Use stored access policies to delegate access to Azure Storage
A shared access signature (SAS) is a secure way to give access to clients without having to share your Azure credentials. This ease of use comes with a downside. Anyone with the correct SAS can access the file while it's still valid. The only way you can revoke access to the storage is to regenerate access keys. Regeneration requires you to update all apps that are using the old shared key to use the new one. Another option is to associate the SASs with a stored access policy.
When you added SAS functionality to your app, it highlighted the inflexibility of creating a SAS for each image, each with its own expiration and access controls. You want to update your app to use a stored access policy on the storage container. With the policy in place, you want to test that you can update the expiration and affect all the created SAS tokens.
In this unit, you learn how to:
- Use a stored access policy.
- Use the C# Storage API to create SAS tokens associated with your new access policy.
- Test that the SAS tokens can all be changed by updating the stored access policy in the Azure portal.
What are stored access policies?
You can create a stored access policy on four kinds of storage resources:
- Blob containers
- File shares
- Queues
- Tables
The stored access policy you create for a blob container can be used for all the blobs in the container and for the container itself. A stored access policy is created with the following properties:
- Identifier: The name you use to reference the stored access policy.
- Start time: A DateTimeOffset value for the date and time when the policy might start to be used. This value can be null.
- Expiry time: A DateTimeOffset value for the date and time when the policy expires. After this time, requests to the storage will fail with a 403 error-code message.
- Permissions: The list of permissions as a string that can be one or all of acdlrw.
Create stored access policies
You can create a stored access policy with C# code by using the Azure portal or Azure CLI commands.
With C# .NET code
BlobSignedIdentifier identifier = new BlobSignedIdentifier
{
Id = "stored access policy identifier",
AccessPolicy = new BlobAccessPolicy
{
ExpiresOn = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.AddHours(1),
Permissions = "rw"
}
};
blobContainer.SetAccessPolicy(permissions: new BlobSignedIdentifier[] { identifier });
With the portal
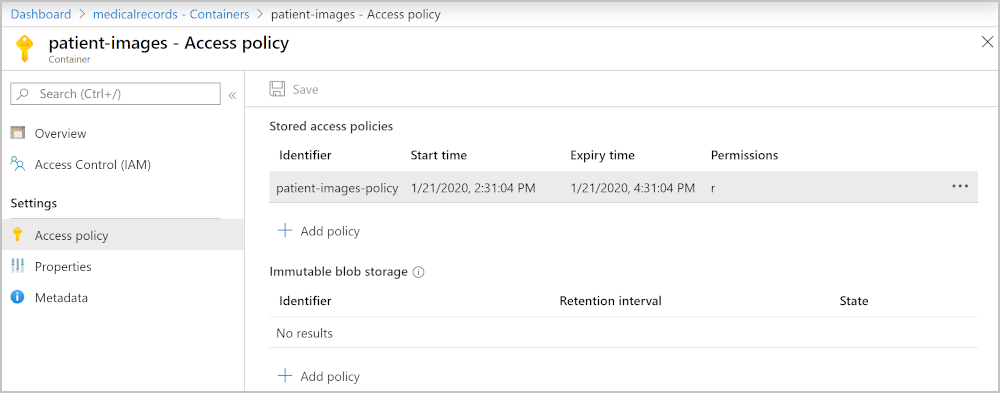
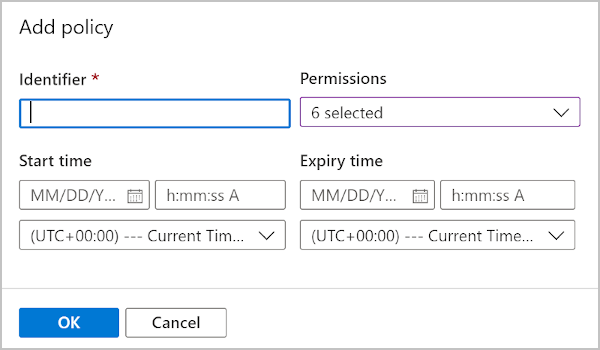
In the portal, go to the storage account and then go to the blob storage container. On the left, select Access policy. To add a new stored access policy, select + Add policy.
You can then enter all the required parameters.
With Azure CLI commands
az storage container policy create \
--name <stored access policy identifier> \
--container-name <container name> \
--start <start time UTC datetime> \
--expiry <expiry time UTC datetime> \
--permissions <(a)dd, (c)reate, (d)elete, (l)ist, (r)ead, or (w)rite> \
--account-key <storage account key> \
--account-name <storage account name> \
Create SAS tokens and associate them with stored access policies
Let's associate the stored access policy you created with any new SAS tokens you need. For your company's patient diagnostic image web app, update the existing code to add the previous code. Then, in the method that creates the SAS token, you reference the new stored access policy.
All of your existing code that's needed to create the SAS token is:
BlobSasBuilder sas = new BlobSasBuilder
{
BlobContainerName = blob.BlobContainerName,
BlobName = blob.Name,
Resource = "b",
ExpiresOn = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.AddMinutes(1)
};
// Allow read access
sas.SetPermissions(BlobSasPermissions.Read);
and it can be replaced by referencing your new access policy.
// Create a user SAS that only allows reading for a minute
BlobSasBuilder sas = new BlobSasBuilder
{
Identifier = "stored access policy identifier"
};
You can have up to five stored access policies for a single blob container.
Next unit: Exercise - Use stored access policies to delegate access to Azure Storage
Having an issue? We can help!
- For issues related to this module, explore existing questions using the #azure training tag or Ask a question on Microsoft Q&A.
- For issues related to Certifications and Exams, post on Certifications Support Forums or visit our Credentials Help.