Install and configure the DHCP role
- 10 minutes
Contoso can install the DHCP Server role only on Windows Server operating systems. They can install the DHCP server on a domain controller, and any server that is running Windows Server can host the DHCP server. For example, a branch office file and print server also might function as the local DHCP server. In addition:
- Installers must have local administrative rights to perform the installation.
- The server must have a static IP address.
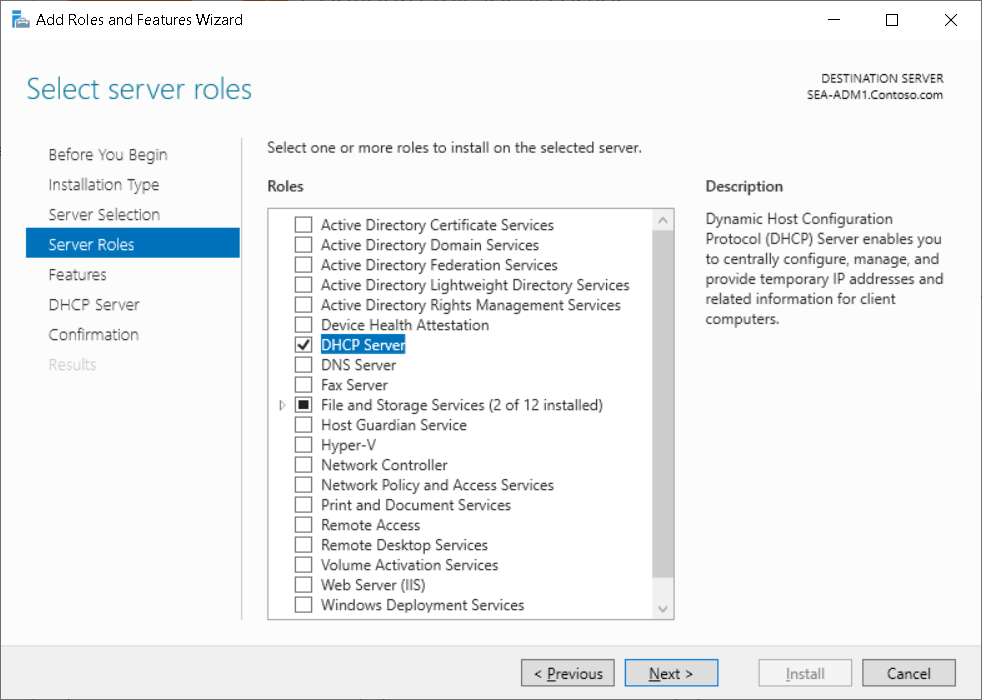
Install the DHCP Server role
You can install the DHCP Server role by using Roles & Features in Windows Admin Center or the Add Roles and Features Wizard in the Server Manager console.
You can also use the following Windows PowerShell command:
Add-WindowsFeature DHCP -IncludeManagementTools
Note
The -IncludeManagementTools parameter is optional.
DHCP management tools
When using Server Manager to install the DHCP Server role, Server Manager also installs the DHCP management tools, Windows DHCP PowerShell module cmdlets, and, if the server includes the Desktop Experience, the DHCP Management console. You can install the DHCP console or Windows PowerShell cmdlets from the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) on a Windows server or Windows client for remote administration.
To manage a DHCP server by using Windows Admin Center, you must install the DHCP management cmdlets on the DHCP server. If they aren't installed, Windows Admin Center displays the message "DHCP PowerShell tools (RSAT) are not installed" and provides an install button to perform the installation remotely.
DHCP management groups
To delegate management of DHCP, each DHCP server includes a DHCP Administrators local group and a DHCP Users local group. The DHCP Administrators group manages the local DHCP server, and the DHCP Users group examines configuration and status information on the local DHCP server.
When you use Server Manager to install the DHCP Server role, the DHCP Post-Install Configuration Wizard creates both groups. If you use Windows Admin Center or Windows PowerShell to install the DHCP role, then you need to manually trigger the creation of the groups.
To create the DHCP management groups by using Windows PowerShell, run the following command:
Add-DhcpServerSecurityGroup -Computer DhcpServerName
DHCP AD DS authorization
DHCP communication typically occurs before any user or computer authentication. Because the DHCP protocol is based on IP broadcasts, an unknown DHCP server can provide invalid information to clients. You can avoid this by authorizing the server. You can use a process called DHCP authorization to register the DHCP server in the Active Directory domain before it can support DHCP clients. Authorizing the DHCP server is one of the post-installation tasks that you must perform after you install the DHCP server.
AD DS requirements
You must authorize the Windows Server DHCP Server role in AD DS before it can begin leasing IP addresses. It's possible to have a single DHCP server providing IP addresses for subnets that contain multiple AD DS domains. Because of this, you must use an Enterprise Administrator account to authorize the DHCP server. In a single-domain environment, membership in Domain Admins is sufficient to authorize a DHCP server.
You can authorize a DHCP server by using the DHCP management console or Windows PowerShell. To authorize a DHCP server by using Windows PowerShell, run the following command:
Add-DHCPServerinDC <hostname or IP address of DHCP server>
Standalone DHCP server considerations
A standalone DHCP server is a computer that is running Windows Server, is not a member of an AD DS, and has the DHCP Server role installed and configured. If a standalone DHCP server detects an authorized DHCP server in the domain, it doesn't lease IP addresses and automatically shuts down.
Unauthorized DHCP servers
Many network devices have built-in DHCP server software that enable them to function as DHCP servers. The DHCP servers on these devices don't typically recognize authorization in AD DS. Therefore, these DHCP servers will lease IP addresses when they connect to the network with the DHCP server software enabled. To find these unauthorized DHCP servers, you must perform an investigation. When you detect unauthorized DHCP servers, you should disable the DHCP service on them. You can find the IP address of the unauthorized DHCP server by running the ipconfig /all command on the DHCP client computer that obtained the incorrect IP address information.
Demonstration
The following video demonstrates how to deploy the DHCP Server role by using Windows Admin Center. The main steps in the process are:
- In Microsoft Edge, navigate to the Windows Admin Center website.
- Connect to a Windows Server computer.
- From the Tools pane, select Roles & Features
- Select DHCP Server.
- Complete installation of the role, and then Authorize the server in AD DS.