information:
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name that will be displayed to users of the app, for example
ciam-msal-dotnet-api. - Under Supported account types, select Accounts in this organizational directory only
- Select Register to create the application.
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name that will be displayed to users of the app, for example
- In the Overview blade, find and note the Application (client) ID. You use this value in your app's configuration file(s) later in your code.
- In the app's registration screen, select the Expose an API blade to the left to open the page where you can publish the permission as an API for which client applications can obtain access tokens for. The first thing that we need to do is to declare the unique resource URI that the clients will be using to obtain access tokens for this API. To declare an resource URI(Application ID URI), follow the following steps:
- Select Set next to the Application ID URI to generate a URI that is unique for this app.
- For this sample, accept the proposed Application ID URI (
api://{clientId}) by selecting Save.ℹ️ Read more about Application ID URI at Validation differences by supported account types (signInAudience).
Publish Delegated Permissions
- All APIs must publish a minimum of one scope, also called Delegated Permission, for the client apps to obtain an access token for a user successfully. To publish a scope, follow these steps:
- Select Add a scope button open the Add a scope screen and Enter the values as indicated below:
- For Scope name, use
ToDoList.Read. - For Admin consent display name type in Read users ToDo list using the 'ciam-msal-dotnet-api'.
- For Admin consent description type in Allow the app to read the user's ToDo list using the 'ciam-msal-dotnet-api'.
- Keep State as Enabled.
- Select the Add scope button on the bottom to save this scope.
⚠️ Repeat the steps above for another scope named ToDoList.ReadWrite
- For Scope name, use
- Select the Manifest blade on the left.
- Set
accessTokenAcceptedVersionproperty to 2. - Select on Save.
- Set
ℹ️ Follow the principle of least privilege when publishing permissions for a web API.
Publish Application Permissions
- All APIs should publish a minimum of one App role for applications, also called Application Permission, for the client apps to obtain an access token as themselves, i.e. when they are not signing-in a user. Application permissions are the type of permissions that APIs should publish when they want to enable client applications to successfully authenticate as themselves and not need to sign-in users. To publish an application permission, follow these steps:
- Still on the same app registration, select the App roles blade to the left.
- Select Create app role:
- For Display name, enter a suitable name for your application permission, for instance ToDoList.Read.All.
- For Allowed member types, choose Application to ensure other applications can be granted this permission.
- For Value, enter ToDoList.Read.All.
- For Description, enter Allow the app to read every user's ToDo list using the 'ciam-msal-dotnet-api'.
- Select Apply to save your changes.
⚠️ Repeat the steps above for another app permission named ToDoList.ReadWrite.All
Configure Optional Claims
- Still on the same app registration, select the Token configuration blade to the left.
- Select Add optional claim:
- Select optional claim type, then choose Access.
- Select the optional claim idtyp.
Indicates token type. This claim is the most accurate way for an API to determine if a token is an app token or an app+user token. This is not issued in tokens issued to users.
- Select Add to save your changes.
Configure the service app (ciam-msal-dotnet-api) to use your app registration
Open the project in your IDE (like Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code) to configure the code.
In the steps below, "ClientID" is the same as "Application ID" or "AppId".
- Open the
API\ToDoListAPI\appsettings.jsonfile. - Find the key
Enter_the_Application_Id_Hereand replace the existing value with the application ID (clientId) ofciam-msal-dotnet-apiapp copied from the Azure portal. - Find the key
Enter_the_Tenant_Id_Hereand replace the existing value with your Azure AD tenant/directory ID. - Find the placeholder
Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Hereand replace it with the Directory (tenant) subdomain. For instance, if your tenant primary domain iscontoso.onmicrosoft.com, usecontoso. If you don't have your tenant domain name, learn how to read your tenant details.
Register the client app (ciam-msal-react-spa)
- Navigate to the Azure portal and select the Azure AD for Customers service.
- Select the App Registrations blade on the left, then select New registration.
- In the Register an application page that appears, enter your application's registration information:
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name that will be displayed to users of the app, for example
ciam-msal-react-spa. - Under Supported account types, select Accounts in this organizational directory only
- Select Register to create the application.
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name that will be displayed to users of the app, for example
- In the Overview blade, find and note the Application (client) ID. You use this value in your app's configuration file(s) later in your code.
- In the app's registration screen, select the Authentication blade to the left.
- If you don't have a platform added, select Add a platform and select the Single-page application option.
- In the Redirect URI section enter the following redirect URIs:
http://localhost:3000http://localhost:3000/redirect
- Click Save to save your changes.
- In the Redirect URI section enter the following redirect URIs:
- Since this app signs-in users, we will now proceed to select delegated permissions, which is is required by apps signing-in users.
- In the app's registration screen, select the API permissions blade in the left to open the page where we add access to the APIs that your application needs:
- Select the Add a permission button and then:
- Ensure that the Microsoft APIs tab is selected.
- In the Commonly used Microsoft APIs section, select Microsoft Graph
- In the Delegated permissions section, select openid, offline_access in the list. Use the search box if necessary.
- Select the Add permissions button at the bottom.
- Select the Add a permission button and then:
- Ensure that the My APIs tab is selected.
- In the list of APIs, select the API
ciam-msal-dotnet-api. - In the Delegated permissions section, select ToDoList.Read, ToDoList.ReadWrite in the list. Use the search box if necessary.
- Select the Add permissions button at the bottom.
- At this stage, the permissions are assigned correctly, but since it's a CIAM tenant, the users themselves cannot consent to these permissions. To get around this problem, we'd let the tenant administrator consent on behalf of all users in the tenant. Select the Grant admin consent for {tenant} button, and then select Yes when you are asked if you want to grant consent for the requested permissions for all accounts in the tenant. You need to be a tenant admin to be able to carry out this operation.
Configure the client app (ciam-msal-react-spa) to use your app registration
Open the project in your IDE (like Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code) to configure the code.
In the steps below, "ClientID" is the same as "Application ID" or "AppId".
- Open the
SPA\src\authConfig.jsfile. - Find the key
Enter_the_Application_Id_Hereand replace the existing value with the application ID (clientId) ofciam-msal-react-spaapp copied from the Azure portal. - Find the placeholder
Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Hereand replace it with the Directory (tenant) subdomain. For instance, if your tenant primary domain iscontoso.onmicrosoft.com, usecontoso. If you don't have your tenant domain name, learn how to read your tenant details. - Find the key
Enter_the_Web_Api_Application_Id_Hereand replace the existing value with the application ID (clientId) ofciam-msal-dotnet-apiapp copied from the Azure portal.
Step 4: Running the sample
From your shell or command line, execute the following commands:
cd 2-Authorization\1-call-api-react\API
dotnet run
Then, open a separate command terminal and run:
cd 2-Authorization\1-call-api-react\SPA
npm start
Explore the sample
- Open your browser and navigate to
http://localhost:3000. - Select the Sign In button on the top right corner.
- Select the ToDoList button on the navigation bar. This will make a call to the ToDoListAPI.
ℹ️ Did the sample not work for you as expected? Then please reach out to us using the GitHub Issues page.
We'd love your feedback!
Were we successful in addressing your learning objective? Consider taking a moment to share your experience with us.
Troubleshooting
Use Stack Overflow to get support from the community. Ask your questions on Stack Overflow first and browse existing issues to see if someone has asked your question before. Make sure that your questions or comments are tagged with [azure-active-directory react ms-identity adal msal].
If you find a bug in the sample, raise the issue on GitHub Issues.
About the code
CORS settings
You need to set cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) policy to be able to call the ToDoListAPI in Program.cs. For the purpose of the sample, CORS is enabled for all domains and methods. This is insecure and only used for demonstration purposes here. In production, you should modify this as to allow only the domains that you designate. If your web API is going to be hosted on Azure App Service, we recommend configuring CORS on the App Service itself.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// ...
services.AddCors(o => o.AddPolicy("default", builder =>
{
builder.AllowAnyOrigin()
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader();
}));
}
Access token validation
On the web API side, the AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApiAuthentication method in Program.cs protects the web API by validating access tokens sent tho this API. Check out Protected web API: Code configuration which explains the inner workings of this method in more detail. Simply add the following line under the ConfigureServices method:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// Adds Microsoft Identity platform (AAD v2.0) support to protect this Api
services.AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApiAuthentication(Configuration);
// ...
}
For validation and debugging purposes, developers can decode JWTs (JSON Web Tokens) using jwt.ms.
Verifying permissions
Access tokens that have neither the scp (for delegated permissions) nor roles (for application permissions) claim with the required scopes/permissions should not be accepted. In the sample, this is illustrated via the RequiredScopeOrAppPermission attribute in ToDoListController.cs:
[HttpGet]
[RequiredScopeOrAppPermission(
RequiredScopesConfigurationKey = "AzureAD:Scopes:Read",
RequiredAppPermissionsConfigurationKey = "AzureAD:AppPermissions:Read"
)]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetAsync()
{
var toDos = await _toDoContext.ToDos!
.Where(td => RequestCanAccessToDo(td.Owner))
.ToListAsync();
return Ok(toDos);
}
Access to data
Web API endpoints should be prepared to accept calls from both users and applications, and should have control structures in place to respond to each accordingly. For instance, a call from a user via delegated permissions should be responded with user's data, while a call from an application via application permissions might be responded with the entire list of toDos. This is illustrated in the ToDoListController controller:
private bool IsAppMakingRequest()
{
// Add in the optional 'idtyp' claim to check if the access token is coming from an application or user.
// See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/active-directory-optional-claims
if (HttpContext.User.Claims.Any(c => c.Type == "idtyp"))
{
return HttpContext.User.Claims.Any(c => c.Type == "idtyp" && c.Value == "app");
}
else
{
// alternatively, if an AT contains the roles claim but no scp claim, that indicates it's an app token
return HttpContext.User.Claims.Any(c => c.Type == "roles") && !HttpContext.User.Claims.Any(c => c.Type == "scp");
}
}
private bool RequestCanAccessToDo(Guid userId)
{
return IsAppMakingRequest() || (userId == GetUserId());
}
[HttpGet]
[RequiredScopeOrAppPermission(
RequiredScopesConfigurationKey = "AzureAD:Scopes:Read",
RequiredAppPermissionsConfigurationKey = "AzureAD:AppPermissions:Read"
)]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetAsync()
{
var toDos = await _toDoContext.ToDos!
.Where(td => RequestCanAccessToDo(td.Owner))
.ToListAsync();
return Ok(toDos);
}
When granting access to data based on scopes, be sure to follow the principle of least privilege.
Debugging the sample
To debug the .NET Core web API that comes with this sample, install the C# extension for Visual Studio Code.
Learn more about using .NET Core with Visual Studio Code.
How to deploy this sample to Azure
Expand the section
Deploying web API to Azure App Services
There is one web API in this sample. To deploy it to Azure App Services, you'll need to:
- create an Azure App Service
- publish the projects to the App Services
⚠️ Please make sure that you have not switched on the Automatic authentication provided by App Service. It interferes the authentication code used in this code example.
Publish your files (ciam-msal-dotnet-api)
Publish using Visual Studio
Follow the link to Publish with Visual Studio.
Publish using Visual Studio Code
- Install the Visual Studio Code extension Azure App Service.
- Follow the link to Publish with Visual Studio Code
Enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) (ciam-msal-dotnet-api)
- Go to Azure portal, and locate the web API project that you've deployed to App Service.
- On the API blade, select CORS. Check the box Enable Access-Control-Allow-Credentials.
- Under Allowed origins, add the URL of your published web app that will call this web API.
Deploying SPA to Azure Storage
There is one single-page application in this sample. To deploy it to Azure Storage, you'll need to:
- create an Azure Storage blob and obtain website coordinates
- build your project and upload it to Azure Storage blob
- update config files with website coordinates
ℹ️ If you would like to use VS Code Azure Tools extension for deployment, watch the tutorial offered by Microsoft Docs.
Build and upload (ciam-msal-react-spa) to an Azure Storage blob
Build your project to get a distributable files folder, where your built html, css and javascript files will be generated. Then follow the steps below:
⚠️ When uploading, make sure you upload the contents of your distributable files folder and not the entire folder itself.
ℹ️ If you don't have an account already, see: How to create a storage account.
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- Locate your storage account and display the account overview.
- Select Static website to display the configuration page for static websites.
- Select Enabled to enable static website hosting for the storage account.
- In the Index document name field, specify a default index page (For example:
index.html). - The default index page is displayed when a user navigates to the root of your static website.
- Select Save. The Azure portal now displays your static website endpoint. Make a note of the Primary endpoint field.
- In the
ciam-msal-react-spaproject source code, update your configuration file with the Primary endpoint field as your new Redirect URI (you will register this URI later). - Next, select Storage Explorer.
- Expand the BLOB CONTAINERS node, and then select the
$webcontainer. - Choose the Upload button to upload files.
- If you intend for the browser to display the contents of file, make sure that the content type of that file is set to
text/html. - In the pane that appears beside the account overview page of your storage account, select Static Website. The URL of your site appears in the Primary endpoint field. In the next section, you will register this URI.
Update the CIAM app registration for ciam-msal-react-spa
- Navigate back to to the Azure portal.
- In the left-hand navigation pane, select the Azure Active Directory service, and then select App registrations.
- In the resulting screen, select
ciam-msal-react-spa. - In the app's registration screen, select Authentication in the menu.
- In the Redirect URIs section, update the reply URLs to match the site URL of your Azure deployment. For example:
https://ciam-msal-react-spa.azurewebsites.net/https://ciam-msal-react-spa.azurewebsites.net/redirect
- In the Redirect URIs section, update the reply URLs to match the site URL of your Azure deployment. For example:
Update authentication configuration parameters (ciam-msal-react-spa)
- In your IDE, locate the
ciam-msal-react-spaproject. Then, openSPA\src\authConfig.js. - Find the key for redirect URI and replace its value with the address of the web app you published, for example, https://ciam-msal-react-spa.azurewebsites.net/redirect.
- Find the key for web API endpoint and replace its value with the address of the web API you published, for example, https://ciam-msal-dotnet-api.azurewebsites.net/api.
Contributing
If you'd like to contribute to this sample, see CONTRIBUTING.MD.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information, see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Learn More
- Customize the default branding
- OAuth 2.0 device authorization grant flow
- Customize sign-in strings
- Building Zero Trust ready apps
- Microsoft.Identity.Web
- Validating Access Tokens
- User and application tokens
- Validation differences by supported account types
- How to manually validate a JWT access token using the Microsoft identity platform