Understand file and folder permissions
You can configure file and folder permissions only on NTFS and ReFS volumes. Permissions are rules that determine what operations specific users can perform on a file or a folder. A file or folder’s owner can grant or deny permissions to it, as can anyone with Full Control permissions, which grants that person rights to modify permissions for that file or folder. You assign permissions to files and folders by granting or denying a specific permission level. Typically, you assign them in groups to minimize administrative overhead. If you assign permissions to a group, every group member has the assigned permission. You can also assign permissions to individual users and computers. If you assign permissions to a group and to individual group members, they are cumulative. This means that a user has the permissions that you assign to him or her, in addition to those you assign to the group.
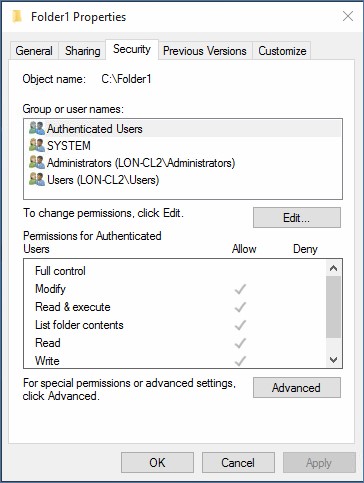
Permissions example
Consider the following example. Adam is a member of the Marketing group, which has Read permission to the Pictures folder. If an administrator assigns Write permissions to Adam for the Pictures folder, Adam will have Read permissions, because he is a member of the Marketing group, and Write permissions, because the administrator assigned them directly to him.
Types of permissions
You can configure two types of permissions for files and folders on NTFS and ReFS volumes:
- Basic permissions. These are the most commonly used permissions. You most often will work with basic permissions and assign them to groups and users. Each basic permission is built from multiple special permissions.
- Advanced permissions. These permissions provide a finer degree of control compared to basic permissions. However, advanced permissions are more complex to document and manage than basic permissions.
Basic file and folder permissions
The following table lists the basic file and folder permissions. You can choose whether to allow or deny each.
| File permissions | Description |
|---|---|
| Full control | Provides complete control of the file or folder and control of permissions. |
| Modify | Allows users to read a file, write changes to it, and modify permissions. The advanced permissions that comprise Modify permissions are Traverse folder/execute file, List folder/read data, Read attributes, Read extended attributes, Create files/write data, Create folders/append data, Write attributes, Write extended attributes, Delete, and Read permissions. |
| Read & execute | Allows users to see folder content, read files, and start programs. This applies to an object and any child objects by default. The advanced permissions that make up Read & execute permissions are Traverse folder/execute file, List folder/read data, Read attributes, Read extended attributes, and Read permissions. |
| Read | Allows users to read a file, but not make any changes to it. This applies to an object and any child objects by default. The advanced permissions that make up Read permissions are List folder/read data, Read attributes and Read extended attributes, and Read permissions. |
| Write | Allows users to change folder and file content. This applies to an object and any child objects by default. The advanced permissions that make up Write permissions are Create files/write data, Create folders/append data, Write attributes, and Write extended attributes. |
| Special permissions | This is a custom configuration. |
Note
Groups or users that have the Full Control permission on a folder can delete any files in that folder, regardless of the permissions that protect the file.
To modify permissions, you must have the Full Control permission for a folder or file. The one exception is for file and folder owners. The owner of a file or folder can modify permissions, even if they do not have any current permission. Administrators can take ownership of files and folders to make modifications to permissions.
Next unit: Understand permission inheritance
Having an issue? We can help!
- For issues related to this module, explore existing questions using the #Windows Training tag or Ask a question on Microsoft Q&A.
- For issues related to Certifications and Exams, post on Certifications Support Forums or visit our Credentials Help.