Prepare to deploy Altair emulator disk services
In this unit, you'll learn about the real-time Altair emulator disk services so that you can deploy them.
The file system for the Altair emulator can read and write files to an SD card or the virtual disk server. The file system uses disks for storage. Disk drive A contains the operating system, utilities, and programming languages. Disk drive B is empty and can be used for the applications that you write.
To deploy the Altair emulator, you need:
- The SD card service running on Azure Sphere (recommended).
- The SD card service requires an Avnet Azure Sphere Starter Kit Rev 1 or Rev 2, plus the MikroE microSD Click.
- The SD card provides file read/write support for both disk drive A and disk drive B.
- The virtual disk server running on your computer or cloud-based virtual machine.
- Install the virtual disk cache service on Azure Sphere to improve the performance of the file system.
- The virtual disk server supports read/write access for disk drive B.
Virtual disk cache-aside service
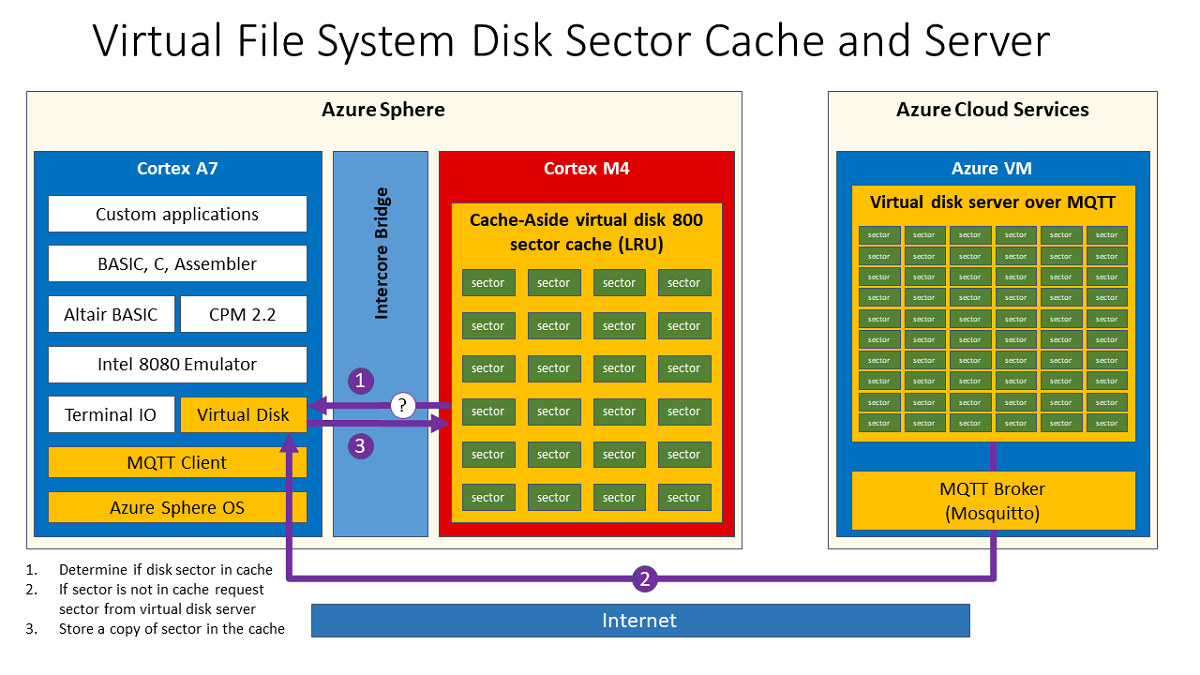
Install the virtual disk cache-aside service if you don't have an SD card and you plan to use the virtual disk server for disk drive B. The virtual disk cache-aside service improves the performance of the virtual disk server.
The Altair emulator file system redirects disk read and write requests for drive B over MQTT to the virtual disk server.
Disk reads work as follows:
The Altair emulator file system checks if the disk sector is available from the disk cache-aside service. The cache-aside service uses a hash table to quickly find the requested disk sector in memory.
If the disk sector is found in the cache, the sector is returned to the Altair emulator. Getting sectors from the cache is much faster than requesting the sector from the virtual disk server.
If the disk sector is not found in the cache, the Altair emulator file system requests the disk sector from the virtual disk server.
When the virtual disk server returns the disk sector, it's added to the disk sector cache. The sector is then returned to the Altair emulator for processing.
Disk writes work as follows:
- The Altair emulator file system sends the disk sector to the cache service.
- The disk sector is sent to the virtual disk server over MQTT.
The space in the cache is managed through a least recently used (LRU) algorithm. If the cache becomes full, the LRU disk sector in the cache is discarded if a new disk sector needs to be stored in the cache.