Exercise - Configure network access
In this exercise, you'll configure the access to the virtual machine (VM) you created earlier in this module.
Important
The Microsoft Learn sandbox should still be running. If the sandbox timed out, you'll need to redo the previous exercise (Exercise - Create an Azure virtual machine).
To verify the VM you created previously is still running, use the following command:
az vm list
If you receive an empty response [], you need to complete the first exercise in this module again. If the result lists your current VM and its settings, you may continue.
Right now, the VM you created and installed Nginx on isn't accessible from the internet. You'll create a network security group that changes that by allowing inbound HTTP access on port 80.
Task 1: Access your web server
In this procedure, you get the IP address for your VM and attempt to access your web server's home page.
Run the following
az vm list-ip-addressescommand to get your VM's IP address and store the result as a Bash variable:IPADDRESS="$(az vm list-ip-addresses \ --resource-group "<rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn>" \ --name my-vm \ --query "[].virtualMachine.network.publicIpAddresses[*].ipAddress" \ --output tsv)"Run the following
curlcommand to download the home page:curl --connect-timeout 5 http://$IPADDRESSThe
--connect-timeoutargument specifies to allow up to five seconds for the connection to occur. After five seconds, you see an error message that states that the connection timed out:curl: (28) Connection timed out after 5001 millisecondsThis message means that the VM was not accessible within the timeout period.
As an optional step, try to access the web server from a browser:
Run the following to print your VM's IP address to the console:
echo $IPADDRESSYou see an IP address, for example, 23.102.42.235.
Copy the IP address that you see to the clipboard.
Open a new browser tab and go to your web server. After a few moments, you see that the connection isn't happening. If you wait for the browser to time out, you'll see something like this:
Keep this browser tab open for later.
Task 2: List the current network security group rules
Your web server wasn't accessible. To find out why, let's examine your current NSG rules.
Run the following
az network nsg listcommand to list the network security groups that are associated with your VM:az network nsg list \ --resource-group "<rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn>" \ --query '[].name' \ --output tsvYou see this:
my-vmNSGEvery VM on Azure is associated with at least one network security group. In this case, Azure created an NSG for you called my-vmNSG.
Run the following
az network nsg rule listcommand to list the rules associated with the NSG named my-vmNSG:az network nsg rule list \ --resource-group "<rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn>" \ --nsg-name my-vmNSGYou see a large block of text in JSON format in the output. In the next step, you'll run a similar command that makes this output easier to read.
Run the
az network nsg rule listcommand a second time. This time, use the--queryargument to retrieve only the name, priority, affected ports, and access (Allow or Deny) for each rule. The--outputargument formats the output as a table so that it's easy to read.az network nsg rule list \ --resource-group "<rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn>" \ --nsg-name my-vmNSG \ --query '[].{Name:name, Priority:priority, Port:destinationPortRange, Access:access}' \ --output tableYou see this:
Name Priority Port Access ----------------- ---------- ------ -------- default-allow-ssh 1000 22 AllowYou see the default rule, default-allow-ssh. This rule allows inbound connections over port 22 (SSH). SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol that's used on Linux to allow administrators to access the system remotely. The priority of this rule is 1000. Rules are processed in priority order, with lower numbers processed before higher numbers.
By default, a Linux VM's NSG allows network access only on port 22. This enables administrators to access the system. You need to also allow inbound connections on port 80, which allows access over HTTP.
Task 3: Create the network security rule
Here, you create a network security rule that allows inbound access on port 80 (HTTP).
Run the following
az network nsg rule createcommand to create a rule called allow-http that allows inbound access on port 80:az network nsg rule create \ --resource-group "<rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn>" \ --nsg-name my-vmNSG \ --name allow-http \ --protocol tcp \ --priority 100 \ --destination-port-range 80 \ --access AllowFor learning purposes, here you set the priority to 100. In this case, the priority doesn't matter. You would need to consider the priority if you had overlapping port ranges.
To verify the configuration, run
az network nsg rule listto see the updated list of rules:az network nsg rule list \ --resource-group "<rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn>" \ --nsg-name my-vmNSG \ --query '[].{Name:name, Priority:priority, Port:destinationPortRange, Access:access}' \ --output tableYou see this both the default-allow-ssh rule and your new rule, allow-http:
Name Priority Port Access ----------------- ---------- ------ -------- default-allow-ssh 1000 22 Allow allow-http 100 80 Allow
Task 4: Access your web server again
Now that you've configured network access to port 80, let's try to access the web server a second time.
Note
After you update the NSG, it may take a few moments before the updated rules propagate. Retry the next step, with pauses between attempts, until you get the desired results.
Run the same
curlcommand that you ran earlier:curl --connect-timeout 5 http://$IPADDRESSYou see this:
<html><body><h2>Welcome to Azure! My name is my-vm.</h2></body></html>As an optional step, refresh your browser tab that points to your web server. You see this:
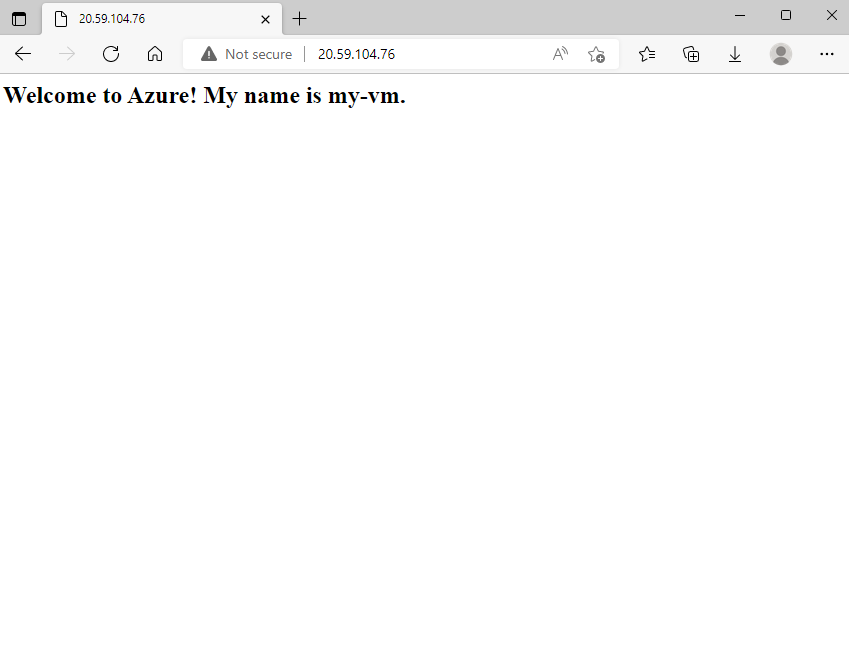
Nice work. In practice, you can create a standalone network security group that includes the inbound and outbound network access rules you need. If you have multiple VMs that serve the same purpose, you can assign that NSG to each VM at the time you create it. This technique enables you to control network access to multiple VMs under a single, central set of rules.
Clean up
The sandbox automatically cleans up your resources when you're finished with this module.
When you're working in your own subscription, it's a good idea at the end of a project to identify whether you still need the resources you created. Resources that you leave running can cost you money. You can delete resources individually or delete the resource group to delete the entire set of resources.