When to use cluster autoscaler
You may need to adjust the number of nodes that run your workloads. The cluster autoscaler component can watch for pods in your cluster that can't be scheduled because of resource constraints. When issues are detected, the number of nodes in a node pool increases to meet the application demand. Nodes are also regularly checked for a lack of running pods, with the number of nodes then decreased as needed. This ability to automatically scale up or down the number of nodes in your AKS cluster lets you run an efficient, cost-effective cluster.
About the cluster autoscaler
To adjust to changing application demands, such as between the workday and evening or on a weekend, clusters often need a way to automatically scale. AKS clusters can scale in one of two ways:
- The cluster autoscaler watches for pods that can't be scheduled on nodes because of resource constraints. The cluster then automatically increases the number of nodes.
- The horizontal pod autoscaler uses the Metrics Server in a Kubernetes cluster to monitor the resource demand of pods. If an application needs more resources, the number of pods is automatically increased to meet the demand.
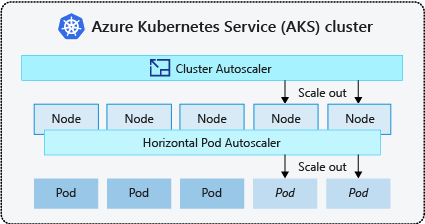
Both the horizontal pod autoscaler and cluster autoscaler can decrease the number of pods and nodes as needed. The cluster autoscaler decreases the number of nodes when there has been unused capacity over time.
The cluster autoscaler may be unable to scale down if pods can't move, such as in the following situations:
- A pod is created by a controller object, such as a deployment or replica set.
- A pod disruption budget (PDB) is too restrictive and doesn't allow the number of pods to fall below a certain threshold.
- A pod uses node selectors or anti-affinity that can't be honored if scheduled on a different node.
The cluster and horizontal pod autoscalers can work together and are often both deployed in a cluster. When combined, the horizontal pod autoscaler runs the number of pods required to meet application demand. The cluster autoscaler runs the number of nodes required to support the scheduled pods.