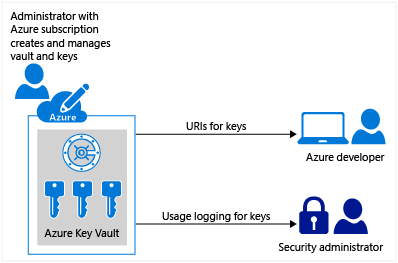
Describe Azure Key Vault
Azure Key Vault is a cloud service for securely storing and accessing secrets. A secret is anything that you want to tightly control access to, such as API keys, passwords, certificates, or cryptographic keys.
Azure Key Vault helps solve the following problems:
- Secrets management. You can use Key Vault to store securely and tightly control access to tokens, passwords, certificates, Application Programming Interface (API) keys, and other secrets.
- Key management. You can use Key Vault as a key management solution. Key Vault makes it easier to create and control the encryption keys used to encrypt your data.
- Certificate management. Key Vault lets you provision, manage, and deploy your public and private Secure Sockets Layer/ Transport Layer Security (SSL/ TLS) certificates for use with Azure and internally connected resources.
Azure Key Vault has two service tiers: Standard, which encrypts with a software key, and a Premium tier, which includes hardware security module (HSM)-protected keys.
Why use Key Vault?
Centralize application secrets. Centralizing storage of application secrets in Azure Key Vault allows you to control their distribution and greatly reduces the chances that secrets may be accidentally leaked. When application developers use Key Vault, they no longer need to store security information as part of the code in their application. Instead, the application can securely access the information it needs by using a Key Vault object identifier that uniquely identifies the object within the Key Vault. Key Vault object identifiers are URLs that allow the application to retrieve specific versions of a secret. There's no need to write custom code to protect any of the secret information stored in Key Vault.
Examples of the URL format for a standard tier Azure Key Vault object identifier and the premium tier managed HSM are as follows:
For standard tier vaults: https://{vault-name}.vault.azure.net/{object-type}/{object-name}/{object-version}
For Managed HSM: https://{hsm-name}.managedhsm.azure.net/{object-type}/{object-name}/{object-version}
Securely store secrets and keys. Access to a key vault requires proper authentication and authorization before a caller (user or application) can get access. Authentication establishes the identity of the caller, while authorization determines the operations that they're allowed to perform.
Authentication is done via Microsoft Entra. Authorization may be done via Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) or Key Vault access policy.
Azure Key Vault is designed so that Microsoft doesn't see or extract your data.
Monitor access and use. Once you've created a couple of Key Vaults, you can monitor activity by enabling logging for your vaults. You have control over your logs and you may secure them by restricting access and you may also delete logs that you no longer need.
Simplified administration of application secrets. Azure Key Vault simplifies the administration that would typically be required to secure your application secrets, including:
- Replicating the contents of your Key Vault within a region and to a secondary region. Data replication ensures high availability and takes away the need of any action from the administrator to trigger the failover.
- Providing standard Azure administration options via the portal, Azure CLI and PowerShell.
- Automating certain tasks on certificates that you purchase from Public Certificate Authorities (CAs), such as enrollment and renewal.
In addition, Azure Key Vaults allow you to segregate application secrets. Applications may access only the vault that they're allowed to access, and they can be limited to only perform specific operations. You can create an Azure Key Vault per application and restrict the secrets stored in a Key Vault to a specific application and team of developers.