Use the INTERSECT and EXCEPT operators
INTERSECT and EXCEPT compare two result sets against each other, and return rows in common, or rows that appear in one but not in the other.
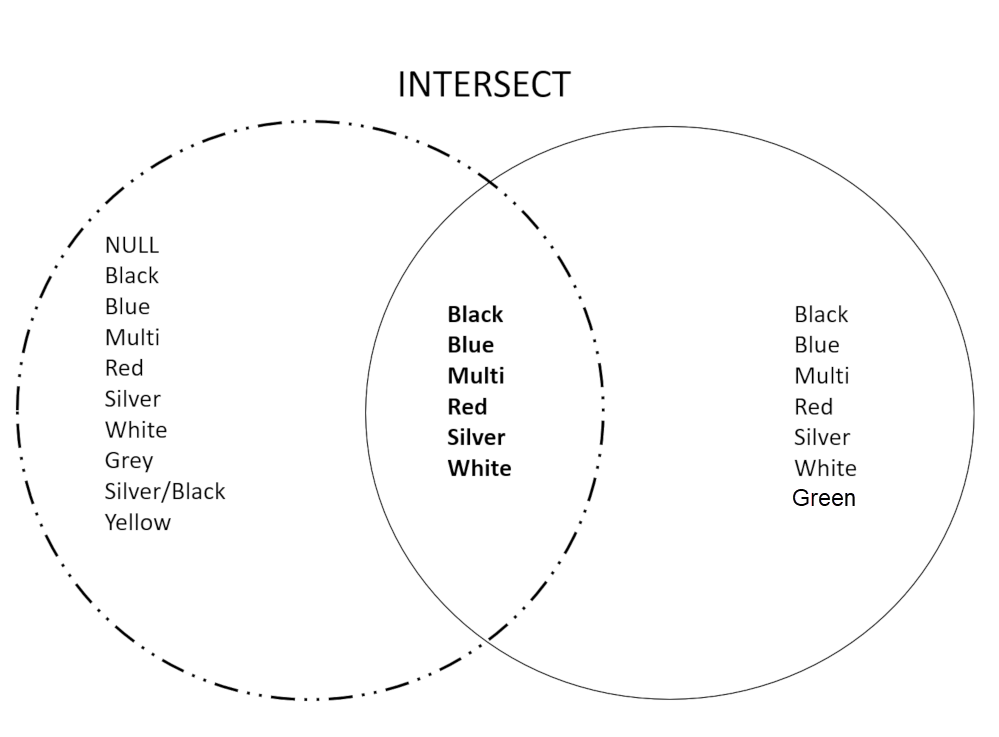
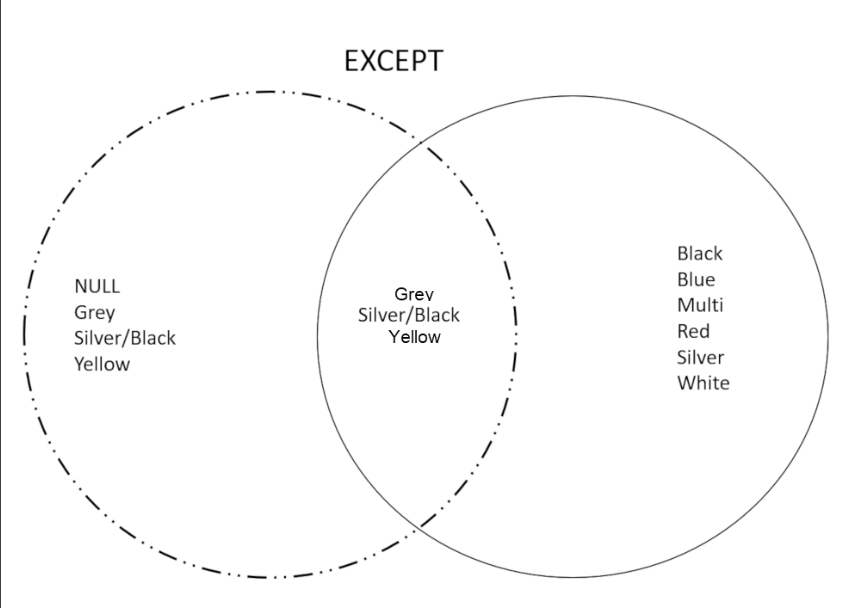
INTERSECT and EXCEPT are best explained using a Venn diagram. The circles in the diagrams below represent two result sets from the products table, one returning ProductIDs 500 to 750, and the second returning ProductIDs 751 to 1000. We want to know which colors are in both result sets, and which colors are in one, but not the other. We will use INTERSECT and EXCEPT to find out.
INTERSECT Returns rows that are present in both sets.
EXCEPT Returns distinct rows from the left input query that aren't output by the right input query.
In the following code example, you want to know which colors appear in both result sets from the products table:
SELECT color FROM SalesLT.Product
WHERE ProductID BETWEEN 500 and 750
INTERSECT
SELECT color FROM SalesLT.Product
WHERE ProductID BETWEEN 751 and 1000;
In this example, you want to know which colors are in the first result set, but NOT in the second result set. In this case, use the EXCEPT operator:
SELECT color FROM SalesLT.Product
WHERE ProductID BETWEEN 500 and 750
EXCEPT
SELECT color FROM SalesLT.Product
WHERE ProductID BETWEEN 751 and 1000;
Note that the results are different, depending on the order of the queries. So the above query will return a different result set to the one below:
SELECT color FROM SalesLT.Product
WHERE ProductID BETWEEN 751 and 1000
EXCEPT
SELECT color FROM SalesLT.Product
WHERE ProductID BETWEEN 500 and 750;