Understand how to ground your language model
Language models excel in generating engaging text, and are ideal as the base for agents. Agents provide users with an intuitive chat-based application to receive assistance in their work. When designing an agent for a specific use case, you want to ensure your language model is grounded and uses factual information that is relevant to what the user needs.
Though language models are trained on a vast amount of data, they may not have access to the knowledge you want to make available to your users. To ensure that an agent is grounded on specific data to provide accurate and domain-specific responses, you can use Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
Understanding RAG
RAG is a technique that you can use to ground a language model. In other words, it's a process for retrieving information that is relevant to the user's initial prompt. In general terms, the RAG pattern incorporates the following steps:
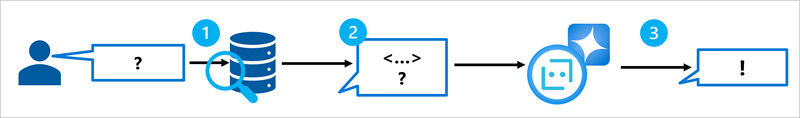
- Retrieve grounding data based on the initial user-entered prompt.
- Augment the prompt with grounding data.
- Use a language model to generate a grounded response.
By retrieving context from a specified data source, you ensure that the language model uses relevant information when responding, instead of relying on its training data.
Using RAG is a powerful and easy-to-use technique for many cases in which you want to ground your language model and improve the factual accuracy of your generative AI app's responses.
Adding grounding data to an Azure AI project
You can use Microsoft Foundry to build a custom agent that uses your own data to ground prompts. Microsoft Foundry supports a range of data connections that you can use to add data to a project, including:
- Azure Blob Storage
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
- Microsoft OneLake
You can also upload files or folders to the storage used by your AI Foundry project.