Implement Custom Script Extensions
Custom Script Extensions can be used to automatically launch and execute virtual machine customization tasks after initial machine configuration. Your script extension can perform simple tasks such as stopping the virtual machine or installing a software component. Scripts can also be more complex and perform a series of tasks.
Things to know about Custom Script Extensions
Let's examine the details about working with Custom Script Extensions.
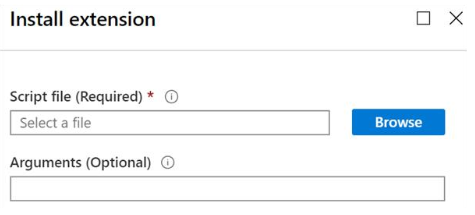
You can install Custom Script Extensions from the Azure portal by accessing your virtual machine's Extensions page.
After the Custom Script Extensions resource is created for your virtual machine, you provide a PowerShell script file with the commands to execute on the machine. You can also specify optional arguments, as required for your scenario. After your PowerShell file is uploaded, your script is executed immediately.
Scripts can be downloaded from Azure Storage or GitHub, or provided to the Azure portal at extension run time.
You can also use the PowerShell
Set-AzVmCustomScriptExtensioncommand to run scripts with Custom Script Extensions. This command requires the URI for the script in the blob container.Set-AzVmCustomScriptExtension -FileUri https://scriptstore.blob.core.windows.net/scripts/Install_IIS.ps1 -Run "PowerShell.exe" -VmName vmName -ResourceGroupName resourceGroup -Location "location"
Things to consider when using Custom Script Extensions
Review the following considerations regarding using Custom Script Extensions with virtual machines. Take a moment to assess how Custom Script Extensions can benefit your virtual machine configuration, deployment, and management tasks.
Consider tasks that might time out. Keep in mind that Custom Script Extensions only have 90 minutes to execute. If your deployment takes longer than 90 minutes, your task is marked as a timeout. Be sure to consider the time-out period when you design your scripts. Your virtual machine must be running to be able to perform the designated tasks.
Consider dependencies. Identify dependencies in your virtual machine task configuration. If your Custom Script Extension requires networking or storage access, make sure the content is available.
Consider failure events. Plan for any errors that might occur when running your script. Identify scenarios where you might run out of disk space, or areas that have security and access restrictions. Establish a strategy for how your script responds to errors.
Consider sensitive data. Your Custom Script Extension might need sensitive information such as credentials, storage account names, and storage account access keys. Think about how you to protect or encrypt your sensitive information.