Understand the Fabric Architecture
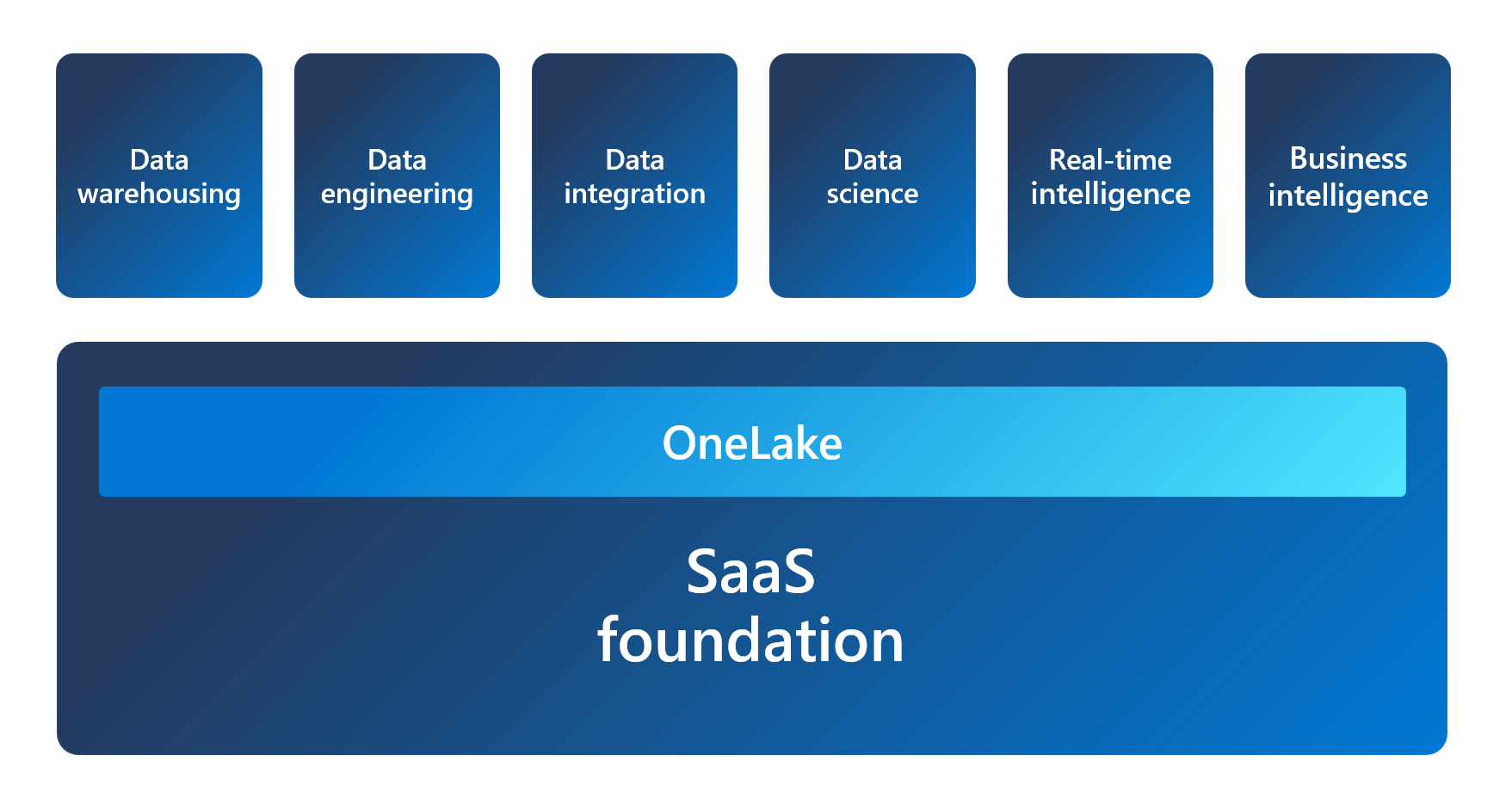
Microsoft Fabric is a Software-as-a-Service platform, which provides a simple and integrated approach while reducing administrative overhead. Fabric provides an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises that covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, and business intelligence. It offers a comprehensive suite of services, including:
- Data warehousing
- Data engineering
- Data integration
- Data science
- Real-time intelligence
- Business intelligence
All data in Fabric is stored in OneLake, which is built on Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) gen2 architecture. OneLake is hierarchical in nature to simplify management across your organization. There's only one OneLake per tenant and it provides a single-pane-of-glass file-system namespace that spans across users, regions, and even clouds.
Understand Fabric concepts
Tenant is a dedicated space for organizations to create, store, and manage Fabric items. There's often a single instance of Fabric for an organization, which is aligned with Microsoft Entra ID. The Fabric tenant maps to the root of OneLake and is at the top level of the hierarchy.
Capacity is a dedicated set of resources that is available at a given time to be used. A tenant can have one or more capacities associated with it. Capacity defines the ability of a resource to perform an activity or to produce output. Different items consume different capacity at a certain time. Fabric offers capacity through the Fabric SKU and Trials.
Domain is a logical grouping of workspaces. Domains are used to organize items in a way that makes sense for your organization. You can group things together in a way that makes it easier for the right people to have access to the right workspaces. For example, you might have a domain for sales, another for marketing, and another for finance.
Workspace is a collection of items that brings together different functionality in a single tenant. It acts as a container that uses capacity for the work that is executed, and provides controls for who can access the items in it. For example, in a sales workspace, users associated with the sales organization can create a data warehouse, run notebooks, create datasets, create reports, and more.
Items are the building blocks of the Fabric platform. They're the objects that you create and manage in Fabric. There are different types of items, such as data warehouses, data pipelines, datasets, reports, and dashboards.
Understanding Fabric concepts is important for you as an admin, because it helps you understand how to manage the Fabric environment.
Note
For more information, see the Start a Fabric trial documentation.