Exercise - Import Python libraries and rocket launch data
You now have a goal: Is a launch likely to happen given specific weather conditions? You have a data set that contains weather data from:
- Several successful launches
- One pushed launch day
- The days leading up to and following each launch
Now you can start to code!
Machine learning in code
You can use various tools and services to solve machine learning problems. These space-themed learning paths use Visual Studio Code, Python, scikit-learn, and Azure.
Watch this Microsoft video to learn how to download and configure a similar environment to the one you'll need.
When you're setting up your local programming environment, we recommend creating an Anaconda environment to ensure you have exactly what you need for that project. You can use your preferred method or set of tools. Most of these modules don't explicitly require Visual Studio Code or Azure.
Set up the local environment
Before continuing, be sure that you have:
- Visual Studio Code, Anaconda, and Python installed. (We'll create our Anaconda environment in the steps below).
- A local folder you created to store all of the code and data.
- The Excel file of our data downloaded and saved to your local folder.
- A blank Jupyter notebook saved in the folder. (In your local folder, create a dummy file called yourfilename.ipynb).
To set up your local environment:
Open the Anaconda prompt.
In the Anaconda prompt, create a new Anaconda environment with Pandas, NumPy, scikit-learn, PyDotPlus, and Jupyter:
conda create -n myenv python=3.8 pandas numpy jupyter seaborn scikit-learn pydotplusIn the Anaconda prompt, activate the new environment:
conda activate myenvIn the Anaconda prompt, install AzureML-SDK:
pip install --upgrade azureml-sdkIn some cases, the install can take several minutes to complete. Let it resolve until it does.
In the Anaconda prompt, install an Excel reader (note that xlrd might not work with the Excel data file you downloaded):
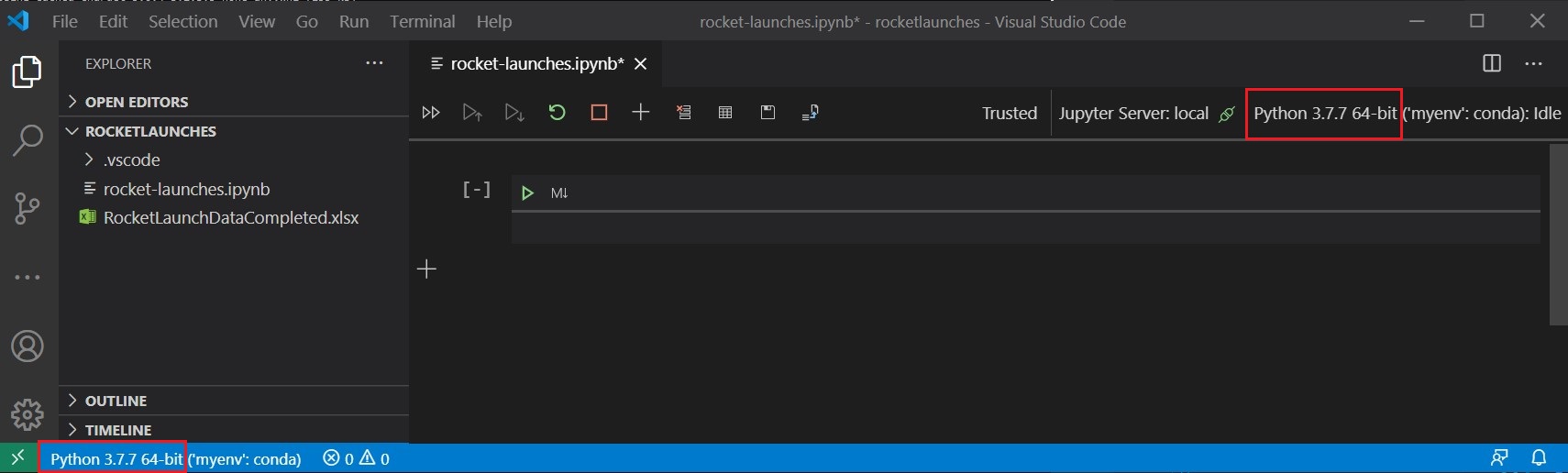
pip install openpyxlIn Visual Studio Code, open the local folder you created to store all of the code and data. Select both the upper-right Jupyter kernel Python version and the lower-left Python interpreter, and set them both to use your Anaconda environment:
Import libraries
With your Visual Studio Code local environment created, you can now import the libraries. They'll help us import and clean the weather data, and create and test the machine learning model.
Copy the following code into a cell and run it to import the libraries.
# Pandas library is used for handling tabular data
import pandas as pd
# NumPy is used for handling numerical series operations (addition, multiplication, and ...)
import numpy as np
# Sklearn library contains all the machine learning packages we need to digest and extract patterns from the data
from sklearn import linear_model, model_selection, metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Machine learning libraries used to build a decision tree
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn import tree
# Sklearn's preprocessing library is used for processing and cleaning the data
from sklearn import preprocessing
# for visualizing the tree
import pydotplus
from IPython.display import Image
Read data into a variable
Now that we have all of the libraries imported, we can use the pandas library to import our data. Use the command pd.read_excel to read the data and save it in a variable. Then, use the .head() function to print the first five rows of the data to ensure that we have read everything correctly.
launch_data = pd.read_excel('RocketLaunchDataCompleted.xlsx')
launch_data.head()
Begin exploring data
Finally, we can use the .columns function call to view all columns in our data. Doing so shows us the attributes that the data has. You'll see some common attributes like names of past rockets that were scheduled to launch, the dates they were scheduled, whether they actually launched, and more. Look at these columns and try to guess which ones will have the greatest effect in determining whether a rocket will launch.
launch_data.columns