What is secret scanning?
In GitHub, secrets are any authentication credentials—like tokens or private keys—you might be using in a project to connect to an external service. If you commit a secret into a repository, anyone with read access to the repository can use it to access the external service with your privileges. That's where secret scanning comes into play.
Secret scanning is a GitHub Advanced Security feature that scans repositories for known types of secrets. It prevents the fraudulent use of secrets that were committed accidentally.
How does secret scanning work?
Secret scanning automatically scans your entire Git history on all branches present in your GitHub repository for any secrets. Additionally, secret scanning scans:
- Descriptions and comments in issues.
- Titles, descriptions, and comments, in open and closed historical issues.
- Titles, descriptions, and comments in pull requests.
- Titles, descriptions, and comments in GitHub Discussions.
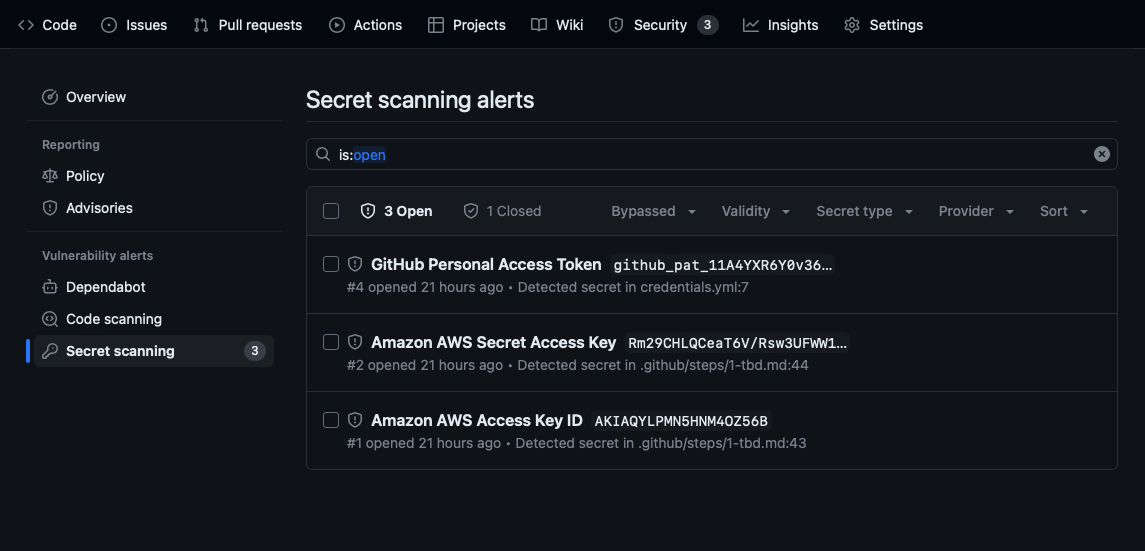
When a secret with a known pattern is committed into a private or public repository in your project, secret scanning sends a notification to all repository administrators about the commit that contains the secret. Repository administrators can then view the list of all detected secrets in the repository's Security tab.
GitHub also notifies the service provider who issued the secret if they're partnered with GitHub. The service provider can then take any appropriate action like revoking the secret, issuing a new secret, or reaching out to you directly depending on the associated risks to you or them.
For a list of the service providers and patterns GitHub automatically detects in public and private repositories, please check out Secret scanning patterns
If you can't see the secrets your organization uses in the list, you might be able to create custom patterns for them that secret scanning will detect. This module covers custom patterns later on in the Use secret scanning unit.
What is push protection?
So far, secret scanning checks for secrets already existing in a project and alerts admins to exposed secrets. When you enable push protection for your organization or repository, secret scanning also checks pushes for supported secrets.
Push protection prevents secret leaks by scanning for highly identifiable secrets before they're pushed. When a secret is detected in code, contributors are prompted directly in their IDE or command-line interface with remediation guidance to ensure that the secret isn't inadvertently exposed. To proceed, contributors must either remove the secret(s) from the push or, if needed, bypass the protection.
Push protection for users is on by default for public projects, and automatically protects you from accidentally committing secrets to public repositories across GitHub.
What are validity checks?
When an exposed credential is found, your first step is probably to check whether the token is still active, and what access it has. With validity checks for select tokens, GitHub can help with exactly that.
Validity checks determine whether a token is still active and, when possible, whether it was ever active. This is useful when you're deciding how to remediate an exposure. For example, you might prioritize remediating active secrets before checking your security logs for unauthorized access via API keys that have already been revoked.
Who is secret scanning available to?
Secret scanning for partners runs automatically on public repositories and public npm packages to notify service providers about leaked secrets on GitHub.com. Secret scanning alerts for users are available for free on all public repositories. Organizations with a license for GitHub Advanced Security can also enable secret scanning on their private and internal repositories.
This means that:
- Secret scanning is enabled by default on public repositories and can't be configured or turned off. If you want to configure or disable secret scanning on a public repository, you must switch the repository to a private one with GitHub Advanced Security.
- Secret scanning must be enabled manually on private repositories. This module's Configure secret scanning unit covers how to do this.
- Secret scanning is not available on private repositories without GitHub Advanced Security.
- Alerts from secret scanning can be enabled or disabled where available.